Over 11 million computers have fallen victim to a devastating Info-stealer scheme.
According to cybersecurity expert Alon Gal, this new type of attack is so sophisticated that even the most popular antivirus programs were not able to stop it. In fact, among the many antivirus options out there, Windows Defender is among the most widely installed – meaning that millions of users are potentially at risk.
Moreover, twenty of the most popular antivirus programs out there – including some of the biggest names in the business – were no match for the info-stealers behind the campaign. With no antivirus program being able to offer a guaranteed protection, things might have turned for the worst.
Shattered shields: Exploring the root causes of failing antivirus protection

The attack has targeted millions of computers worldwide – and it turns out that some of the most widely-used antivirus programs are unable to stop it. Among the many programs that failed to fend off the assault were some of the biggest names in the business, including Avast Antivirus, McAfee Firewall, and Reason Cybersecurity.
Other commonly installed programs like McAfee VirusScan, 360 Total Security, and Norton Security Ultra also fell prey to the info-stealers.
Kaspersky software was heavily represented on the list, with Kaspersky Internet Security, Kaspersky Total Security, Kaspersky Antivirus, and Kaspersky Security Cloud all appearing. Other notable antivirus software included Malwarebytes, Panda Dome, Microsoft Security Essentials, and Avira Antivirus.
Here is a list of all the antivirus programs that have been compromised so far.
- Windows Defender
- Avast Antivirus
- McAfee Firewall
- Reason Cybersecurity
- McAfee VirusScan
- 360 Total Security
- AVG Antivirus
- ESET Security
- Norton Security Ultra
- Norton Security
- Kaspersky Internet Security
- Malwarebytes
- VirusScan de McAfee
- Panda Dome
- Kaspersky Total Security
- Microsoft Security Essentials
- Avira Antivirus
- Kaspersky Antivirus
- Kaspersky Security Cloud
- Total AV
Unmasking the complex relationship between antivirus and info-stealers
Alon Gal, Co-Founder & CTO at Hudson Rock, explained why Infostealers are creating havoc in the cyber world. “Infostealers are becoming an increasingly concerning trend in the world of cybercrime. These malicious programs are designed to steal sensitive information from victims, such as login credentials and financial data, and can have serious consequences for individuals and organizations,” Alon told The Cyber Express.
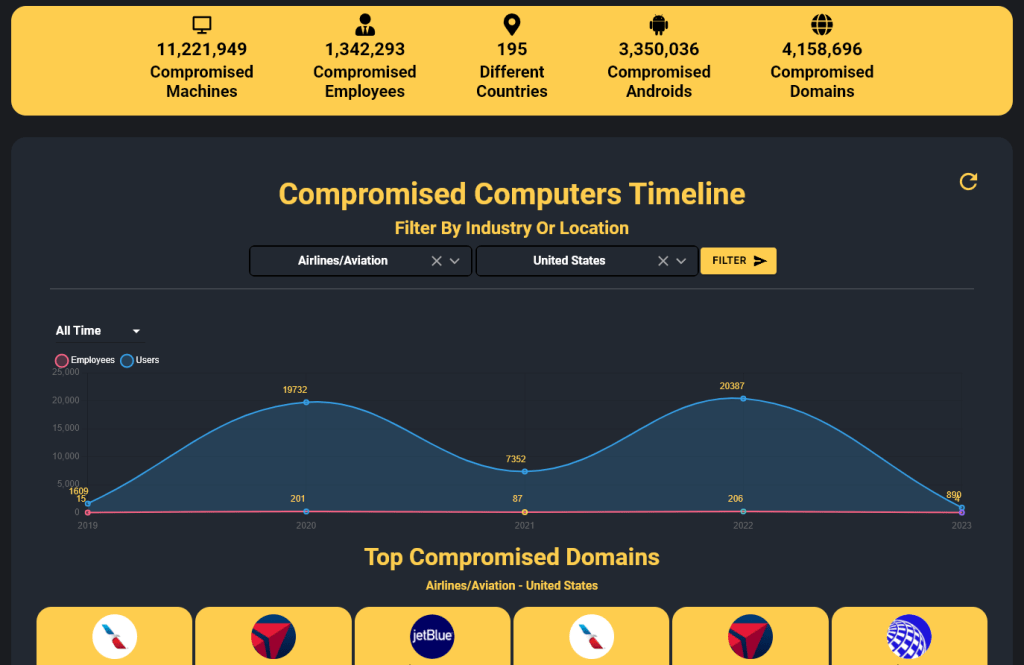
As per Hudson Rock’s database, the info-stealer scheme has compromised 11,221,949 machines and 1,342,293 employee accounts across 195 countries, utilizing info-stealers as their preferred digital weapon.
The report highlights a concerning trend of compromised Android devices, currently at 3,350,036, along with 4,158,695 compromised domains.

These findings align with the antivirus programs used globally, with 71.58% of users opting for Windows Defender and 18.48% without any security program.
Avast Antivirus, Reason cybersecurity, and McAfee Firewall were used by 4.19%, 2.9%, and 2.85% of users, respectively. Furthermore, India emerged as the most vulnerable country, with 560,044 compromised computers.
Here is a list of the countries that have the most info-stealers infections:
- India 560,044
- Brazil 526,762
- Indonesia 354,345
- United States 264,456
- Egypt 245,980
- Vietnam 214,745
- Turkey 180,829
- Philippines 159,485
- Mexico 152,767
- Pakistan 151,150
- Thailand 150,834
- United Kingdom 133,788
- Algeria 124,527
- France 117,213
- Germany 116,013
Who is behind info-stealer campaigns?

Many groups and individuals are responsible for running worldwide campaigns that aim to spread info-stealing malware. These campaigns opportunistically target anyone willing to download their malicious files. These malicious files are often promoted through Google ads, YouTube, and websites infected with malware.
Information-stealing malware, also known as info-stealers, is designed to secretly collect sensitive data from victims’ devices and transmit it to an attacker-controlled server. This malware can infiltrate systems via email attachments, social engineering, or compromised websites and operate in the background undetected.
The potential harm from info-stealers is vast, as they can compromise personal and financial data, passwords, and business information, leading to identity theft, financial fraud, and corporate espionage. The stolen information is often put on sale on the dark web, fueling an illicit market for sensitive data.
In addition to their speed and wide reach, info-stealers can propagate through networks via self-replication or communication channels, presenting significant containment challenges.
Once a device is infected, the damage can spread to other devices, magnifying the impact. Furthermore, info-stealers are designed to be elusive and escape traditional antivirus software, with frequent updates that surpass the latest security measures, making detection and removal a complex task, and the damage caused can be irreversible.
How to protect yourself against info stealers?
The most useful measures to avoid infecting your computer with an info-stealer is by downloading files from reputable websites, not opening email attachments, or clicking links from unknown or suspicious sources.
“Unfortunately, info stealers can bypass all traditional antiviruses, as seen in our report; it is up to individuals to be aware of infection risks to ensure the safety and security of their personal and corporate data,” Alon said.
Individuals and organizations must implement several preventative measures to mitigate info-stealers’ risks. This includes ensuring that software is regularly updated, using strong and unique passwords, being cautious when handling suspicious emails and websites, and utilizing antivirus and anti-malware software.
It is also essential to have routine backups of critical data to avoid data loss and ransomware payments in case of a breach.
In summary, info-stealers pose a severe threat to the security of personal and organizational information, given their ability to spread rapidly, compromise sensitive data, and evade detection. By adopting these measures and remaining vigilant, we can enhance our protection against this type of malware.
