Proofpoint has uncovered a rebranded and significantly enhanced information stealer named Amatera Stealer, derived from the previously known ACR Stealer.
Identified in early 2025, this malware exhibits substantial code overlap with its predecessor but introduces advanced features and stealth mechanisms that mark it as a distinct and formidable threat.
A Sophisticated Evolution of ACR Stealer
Sold as a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) with subscription plans ranging from $199 per month to $1,499 annually, Amatera Stealer is actively evolving, incorporating anti-analysis techniques and sophisticated attack chains to evade detection and maximize impact.
Its emergence follows the suspension of ACR Stealer sales in July 2024 and coincides with the disruption of Lumma Stealer, potentially positioning Amatera as a go-to option for cybercriminals seeking reliable MaaS solutions.
Amatera Stealer is primarily distributed through intricate web injection campaigns, notably via the ClearFake cluster, which compromises legitimate websites with malicious HTML and JavaScript.
Observed in April and May 2025, these campaigns leverage techniques like EtherHiding, using Binance Smart Chain contracts to host malicious scripts, and ClickFix, a social engineering method that tricks users into executing commands via fake CAPTCHA verifications.
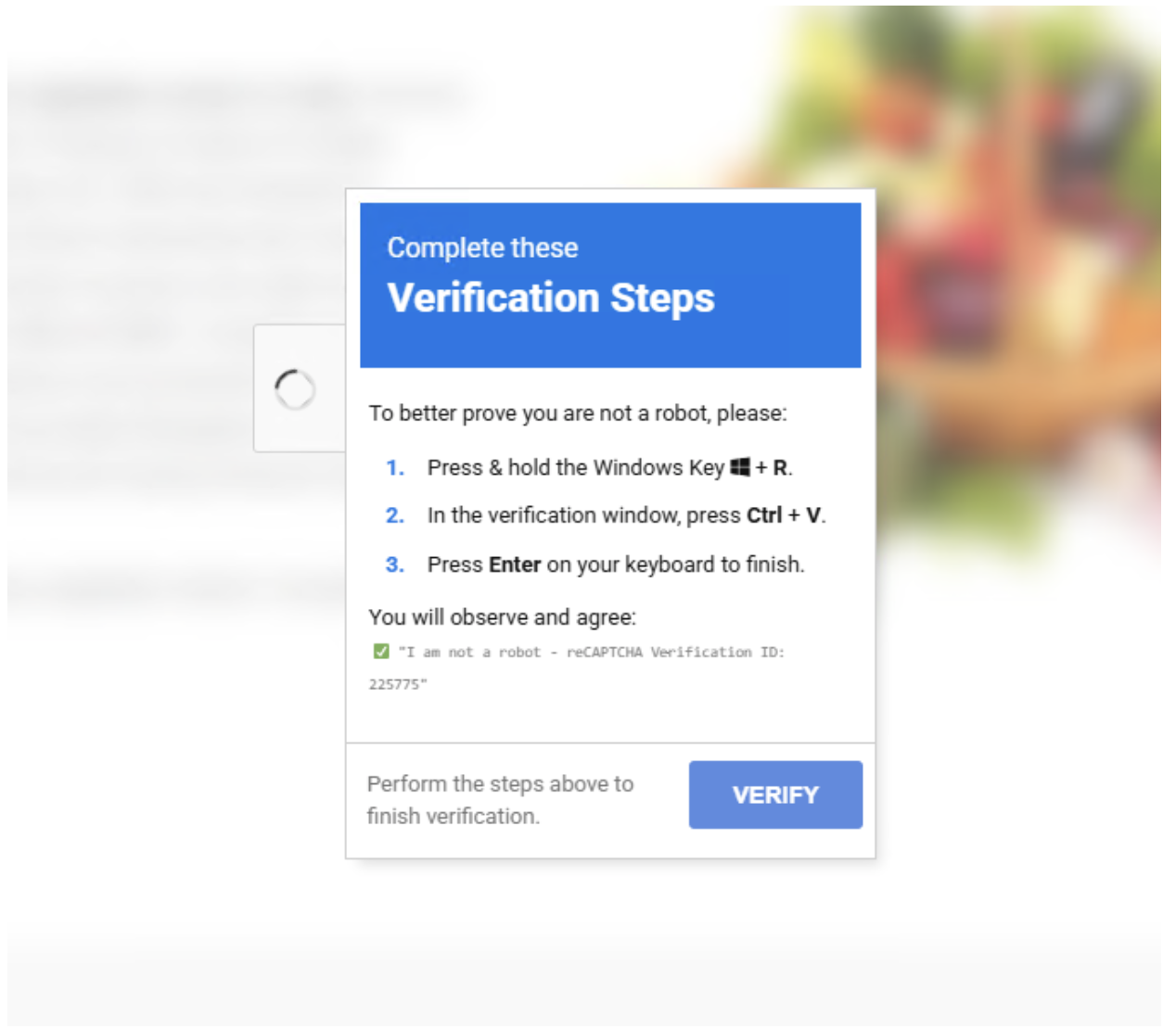
According to Proofpoint Report, these lures prompt users to open the Windows Run dialog with Windows key + R, paste malicious PowerShell commands, and execute them, ultimately deploying Amatera Stealer through multilayered loaders and shellcode injection.
Innovative Distribution
Beyond web injects, the malware is also spread through software cracks and fake downloads, showcasing its versatility.
On the technical front, Amatera employs NTSockets for command and control (C2) communication, bypassing standard Windows networking APIs to enhance stealth.
It also uses WoW64 Syscalls to dynamically resolve and execute APIs, evading user-mode hooks commonly employed by endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools.

Additionally, the malware connects to C2 servers via hardcoded IP addresses linked to legitimate content delivery networks like Cloudflare, further obscuring its malicious intent by avoiding DNS resolution and leveraging CDN protection against researcher interference.
The malware’s capabilities are extensive, focusing on stealing sensitive data from browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, email clients, and messaging apps, while also supporting secondary payload execution for further exploitation.
Its C2 configuration, delivered as JSON blobs over HTTP, enables dynamic behavior adjustment, including the execution of additional malicious files or scripts.
As Amatera Stealer continues to evolve with features like potential HTTPS support for C2 interactions, its ability to bypass detection through obfuscation, encryption, and innovative delivery methods poses a significant challenge to cybersecurity defenses.
Organizations are urged to bolster user training on social engineering tactics and restrict unauthorized PowerShell script execution to mitigate these risks.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Type | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 120316ecaf06b76a564ce42e11f7074c52df6d79b85d3526c5b4e9f362d2f1c2 | Amatera Stealer: NTSockets usage, no HTTPS support |
| IP Address | 104.21.80.1 | Amatera C2, linked to overplanteasiest[.]top |
| Domain/URL | amaprox[.]icu | Amatera Infrastructure for HTTPS security context initialization |
| Smart Contract | 0x80d31D935f0EC978253A26D48B5593599B9542C7 | ClearFake smart contract address on BNB Smart Chain Testnet |
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates
