In mid-2025, a new surge of targeted intrusions, attributed to the threat group known variously as Scattered Spider, Octo Tempest, UNC3944, Muddled Libra, and 0ktapus, began impacting multiple industries.
Initially identified by unusual SMS-based phishing campaigns leveraging adversary-in-the-middle (AiTM) domains, these operators have since refined their approach to combine sophisticated social engineering with stealthy network exploitation.
Their primary goal remains financial gain through extortion or ransomware deployment, often after months of reconnaissance and credential harvesting.
Microsoft analysts noted that these campaigns typically commence with a carefully crafted spear-phishing message or direct service-desk impersonation via phone, email, or messaging platforms.
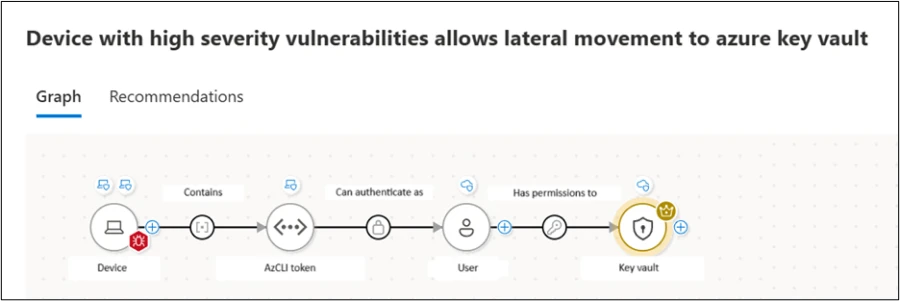
Once initial access is achieved, Scattered Spider pivots rapidly to reconnaissance, enumeration of Active Directory attributes, and credential dumping, frequently using tools like Mimikatz and AADInternals.
Concurrently, the attackers establish persistence via trusted backdoors and leverage ngrok or Chisel tunnels to maintain covert communications with compromised assets.
Shortly after these initial moves, Microsoft researchers observed the deployment of DragonForce ransomware, with a distinct focus on VMware ESX hypervisor environments.
This choice allows the threat actors to encrypt entire datastores, maximizing operational disruption and ransom demands.
Complicating defenses further, Scattered Spider’s recent tactics blend on-premises and cloud identity exploitation, attacking critical Entra Connect servers to cross domain boundaries.
Such hybrid strikes underline the group’s evolution from purely cloud-focused assaults to full-spectrum intrusions.
Detection of these tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) has been thoroughly mapped across Microsoft Defender’s XDR ecosystem.
From unusual password reset alerts in virtual machines (MDC) to detection of DCSync attempts (MDI) and suspicious elevate-access operations (MDC), defenders can monitor high-fidelity signals across endpoints, identities, and cloud workloads.
.webp)
Persistence Tactics: Establishing a Covert Foothold
A critical subtopic in Scattered Spider’s arsenal is its use of ADFS persistent backdoors to guarantee long-term access.
Once administrative privileges are obtained, the group deploys custom scripts that modify the ADFS configuration database, injecting malicious service hooks.
These hooks execute automatically upon user authentication, granting attackers elevated privileges without further credential prompts.
Microsoft analysts identified the following PowerShell snippet within affected environments, used to implant the backdoor:-
Import-Module AADInternals
$cred = Get-Credential
Set-AdfsProperties -AutoCertificateRollover $false
Add-AdfsServicePrincipalName -Principal $cred.UserName -ServicePrimaryRefreshToken $true This code disables automatic certificate renewal to prevent inadvertent removal of the backdoor and registers a service principal name linked to attacker-controlled credentials.
By leveraging entra ID APIs, the adversary ensures that any authentication event triggers a silent elevation of privileges, effectively bypassing multifactor authentication checks.
Continued vigilance through advanced hunting queries for anomalous ADFS configuration changes enables SOC teams to detect and remediate these persistence mechanisms before attackers can fully exploit them.
Boost detection, reduce alert fatigue, accelerate response; all with an interactive sandbox built for security teams -> Try ANY.RUN Now
