Researchers at Hunt.io have made a significant discovery in the cybersecurity field by obtaining and analyzing the complete source code of ERMAC V3.0. This advanced Android banking trojan targets over 700 financial applications worldwide.
This unique insight into an active malware-as-a-service platform offers a valuable understanding of modern cybercriminal operations and highlights critical vulnerabilities that could assist defenders in combating ongoing threats.
Criminal Infrastructure Exposed
In March 2024, Hunt.io’s research team discovered an exposed server containing the complete ERMAC V3.0 source code through their AttackCapture tool.

The leaked archive contained five distinct components: a PHP-based backend server, a React frontend panel, a Golang exfiltration server, Docker configuration files, and an Android application builder.
This comprehensive leak represents one of the most detailed exposures of an active banking trojan’s infrastructure in recent years.
The discovery has significant implications for cybersecurity professionals worldwide, as complete source code leaks of operational malware are broken.
Security researchers can now understand exactly how modern banking trojans operate, communicate with command-and-control servers, and steal sensitive financial information from mobile devices.
Sophisticated Multi-Platform Architecture
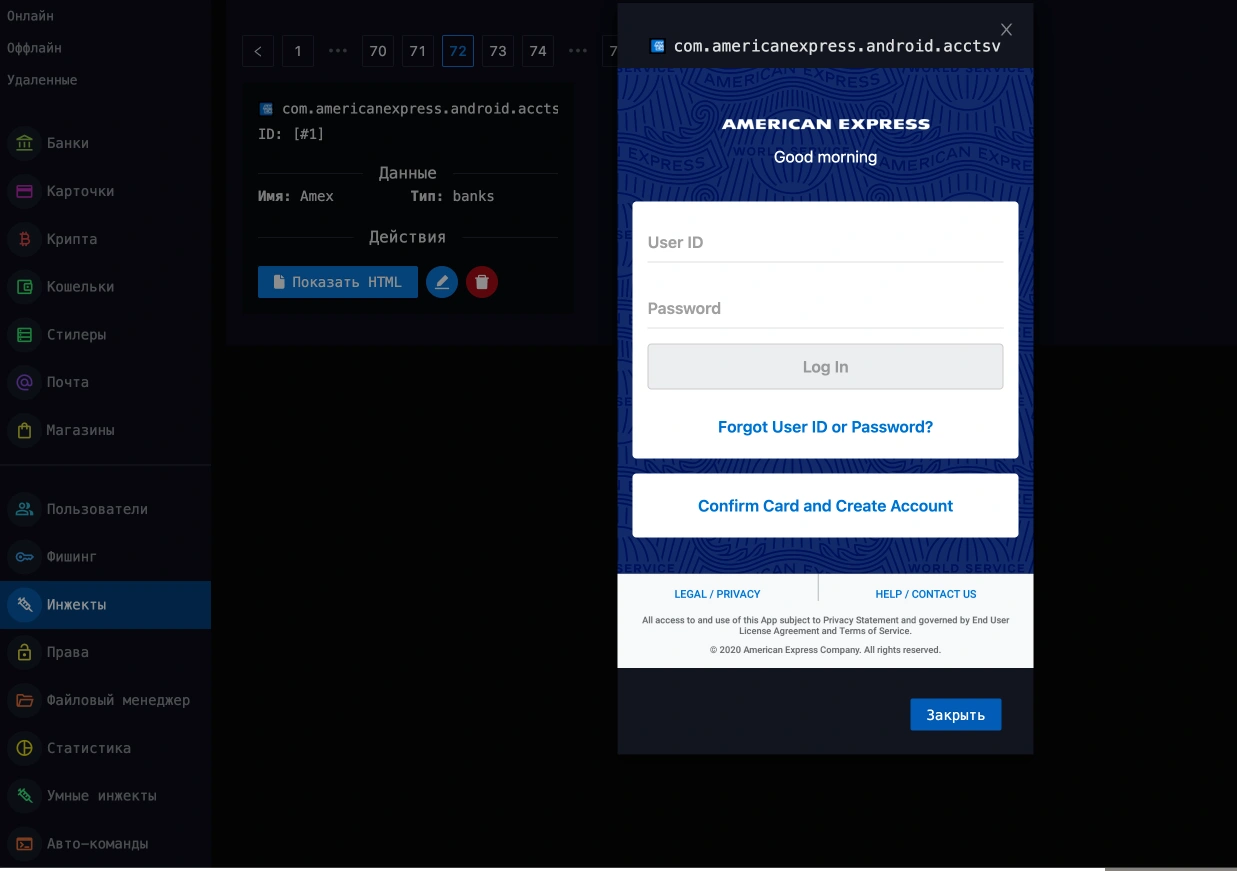
ERMAC V3.0 demonstrates remarkable sophistication in its design and capabilities. The malware targets more than 700 banking, shopping, and cryptocurrency applications using advanced form injection techniques.

Unlike its predecessors, which were based on leaked Cerberus code, version 3.0 represents a significant evolution with a completely rewritten infrastructure and enhanced data theft capabilities.
The Trojan uses AES-CBC encryption for all communications between infected devices and its command-and-control servers, making detection more challenging for traditional security tools.
The malware also includes geographic restrictions, automatically uninstalling itself if detected in Commonwealth of Independent States countries or emulator environments, suggesting the operators’ attempts to avoid prosecution in certain regions.
Key Technical Capabilities:
- Multi-language support: Supports 71 different languages for global operations.
- Advanced encryption: Uses AES-CBC PKCS5 padding with hardcoded nonce for secure communications.
- Comprehensive targeting: Injects malicious overlays into 700+ financial and cryptocurrency applications.
- Anti-analysis features: Automatically detects and evades emulator environments and specific geographic regions.
- Flexible command structure: Supports 71 different remote commands including SMS theft, call forwarding, and file management.

Critical Security Flaws Discovered
Hunt.io’s analysis revealed several critical vulnerabilities within ERMAC’s infrastructure that security researchers and law enforcement could exploit.
These include hardcoded JWT tokens, default root credentials with the password “changemeplease,” and the ability for anyone to register administrator accounts through the API without proper authentication controls.

These security flaws represent significant operational risks for cybercriminals using the platform and provide opportunities for defenders to identify and disrupt active ERMAC operations.
The researchers successfully used these indicators to locate additional active ERMAC infrastructure, including multiple command-and-control panels and data exfiltration servers currently operating online.
The research team has developed specific detection methods and provided actionable intelligence for cybersecurity professionals.
They created YARA rules for identifying ERMAC Android applications and SQL queries for discovering related infrastructure components across the internet.
These tools enable proactive threat hunting and help security teams identify potential ERMAC infections before they can cause significant damage.
Hunt.io’s findings demonstrate the value of comprehensive threat intelligence platforms in modern cybersecurity defense.
By scanning the entire IPv4 address space and monitoring for exposed directories, the company’s platform can identify emerging threats and provide early warning systems for the security community.
This discovery highlights both the sophistication of modern cybercriminal operations and the potential for security researchers to gain critical insights into their activities.
The ERMAC V3.0 analysis provides a blueprint for understanding malware-as-a-service platforms and developing more effective defensive strategies against banking trojans targeting mobile devices.
As financial institutions and mobile application developers continue to strengthen their security measures, access to detailed threat intelligence like this ERMAC analysis becomes increasingly valuable for staying ahead of evolving cyber threats and protecting users’ sensitive financial information.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs):
Network Observables
| IP Address & Port | ASN | Behavior | Last Seen |
|---|---|---|---|
| 43[.]160[.]253[.]145:80 | AS132203 | ERMAC 3.0 Panel | 2025-08-08 |
| 91[.]92[.]46[.]12:80 | AS214196 | ERMAC 3.0 Panel | 2025-07-17 |
| 206[.]123[.]128[.]81:80 | AS207184 | ERMAC 1.0–2.0 Panel | N/A |
| 43[.]160[.]253[.]145:8080 | AS132203 | ERMAC Exfiltration Server | 2025-08-08 |
| 121[.]127[.]231[.]163:8082 | AS152194 | ERMAC Exfiltration Server | 2025-07-11 |
| 121[.]127[.]231[.]198:8082 | AS152194 | ERMAC Exfiltration Server | 2025-07-12 |
| 121[.]127[.]231[.]161:8082 | AS152194 | ERMAC Exfiltration Server | 2025-07-12 |
| 43[.]160[.]253[.]145:8089 | AS132203 | ERMAC C2 Server | 2025-08-08 |
| 172[.]191[.]69[.]182:8089 | AS8075 | ERMAC C2 Server | 2025-07-13 |
| 98[.]71[.]173[.]119:8089 | AS8075 | ERMAC C2 Server | 2025-07-25 |
| 20[.]162[.]226[.]228:8089 | AS8075 | ERMAC C2 Server | 2025-07-25 |
| 141[.]164[.]62[.]236:80 | AS20473 | Open directory with ERMAC source code | 2024-03-06 |
| 5[.]188[.]33[.]192:443 | AS202422 | Mentioned in source code, possibly outdated panel/C2 | N/A |
Host-Based Observables
| Filename | SHA-256 Hash | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Ermac 3.0.zip | 175d4adc5fc0b0d8eb4b7d93b6f9694e4a3089e4ed4c59a2828d0667a9992aaa | ERMAC Source Code |
| server_go | 8c81cebbaff9c9cdad69257f50af0f5208a0d5923659b4e0c3319333f9e8d545 | ERMAC compiled exfiltration server |
Boost your SOC and help your team protect your business with free top-notch threat intelligence: Request TI Lookup Premium Trial.
