A groundbreaking open-source benchmark suite called CyberSOCEval has emerged as the first comprehensive evaluation framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) in Security Operations Center (SOC) environments.
Released as part of CyberSecEval 4, this innovative benchmark addresses critical gaps in cybersecurity AI evaluation by focusing on two essential defensive domains: Malware Analysis and Threat Intelligence Reasoning.
The research, conducted by Meta and CrowdStrike, reveals that current AI systems are far from saturating these security-focused evaluations, with accuracy scores ranging from approximately 15% to 28% on malware analysis tasks and 43% to 53% on threat intelligence reasoning.
Key Takeaways
1. CyberSOCEval, the first open-source benchmark testing LLMs on Security Operations Center tasks.
2. Current LLMs achieve only 15-28% accuracy on malware analysis and 43-53% on threat intelligence.
3. 609 malware questions and 588 threat intelligence questions evaluate AI systems on JSON logs, MITRE ATT&CK mappings, and complex attack chains.
These results highlight significant opportunities for improvement in AI cyber defense capabilities.
CyberSOCEval Malware Analysis
CyberSOCEval’s Malware Analysis component leverages real sandbox detonation data from CrowdStrike Falcon® Sandbox, creating 609 question-answer pairs across five malware categories, including ransomware, Remote Access Trojans (RATs), infostealers, EDR/AV killers, and UM unhooking techniques.
The benchmark evaluates AI systems’ ability to interpret complex JSON-formatted system logs, process trees, network traffic, and MITRE ATT&CK framework mappings.
Technical specifications include support for models with up to 128,000 token context windows, with filtering mechanisms that reduce report size while maintaining performance integrity.
The evaluation covers critical cybersecurity concepts, including T1055.001 (Process Injection), T1112 (Registry Run Keys), and API calls like CreateRemoteThread, VirtualAlloc, and WriteProcessMemory.
The Threat Intelligence Reasoning benchmark processes 588 question-answer pairs derived from 45 distinct threat intelligence reports sourced from CrowdStrike, CISA, NSA, and IC3.
Unlike existing frameworks such as CTIBench and SEvenLLM, CyberSOCEval incorporates multimodal intelligence reports combining textual indicators of compromise (IOCs) with tables and diagrams.
The evaluation methodology employs both category-based and relationship-based question generation using Llama 3.2 90B and Llama 4 Maverick models.
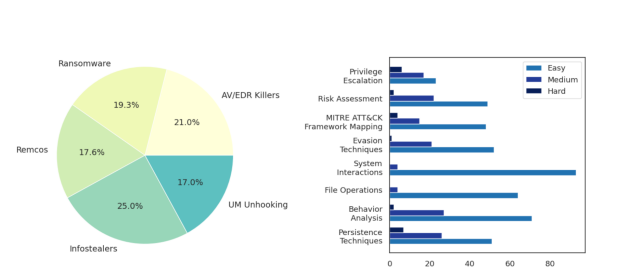
Detonation report distribution by malware attack & Distribution by topic and difficulty
Questions require multi-hop reasoning across threat actor relationships, malware attribution, and complex attack chain analysis mapped to frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK.
Reasoning models leveraging test-time scaling did not demonstrate the performance improvements observed in coding and mathematics domains, suggesting cybersecurity-specific reasoning training represents a key development opportunity, Meta said.
The benchmark’s open-source nature encourages community contributions and provides practitioners with reliable model selection metrics while offering AI developers a clear development roadmap for enhancing cyber defense capabilities.
Free live webinar on new malware tactics from our analysts! Learn advanced detection techniques -> Register for Free
