Critical vulnerabilities were identified in Chaos Mesh, a popular Cloud Native Computing Foundation chaos engineering platform used for fault injection testing in Kubernetes environments.
The security flaws, collectively dubbed “Chaotic Deputy,” comprise four CVEs that enable complete cluster compromise through relatively simple exploitation techniques.
Key Takeaways
1. “Chaotic Deputy” in Chaos Mesh <2.7.3 allows unauthenticated GraphQL and command injection.
2. Attackers exploit port 10082 and Chaos Daemon to hijack pods and steal tokens.
3. Upgrade or disable the control server.
The vulnerability set includes CVE-2025-59358, CVE-2025-59359, CVE-2025-59360, and CVE-2025-59361, with three of these carrying critical CVSS 9.8 severity ratings.
These vulnerabilities affect Chaos Mesh versions prior to 2.7.3 and can be exploited by attackers with initial network access to the Kubernetes cluster, even when running within unprivileged pods.
Chaos Mesh Vulnerabilities
JFrog reports that the primary attack vector involves exploiting an unauthenticated GraphQL server exposed by the Chaos Controller Manager component.
CVE-2025-59358 represents a missing authentication flaw that allows unauthorized access to the /query endpoint on port 10082.
This GraphQL interface, intended as a debugging tool, operates without proper authentication controls in default configurations.
The remaining three CVEs involve OS command injection vulnerabilities within GraphQL mutations including cleanTcs, killProcesses, and cleanIptables.
These mutations directly concatenate user input into command execution functions, allowing attackers to inject arbitrary shell commands through parameters like device names, process IDs, and iptables chains.
Attackers can exploit these command injection flaws to execute the tc qdisc del dev [DEVICE] root, kill [PIDS], and iptables -F [CHAIN] commands with malicious payloads.
The vulnerable code paths sink directly into the ExecBypass method, which executes commands on target pods without proper input sanitization.
The Chaos Daemon component runs with privileged permissions in DaemonSet mode, providing attackers with extensive cluster access once initial exploitation succeeds.
Through the /proc/
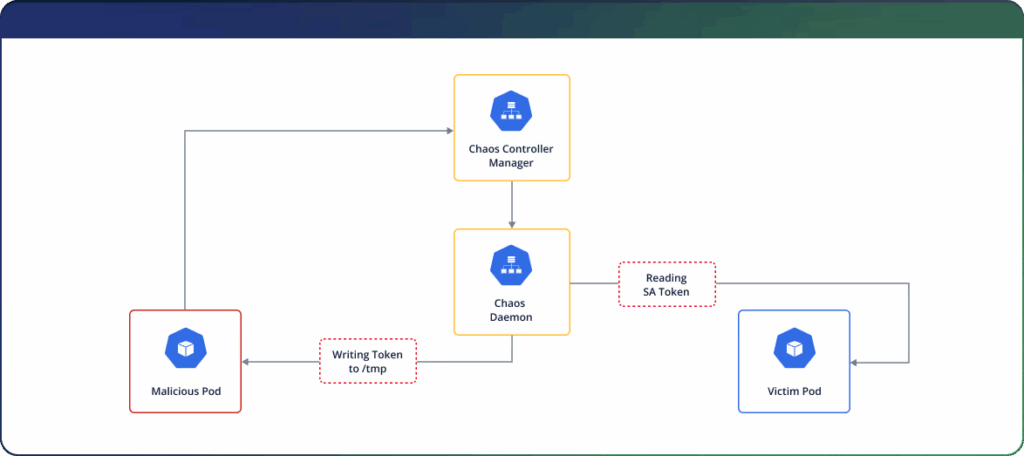
The attack progression involves mapping pod names to process IDs through exposed APIs, then leveraging the proc filesystem to access service account tokens located at /proc/
This technique enables privilege escalation by stealing tokens from high-privilege service accounts.
| CVE | Title | Impact | CVSS 3.1 Score | Severity |
| CVE-2025-59358 | Missing authentication (DoS) | Unauthorized access to GraphQL server, causing cluster-wide DoS | 7.5 | High |
| CVE-2025-59359 | OS command injection in cleanTcs | Arbitrary shell command execution on pods | 9.8 | Critical |
| CVE-2025-59360 | OS command injection in killProcesses | Arbitrary shell command execution on pods | 9.8 | Critical |
| CVE-2025-59361 | OS command injection in cleanIptables | Arbitrary shell command execution on pods | 9.8 | Critical |
Organizations using Chaos Mesh should immediately upgrade to version 2.7.3 or implement the temporary workaround by disabling the control server using helm install chaos-mesh chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh -n=chaos-mesh –version 2.7.x –set enableCtrlServer=false.
Detection can be performed using kubectl commands to identify vulnerable deployments and confirm the presence of the exposed GraphQL endpoint on port 10082.
Free live webinar on new malware tactics from our analysts! Learn advanced detection techniques -> Register for Free
