GitLab has disclosed multiple high-severity Denial-of-Service (DoS) vulnerabilities that could allow unauthenticated attackers to crash self-managed GitLab instances.
These flaws impact Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) versions prior to 18.4.1, 18.3.3, and 18.2.7, and exploit both HTTP endpoints and GraphQL APIs.
Administrators must upgrade immediately to prevent service interruptions and potential data loss.
High-Severity DoS Vulnerability
Two of the most severe issues, CVE-2025-10858 and CVE-2025-8014, carry a CVSS score of 7.5 and permit unauthenticated Denial-of-Service via malformed JSON payloads and by bypassing GraphQL query complexity limits.
In CVE-2025-10858, attackers can send a specifically crafted JSON file to endpoints like /api/v4/projects/:id/uploads to exhaust CPU and memory, rendering the Rails web server unresponsive.
The vulnerability may cause unintended harm to co-hosted services in multi-tenant systems and does not require authentication.
Similarly, CVE-2025-8014 leverages unbounded GraphQL queries; by constructing deeply nested or overly complex queries against /api/graphql, an attacker can exceed internal query cost thresholds, triggering a crash loop in the unicorn worker pool.
The flaw also affects self-managed GitLab instances and internal graphs, potentially disrupting CI/CD pipelines.
Additional medium-severity issues, including CVE-2025-9958 (CVSS 6.8) and CVE-2025-7691 (CVSS 6.5), allow information disclosure and privilege escalation.
CVE-2025-9958 exposes virtual registry configurations to low-privileged users via the /api/v4/registry/repositories/:id endpoint, potentially leaking registry tokens.
CVE-2025-7691 enables developers with group-management permissions to elevate privileges through crafted API calls to /api/v4/groups/:group_id/members, bypassing role checks in the EE backend.
Several additional DoS vectors in GraphQL unbounded array parameters, blobSearch, and string conversion methods carry lower CVSS ratings but still risk degraded performance.
The GraphQL resolver for blobSearch could enter an infinite loop on specially crafted queries, while recursive string conversion in GitLab’s Ruby middleware can exhaust Ruby VM resources.
| CVE | Title | CVSS 3.1 Score | Severity |
| CVE-2025-10858 | Denial of Service via crafted JSON uploads | 7.5 | High |
| CVE-2025-8014 | Denial of Service bypassing query complexity limits | 7.5 | High |
| CVE-2025-9958 | Information disclosure in virtual registry configuration | 6.8 | Medium |
| CVE-2025-7691 | Privilege Escalation from within the Developer role | 6.5 | Medium |
| CVE-2025-10871 | Improper authorization for Project Maintainers when assigning roles | 3.8 | Low |
| CVE-2025-10867 | Denial of Service in GraphQL API blobSearch | 3.5 | Low |
| CVE-2025-5069 | Incorrect ownership assignment via Move Issue drop-down | 3.5 | Low |
| CVE-2025-10868 | Denial of Service via string conversion methods | 3.5 | Low |
Patched Versions
Today’s patch release updates GitLab CE and EE to versions 18.4.1, 18.3.3, and 18.2.7, incorporating critical bug and security fixes.
GitLab Dedicated customers are already on the patched versions; self-managed installations should upgrade without delay.
No new database migrations are required, and multi-node deployments can apply the patch with zero downtime by leveraging the /etc/gitlab/skip-auto-reconfigure flag.
The release also bundles a PostgreSQL upgrade to version 16.10, addressing CVE-2025-8713, CVE-2025-8714, and CVE-2025-8715.
Bug backports in 18.4.1 include fixes for project forking, scanner suggestion errors, and performance optimizations in the HandleMalformedStrings middleware.
To upgrade, follow the official Update guide or use the Omnibus packages:
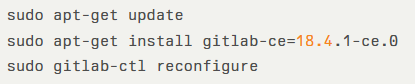
Maintainers should ensure the timely application of these patches to maintain the integrity and availability of your GitLab instance.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X for daily cybersecurity updates. Contact us to feature your stories.
