A sophisticated new ransomware variant, CrazyHunter, has emerged as a critical threat to the healthcare sector, employing advanced anti-malware evasion techniques and rapid network propagation that have security researchers deeply concerned.
Trellix, which has been actively tracking this threat since its initial appearance, reports that the ransomware represents a significant evolution in cybercriminal tactics targeting medical institutions.
CrazyHunter ransomware is a derivative of the Prince ransomware builder that surfaced in mid-2024. Developed in the Go programming language, this Windows-focused threat has introduced notable advancements in network compromise techniques and defense evasion mechanisms.
The threat actors behind CrazyHunter noted a data leak site where they publicly expose victim information, adding reputational damage to the operational disruption caused by file encryption.
Healthcare Under Siege
The primary targets of CrazyHunter operations have been healthcare organizations in Taiwan, with six confirmed compromised institutions.
The attackers’ preference for medical facilities stems from the critical nature of healthcare services and the vast repositories of sensitive patient data these organizations maintain.
Hospital downtime can have life-threatening consequences, creating immense pressure on victims to pay ransoms quickly a calculus the CrazyHunter operators clearly understand and exploit.
CrazyHunter attacks follow a methodical four-stage approach that demonstrates a deep understanding of enterprise network vulnerabilities.
Initial compromise typically exploits weak passwords in Active Directory infrastructure, providing attackers with domain-level access.
The ransomware then leverages SharpGPOAbuse, a publicly available tool, to distribute malicious payloads through Group Policy Objects, enabling rapid propagation across entire networks.
The most concerning aspect of CrazyHunter is its advanced privilege escalation technique. The ransomware employs a bring-your-own-vulnerable-driver (BYOVD) attack using a weaponized version of the Zemana anti-malware driver (zam64.sys).
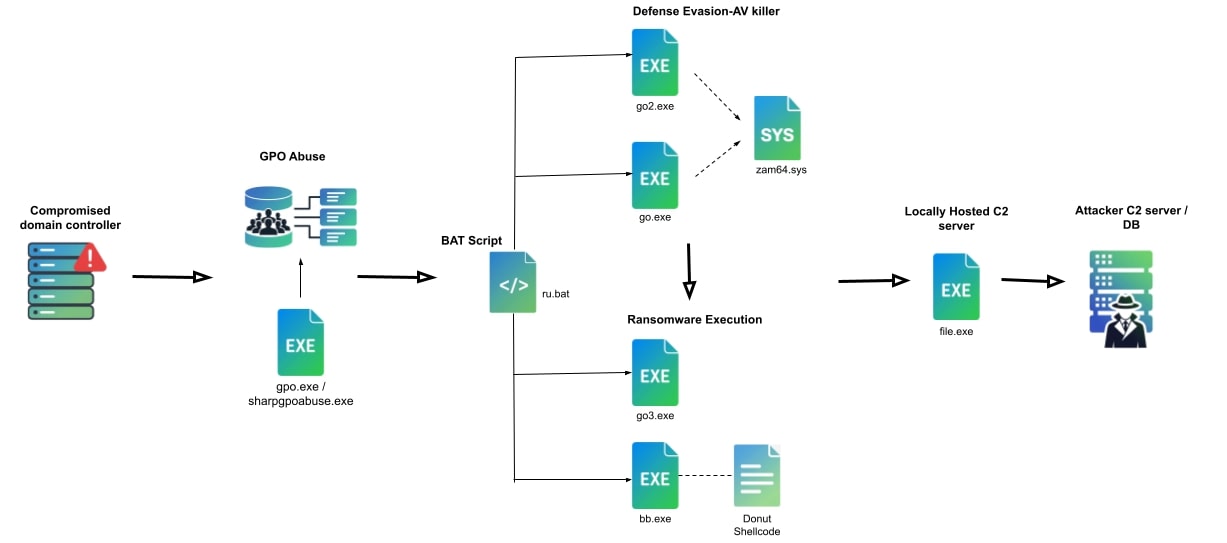
This sophisticated approach allows attackers to operate at kernel level, systematically terminating security software before deploying the encryption payload.
Multi-Layered Encryption Arsenal
CrazyHunter deploys multiple components to ensure successful encryption. The attack chain includes specialized “AV killer” executables (go.exe and go2.exe) that neutralize security defenses, followed by the primary ransomware payload (go3.exe).
A Donut Loader (bb.exe) enables fileless execution by loading shellcode directly into memory, evading disk-based detection mechanisms.
Downloaded file is saved in the temp directory as “Wallpaper.png”. Another PowerShell command is executed to set it as wallpaper.

The ransomware uses ChaCha20 stream cipher for file encryption with a distinctive 1:2 pattern encrypting one byte while leaving two unencrypted to accelerate the encryption process.
Endpoint detection capabilities are essential for identifying and blocking BYOVD attacks and AV killer components. Network segmentation can limit lateral movement, while immutable, offline backups provide recovery options without paying ransoms.
Encryption keys are protected using Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme (ECIES), ensuring victims cannot decrypt files without the attacker’s private key. Encrypted files receive the Hunter extension.
Security experts emphasize several critical defensive measures against CrazyHunter. Organizations must enforce multi-factor authentication for all domain accounts and strictly control Group Policy Object modification rights.
Trellix has implemented comprehensive protection measures covering all known CrazyHunter-related executables, providing customers with robust defense against this evolving threat.
As ransomware operators continue developing sophisticated evasion techniques, healthcare organizations must prioritize cybersecurity investments to protect patient data and maintain critical care operations.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
