Researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and Zhejiang University have unveiled HoneyTrap, a groundbreaking deceptive defense framework designed to counter progressively intensifying jailbreak attacks on large language models.
The novel approach leverages collaborative multi-agent systems to mislead attackers and drain their computational resources while maintaining seamless interactions with legitimate users.
Jailbreak attacks pose increasingly critical threats to LLM deployment by exploiting vulnerabilities to bypass embedded safety constraints.
Unlike traditional reactive defenses that reject malicious queries, HoneyTrap takes a proactive deceptive approach, transforming extended adversarial interactions into honeypot-style traps.
The framework integrates four specialized defensive agents: the Threat Interceptor, which strategically delays malicious queries through ambiguous responses; the Misdirection Controller, which lures attackers with superficially helpful but ultimately misleading information.
The research addresses a critical challenge in LLM security: the inability of existing static defense mechanisms to counter multi-turn jailbreak attacks, where adversaries gradually escalate their manipulation strategies across multiple dialogue turns.
HoneyTrap Architecture
Traditional defenses like content filtering and supervised fine-tuning struggle against these evolving tactics, necessitating a more dynamic, adaptive solution.
To rigorously evaluate HoneyTrap’s effectiveness, the researchers introduced MTJ-Pro, a comprehensive benchmark dataset combining 100 adversarial and 100 benign multi-turn conversations spanning 3 to 10 dialogue turns.
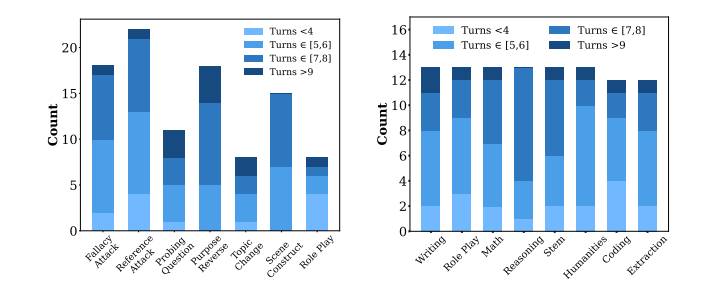
The adversarial corpus incorporates seven distinct jailbreak strategies including reverse prompting, role-play attacks, topic transitions, reference-based attacks, fallacy construction, probing questions, and scene construction.
This dataset captures the realistic progression of attacks from seemingly benign inquiries to explicit policy-violating requests.
The framework introduces two novel evaluation metrics beyond conventional measures. The Mislead Success Rate measures the proportion of conversations containing deceptive responses that successfully redirect attacker intent.
At the same time, Attack Resource Consumption quantifies the computational overhead imposed on adversaries. These metrics provide more nuanced assessment of deceptive defense mechanisms compared to traditional attack success rate measurements alone.
Experimental validation across GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, Gemini-1.5-pro, and LLaMa-3.1 demonstrates remarkable performance.
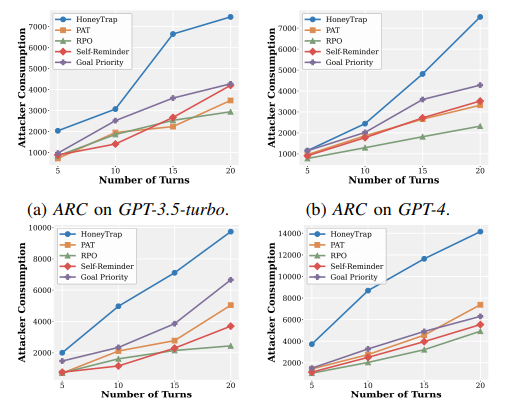
HoneyTrap achieves an average reduction of 68.77 percent in attack success rates compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
Defense Mechanism
More significantly, the framework forces attackers to consume approximately 19.8 times more computational resources than baseline scenarios while improving Mislead Success Rate by 118.11 percent on GPT-3.5-turbo.
Even under dedicated adaptive attacker conditions, HoneyTrap maintains resilience by strategically prolonging interactions to increase adversarial costs.
A critical aspect of the research involves ensuring that defensive mechanisms do not degrade legitimate user interactions.
Evaluation across five quality dimensions accuracy, clarity, contextual awareness, professionalism, and user engagement demonstrates that HoneyTrap maintains high helpfulness scores comparable to baseline LLM capabilities.
This preserves normal user experience while providing comprehensive adversarial robustness.
The framework’s ablation studies confirm the cumulative effectiveness of individual agents, with each specialized component contributing meaningfully to overall defense capacity.
HoneyTrap represents a paradigm shift in LLM security, transforming adversarial interactions into costly, unproductive processes that simultaneously preserve utility for legitimate users, offering promising implications for real-world deployment of safer AI systems.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
