Pulsar RAT, an advanced evolution of the open-source Quasar RAT, is actively targeting Windows systems with enhanced stealth capabilities and fileless execution techniques.
This modular remote access trojan combines memory-only loading, hidden virtual network computing (HVNC), and cryptocurrency wallet clipping to establish persistent backdoor access while evading traditional security defenses.
Advanced Evasion Through Memory-Only Deployment
The malware distinguishes itself through sophisticated anti-analysis mechanisms that bypass conventional detection methods.
Pulsar employs anti-virtualization checks by inspecting disk labels for strings such as “QEMU HARDDISK,” which are commonly found in sandbox environments.
When virtual machine indicators are detected, execution immediately terminates to avoid analysis.
The RAT uses .NET reflection to load payloads directly into memory, avoiding disk writes and implementing a fileless approach that circumvents disk-based security monitoring.
Code-injection capabilities enable execution within legitimate processes, rendering process-name-based detection ineffective.
This combination of techniques significantly reduces forensic visibility and complicates incident response efforts.
Network communications use TLS encryption, with configuration data retrieved from public Pastebin sites.
The malware decrypts C2 configurations using embedded keys to obtain server IP addresses, then establishes BCrypt-encrypted connections using MessagePack binary protocol for efficient command serialization.
Pulsar RAT primarily spreads through supply-chain compromises and social engineering.
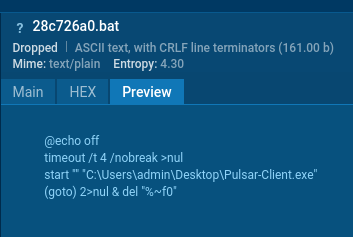
The 2025 npm supply chain attack involved malicious packages “solders” and “@mediawave/lib” that used extreme obfuscation, including 7+ layers of encoding Unicode variables, hex encoding, Base64, and steganography embedded in PNG images.
Initial access typically occurs through phishing emails with malicious attachments, cracked software distributions, or compromised third-party libraries.
Once executed, the malware establishes persistence through startup entries or scheduled tasks configured with HIGHEST privileges.
A notable UAC bypass technique clears the DelegateExecute registry value in HKEY_CLASSES_ROOTms-settingsShellOpencommand before writing malicious commands into the (Default) value.
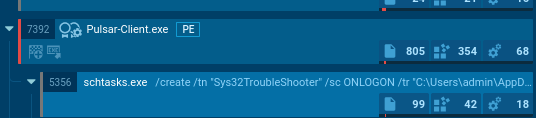
The malware’s modular plugin architecture supports extensive functionality, including keylogging, webcam and microphone access, credential harvesting through the Kematian Grabber module, and cryptocurrency clipboard hijacking, as reported by AnyRun.
Hidden virtual network computing (HVNC) enables attackers to control infected systems remotely without triggering visual indicators that would alert users.
Additional modules labeled “FunStuff” provide GDI effects, blue-screen-of-death triggers, mouse swapping, and taskbar hiding capabilities.
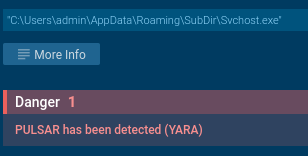
The reverse proxy support and remote shell execution features facilitate lateral movement across compromised networks.
Organizations face intellectual property theft, regulatory violations, and operational disruptions that require 200-500 person-hours for remediation.
Defense requires layered security controls combining EDR platforms, network segmentation, and user security awareness training to prevent 60-90% of social engineering attacks targeting this threat.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates ancd Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
