A new cyber-espionage threat group dubbed Amaranth-Dragon. Active throughout 2025, this group has launched highly targeted attacks against government and law enforcement agencies across Southeast Asia.
Evidence links Amaranth-Dragon to APT-41, a notorious Chinese state-sponsored hacking group, due to shared tools and operational time zones (UTC+8) .
The group creates attack campaigns based on local geopolitical events, such as the Philippine Coast Guard’s anniversary or joint air force exercises.
Distinct tactic involves rapidly weaponizing a WinRAR vulnerability (CVE-2025-8088) less than 10 days after its disclosure in August 2025.
The WinRAR Vulnerability
The core of their recent success is CVE-2025-8088, a “path traversal” vulnerability in WinRAR. This vulnerability allows attackers to create malicious RAR archives that, when opened, drop files into restricted areas of a victim’s computer without permission .
Amaranth-Dragon uses this vulnerability to drop a malicious script into the Windows Startup folder secretly. This ensures that the malware executes automatically every time the victim reboots their computer, granting the attackers “persistent” access .
The group utilizes a sophisticated arsenal to infiltrate networks and steal data:
- Amaranth Loader: This custom tool is often “side-loaded” (piggybacked) onto legitimate files to avoid detection. It retrieves encrypted payloads from the attackers’ servers.
- Havoc C2 Framework: The loader primarily installs Havoc, an open-source command-and-control system. This allows the hackers to manage infected devices remotely.
- Cloudflare Geofencing: To stay hidden, the group protects its servers behind Cloudflare. They configure these servers to only accept connections from specific target countries (like Thailand or Indonesia). If a researcher or victim outside the target region tries to connect, the server blocks them with a 403 error.
The AES key is retrieved from Pastebin or hosted on the group’s server, however, there were some campaigns where the key was embedded in the loader.
TGAmaranth RAT
In September 2025, the group introduced a new tool called TGAmaranth RAT. This remote access trojan uses Telegram bots to send and receive commands, making the malicious traffic look like normal chat application usage.
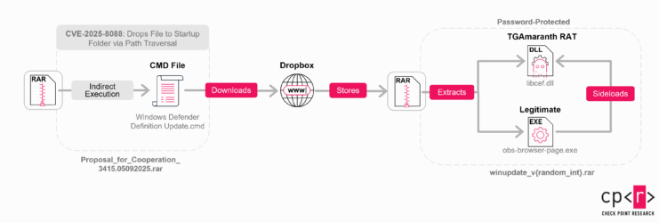
This tool is highly advanced, featuring capabilities to evade antivirus software (Anti-AV) and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) systems. It achieves this by “unhooking” security monitoring tools from the system memory, effectively blinding the victim’s defenses.
Amaranth-Dragon represents a significant evolution in regional cyber threats. By combining precise geopolitical targeting with the rapid adoption of new vulnerabilities like CVE-2025-8088, they have successfully compromised high-value targets.
Their ability to filter victims by country and hide behind legitimate services like Dropbox and Telegram makes them difficult to track and mitigate.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
