Threat actors are exploiting a critical security vulnerability in Ruckus Wireless products, putting their users at risk, researchers found.
Cyble Global Sensor Network (CGSI) has successfully identified an ongoing exploitation of CVE-2023-25717.
Additionally, an emerging menace known as AndoryuBot DDoS Botnet has been released by hackers. This alarming development strongly suggests that Threat Actors (TAs) are diligently scouring the digital landscape, seeking out susceptible Ruckus Wireless products to prey upon.
On February 8, 2023, customers were alerted by a vendor about CVE-2023-25717, a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting Ruckus Wireless Admin.
This vulnerability arises from insufficient handling of a specially crafted HTTP request. The vulnerability, CVE-2023-25717, is exploited by sending the following HTTP GET request: “/forms/doLogin?login_username=admin&password=password$(curl substring)”.
![]()
Ruckus Wireless products and AndoryuBot DDoS Botnet
The availability of a publicly accessible Proof of Concept (POC) for the vulnerability suggests that threat actors will likely exploit it on a large scale.
In April, FortiGuard Labs observed a unique botnet based on the SOCKS protocol distributed through the vulnerability CVE-2023-25717, specifically targeting Ruckus Wireless products.
“This botnet, known as AndoryuBot, first appeared in February 2023. It contains DDoS attack modules for different protocols and communicates with its command-and-control server using SOCKS5 proxies,” said the Fortinet blog post the attack.
“Based on our IPS signatures trigger count (Figure 1), this campaign started distributing the current version sometime after mid-April.”
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) added CVE-2023-25717 to their Known Exploited Vulnerability catalog on May 15, 2023.
AndoryuBot DDoS Botnet, sold on Telegram as a subscription-based service, is a Botnet malware that enables Threat Actors to orchestrate large-scale Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Such attacks can overwhelm targeted servers and infrastructure by flooding them with an enormous volume of traffic.
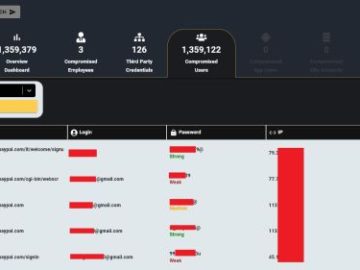
Considering the critical severity of the vulnerability and the exploitation by AndoryuBot DDoS Botnet, researchers at Cyble decided to investigate the presence of internet-exposed Ruckus Wireless Admin panels using online scanners. Their findings revealed approximately 52,000 instances exposed over the internet.

Technical analysis of AndoryuBot DDoS Botnet
The AndoryuBot DDoS Botnet binary (SHA256: c4925a91ed853920d8acee79bf0bb9342da4dabc0a2970823027f39ede399bce) is a 32-bit Linux executable.

Upon execution, the malware binary checks the count of command line arguments provided. It proceeds with its execution only if a single argument is detected.

Next, the malware employs the prctl() function, using the option variable set to 15 to modify the process name. It changes the process name to “DvrHelper,” a defense evasion technique employed to conceal.
Following this, using a decryption loop, the AndoryuBot DDoS Botnet binary decrypts the encrypted strings within the “.rodata” section.

The malware establishes sockets to communicate with a Command and Control (C&C) Server. Based on the instructions received from the server, the malware carries out various malicious activities, including initiating Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
To facilitate network communication, the malware utilizes the socket() function to create a socket.
Ruckus Wireless products and vulnerability management
Ruckus offers cutting-edge networking solutions and services that diverse organizations widely embrace. However, the immense popularity of Ruckus Wireless products has garnered the attention of malicious threat actors who actively exploit vulnerabilities for their nefarious purposes.
Recent incidents involving the exploitation of vulnerabilities in Goanywhere, PaperCut, and now Ruckus indicate that threat actors are relentlessly searching for internet-exposed instances that are susceptible to attacks.
To fortify the security infrastructure, it is imperative to diligently maintain up-to-date software, firmware, and applications by promptly installing the latest patches and security measures released by the authorized vendor. By doing so, potential attackers are thwarted from capitalizing on vulnerabilities.
Employing effective network segmentation techniques is another crucial recommendation to prevent adversaries from executing lateral movement and restrict the potential compromise of vital online resources.
Additionally, conducting routine audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing exercises plays a pivotal role in identifying and rectifying any security vulnerabilities that malicious actors may seek to exploit. These proactive measures are instrumental in fortifying the network’s security.
Moreover, continuous monitoring and comprehensive logging hold immeasurable value in the timely detection of network anomalies. By swiftly identifying any irregularities, potential threats can be addressed and mitigated at the earliest stages, ensuring the network’s overall security.