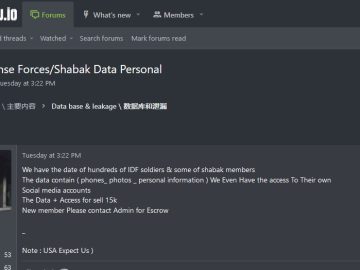
The Antidot Android banking trojan is a new threat on the surface web, disguising itself as a Google Play update, targeting Android users worldwide. The android banking trojan is a stealthy malware strategically designed to infiltrate devices, harvest sensitive information, and wreak havoc across diverse language-speaking regions.
Revealed by cybersecurity experts at Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL), the Antidot banking trojan represents a sophisticated evolution in mobile malware. Unlike its predecessors, Antidot employs a range of malicious tactics, including overlay attacks, keylogging, and VNC features, to compromise devices and extract valuable data.
Decoding the Antidot Android Banking Trojan Campaign

At its core, Antidot masquerades as a legitimate Google Play update application, luring unsuspecting users into its trap. Upon installation, it presents counterfeit Google Play update pages meticulously crafted in various languages, including German, French, Spanish, Russian, Portuguese, Romanian, and English. This strategic approach indicates a broad spectrum of targets, spanning multiple regions and demographics.


Behind its deceptive façade, Antidot operates with alarming sophistication. Leveraging overlay attacks as its primary modus operandi, the Trojan seamlessly overlays phishing pages onto legitimate applications, capturing sensitive credentials without the user’s knowledge.
Additionally, Antidot integrates keylogging functionality, surreptitiously recording keystrokes to further enhance its data harvesting capabilities.
Sophisticated Communication and Control (C&C) Server


Antidot maintains a stealthy line of communication with its Command and Control (C&C) server, facilitating real-time interaction for executing commands and transmitting stolen data. Through WebSocket communication, the malware establishes bidirectional connections, enabling seamless coordination between the infected devices and the malicious actors behind the scenes.


One of Antidot’s most insidious features is its implementation of VNC (Virtual Network Computing), enabling remote control of infected devices. By leveraging the MediaProjection feature, the Trojan captures and transmits display content to the C&C server, allowing attackers to remotely execute commands and manipulate device functions.


To combat the growing threat posed by Antidot and similar Android banking trojans, cybersecurity experts from Cyble recommend adhering to essential best practices. These include downloading software from official app stores like Google Play or the iOS App Store.
Users can also utilize reputable antivirus and internet security software on all connected devices. Other precautionary methods include enforcing strong passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication whenever possible. Exercise caution when clicking on links received via SMS or email. Keep devices, operating systems, and applications up to date to mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.