What is the importance of Cyber threat intelligence in 2023?
Ridiculous question.
The fact that you are reading it, and that at least one entity is aware of it and is storing the information that you read it, and the extremely high possibility of at least one person being aware of it without your consent, increase the relevance of cyber threat intelligence in 2023.
From right defense against ransomware gangs to getting your incident disclosure right, cyber threat intelligence plays a major role in organizational operations.
“Threat intelligence is data that is collected, processed, and analyzed to understand a threat actor’s motives, targets, and attack behaviors,” according to cybersecurity firm Crowdstrike.
Threat intelligence enables us to make faster, more informed, data-backed security decisions and change their behavior from reactive to proactive in the fight against threat actors.
Simply put, cyber threat Intelligence is nothing but information about threats that may leave information exposed, and depending upon specific cyberattacks, financial loss.
Cyber threat intelligence or online threat information helps companies, enterprises, and individuals take better precautions so incoming attacks are prevented.
Cyber threat intelligence is secured by analysts and researchers besides legal authorities who employ digital tools and human resources to keep a tab on online crime. There are several mediums where cybercriminals join to sell malware, develop malicious software, leak data, and hire hackers.
A cyber threat team belonging to the government, organizations, or independent researchers keeps a close eye on underground forums, Telegram channels of notorious gangs, leak sites, breach forums, etc.
Each is used for several general and specific information sharing by cybercriminal groups.
How do we gather cyber threat intelligence in 2023?
Cyber threat intelligence has grown much bigger from the simplistic explanation. The possibility of a cyber attack comes in-built with any connected device. Entire businesses have cropped up to address the growing demand for threat intelligence.
The implementation of artificial intelligence for cybersecurity is driving the expansion of the global Threat Intelligence Market.
It is projected to grow from USD 4.93 billion in 2023 to USD 18.11 billion by 2030, according to a research report by Fortune Business Insights.
Cyber threat intelligence gathers information about risks to online security posed by any individual. These individuals or groups may plot, create specialized software, launch phishing emails, attack vulnerability, or leak exfiltrated data.
Information about online threats to individuals, organizations, governments, etc., is collected and defenses are put in place to stop them before it strikes. Or, appropriate measures are taken to prevent a further attack if the incident has already occurred.
Cyber threat intelligence reports also help in nabbing cybercriminals and closing their websites as seen in the seizure of the Hive ransomware group network, and nabbing of Conor Fitzpatrick.
Fitzpatrick aka Pompompurin ran the infamous BreachForums where several illegal data leaks and breaches were publicized and sold by threat actors.
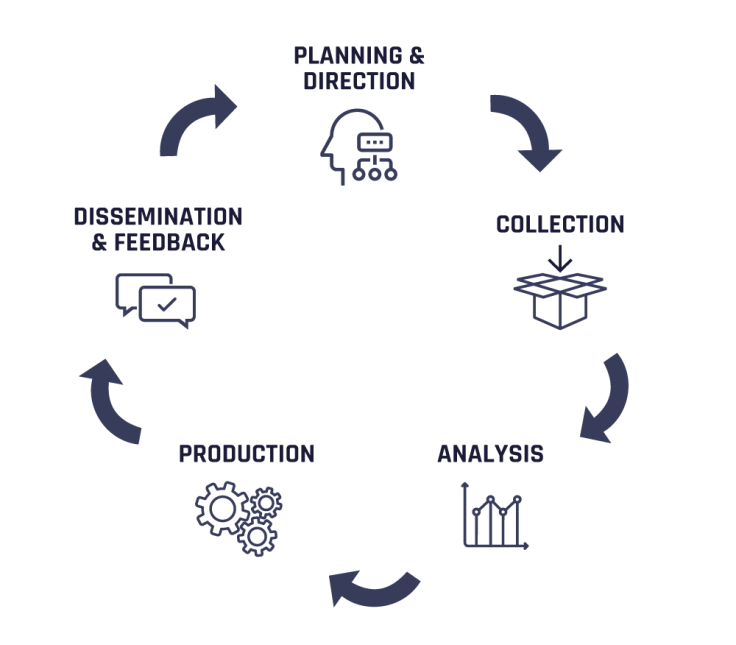
The information gathered has to go through a five-step process of conversion, from threat intelligence to actionable intelligence, according to cybersecurity company Flashpoint.
The five phases of cyber threat intelligence
PHASE 1: Planning and Direction
“The first step in this process is to set the direction of your program, meaning you need to outline what you’re looking for and what questions you want to ask and answer,” said an analysis by cybersecurity business Rapid7.
In phase one of the threat intelligence lifecycle, the main goals and tasks for your threat intelligence program are laid out, which are often referred to as intelligence requirements (IRs). The IRs should reflect the core objectives of the team and the value that finished intelligence will ultimately deliver.
Senior leadership, such as the Chief Information Security Officer (i.e., the CISO or CSO), will guide planning and direction at this stage and establish the core program goals and challenges, along with all potent external threats.
Key considerations in phase one include determining which types of assets, processes, and personnel are at risk, how threat intelligence can improve operational efficiency for the team, and what other systems and applications could benefit.
PHASE 2: Collection and Processing
In phase two, data quantity and quality are both crucial aspects of the threat intelligence collection stage.
“Your goal is collect as much information as possible about potential threat vectors, existing vulnerabilities, and publicly available information a threat actor could use to gain unauthorized access to your systems,” noted cybersecurity company Synk.
Intelligence collection establishes the scope of your sources, both in terms of the data volume and type. The processing component then seeks to normalize, structure, and deduplicate all of the amassed data.
Specific processing procedures often include reducing the volume of raw data, translating conversations obtained from foreign-language dark web marketplaces and illicit forums, and metadata extraction from malware samples.
Key considerations in phase two include identifying current internal and external blindspots, determining what technical and automated collection techniques can be employed, and assessing how well your team can infiltrate cybercriminal forums and closed sources on the dark web.
PHASE 3: Analysis
“Threat intel analysis is an integral phase of the threat intelligence lifecycle where security analysts make sense of collected threat data by adding context,” said a report by cybersecurity business Cyware.
“It is in this stage that threat information is correlated and contextualized to identify potential security issues and develop actionable insights that are needed to create appropriate countermeasures to respond to the identified threats.”
During the analysis phase, the enriched and contextualized threat intelligence is derived through the application of known structural data or advanced correlation and data modeling techniques.
As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies continue to advance, certain human-oriented tasks will become increasingly automated, allowing operational resources and staff to focus on more strategic tasks and investigations.
Phase three involves identifying which assets, processes, and personnel are at risk, assessing how threat intelligence can improve operational efficiency for the team, and identifying other systems and applications that could benefit from the same.
PHASE 4: Production
After completing the threat intelligence analysis, the focus of phase four shifts towards developing easy-to-understand graphical charts, dashboards, and reports based on the finished intelligence.
“During production, it’s essential to identify the most meaningful information and derive logical conclusions from the data and analysis completed in the prior phase,” said the Flashpoint report.
“Recommendations that outline appropriate courses of action will often include prepared decision trees and procedures to initiate incident and ransomware response, threat remediation, and patch management, among many others.”
Phase four involves identifying the most critical findings of the analysis, determining the best way to present them visually, evaluating the reliability, relevance, and accuracy of the analysis, and determining any clear and concrete recommendations or next steps for the final analysis.
PHASE 5: Dissemination and Feedback
“Dissemination involves getting the finished intelligence output to the places it needs to go,” noted cybersecurity company Recorded Future.
Finished intelligence reports are distributed to the appropriate stakeholders, including dedicated fraud teams, cyber threat intelligence (CTI) teams, security operations (SecOps) teams, vulnerability management teams, third-party risk teams, and senior leadership teams responsible for resource allocation and strategic planning.
Upon receiving the finished intelligence, stakeholders evaluate the findings, make key decisions, and provide feedback to continually refine intelligence operations.
Data collection can be automated, but detecting patterns and threats from them require the seasoned eyes of an analyst.
Cyber Threat Intelligence in 2023: What is the role of analysts?
“Cyber threat intelligence analysts are specialists in cyber threat, who use their analytical and technological skills to address complex cyber threat challenge issues, generate detailed reports, and brief the company on short and long-term security concerns,” explained SOCRadar.
“This work involves effort, creativity, research, and technical skills.”
CTI analysts don’t just work with present cyber intelligence threats but also create future plans to create better defenses. Their insights offer regular guidance to engineers in developing tools to have better detection, prevention, and reporting of online threats.
They have expertise in gathering raw data, filtering what is relevant and critical, investigating, and deciding on the best course of action to assure digital security.
CTI analysts working for cyber threat intelligence firms make sure they have the best tools in place while making way for adapting to future trends that might prevail.
Cyber threat intelligence teams also keep key focus on raw data which is analyzed to further understand what the cybercriminals might have intended to do with the software and how they were able to perform security breaches.
Several cyber threat intelligence companies follow models and patterns that help them detect threats and gain greater knowledge. Some of the prominent threat intelligence companies are Mimecast threat intelligence, Palo Alto Networks, VirusTotal Intelligence, and Y Combinator-backed Cyble.
- The dynamic intelligence feed offers the data they use to investigate threats.
- Using cognitive technologies to foretell if threat actors placed specific automation processes helps in swiftly completing investigations.
- Employing a bidirectional integration platform by the cyber threat intelligence team elevates functionality across the IT ecosystems and eases better communications.
- Smart data visualization is nothing but the presentation of complex or any found data about threats in an easy manner. The complexity of attacks is unfolded with simpler maps, graphs, charts, and diagrams.
- Analysis tools make several detection and representation work easier with reports that explain what it is fed to understand. It may also help efforts in having better collaboration between intelligence agencies in different countries to take better cohesive actions.
The kind of data and its analysis used by cyber threat intelligence officials
Different pieces of information, tech, and previous reports are investigated to perform analysis and functions leading to creating guards against cyber threats. There are several ways different teams approach this work.
However, a few techniques are commonly observed in cyber threat intelligence work.
.png?resize=1174%2C660&ssl=1)
- Tactical Threat Intelligence
Suspicious IP addresses, file hashes, unexpected network traffic, and malicious domain names are investigated to stop them from reaching their targets. This is often done in tactical threat intelligence.
- Operational Threat Intelligence
Cybercriminals are investigated to further investigate their attacks and attack vector. A large portion of this analysis relies on human intelligence besides artificial intelligence feed. Information and experiential data are correlated to draw conclusions and come closer to the threat in operational threat intelligence.
- Strategic Threat Intelligence
The motivations of cybercriminals combined with their connection with other criminal networks are closely analyzed in this method.
Geographical targets that are outside the jurisdiction of specific threat intelligence groups are investigated by collaborating with officials across the globe. War crimes and cyber espionage are closely monitored in this threat intelligence with attention to concrete actions to prevent them.
Cyber Threat Intelligence in 2023: In a nutshell
An active, diligent, and proactive team of cyber threat intelligence can help create one of the best defensive infrastructures to combat or thwart any online threat. Artificial Intelligence lends a helpful hand in minute data analysis and creating reports to facilitate research and results.
The best practices are updated based on cyber threat intelligence reports that identify common factors and unique activities in malicious software and online platforms. It helps to create defenses while proactively anticipating the Tactics, Techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by cybercriminals.
Cyber threat intelligence is nothing but foreseeing threats, understanding the likelihood of tricks to be used by hackers and developers, and analyzing risk to cover it before it hits the infrastructure. Cybercriminals, no matter how far ahead they plan to reach, their footprints and traces of crime lead cyber threat intelligence teams to them.
