The cybersecurity landscape entered a critical new era in the second half of 2025 as AI-powered malware transitioned from theoretical threat to tangible reality, while the ransomware-as-a-service economy expanded at an unprecedented pace.
According to ESET Research’s latest Threat Report, these twin forces are reshaping how organizations must approach cyber defense.
ESET discovered PromptLock, the first known AI-powered ransomware, marking a watershed moment in threat evolution.
Unlike traditional malware with static code, PromptLock leverages OpenAI models via the Ollama API to generate malicious Lua scripts dynamically during execution.
This approach fundamentally changes the detection landscape each variant is unique, making signature-based defenses increasingly ineffective.
The malware operates through a two-component architecture: a static Go module that communicates with an AI server and hardcoded prompts, paired with dynamically generated cross-platform Lua scripts that can perform filesystem enumeration, data exfiltration, encryption, and deletion.
What makes this particularly dangerous is PromptLock’s built-in verification loop. When the AI model generates non-functional code a known limitation of large language models the malware feeds execution logs back to the model for correction, essentially creating a self-improving threat.
“The emergence of tools like PromptLock highlights a significant shift in the cyberthreat landscape,” noted Anton Cherepanov, ESET Senior Malware Researcher.
“With the help of AI, launching sophisticated attacks has become dramatically easier, eliminating the need for teams of skilled developers.”
While security researchers initially assessed PromptLock as a proof-of-concept, ESET identified three additional AI-powered threats in the wild: PromptFlux, PromptSteal (LameHug), and QuietVault.
Lumma Stealer detections started appearing more and more frequently, soon reaching levels similar to those registered before the takedown.
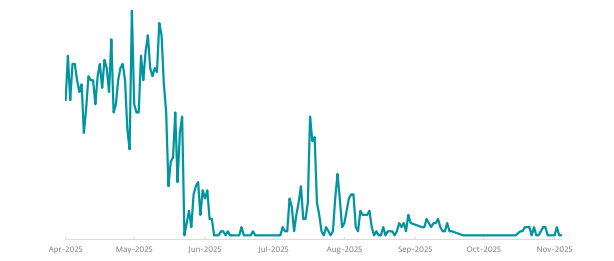
The latter two have already been weaponized in espionage campaigns attributed to Russia-aligned Sednit and China-aligned threat actors, demonstrating that AI-powered malware has moved beyond experimentation.
The Ransomware Explosion
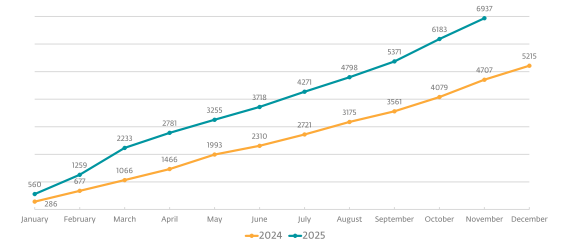
The ransomware economy’s expansion parallels the AI threat surge. ESET’s analysis projects a 40% year-over-year increase in ransomware victims, with 2025 cumulative totals already exceeding 2024 by over 1,700 cases.
Public data from ransomware gangs’ leak sites showed 6,937 known victims in 2025, with manufacturing, construction, retail, healthcare, and technology sectors bearing the brunt of attacks.
Qilin and Akira now dominate the ransomware-as-a-service market, each responsible for approximately 10% of analyzed attacks.
However, a newcomer group called Warlock has emerged with particularly sophisticated evasion techniques, including exploitation of ToolShell vulnerabilities and abuse of legitimate tools like Velociraptor and VS Code.
The Jaguar Land Rover ransomware incident exemplifies the escalating threat. A coordinated attack involving members from Scattered Spider, Lapsus, and ShinyHunters forced a global shutdown, causing nearly $2.5 billion in damage now the costliest cyberattack in UK history.
EDR Killers Proliferate
A concerning parallel trend is the explosion of endpoint detection and response (EDR) killer tools.
Over a dozen new EDR-killing variants emerged in H2 2025, with the bring-your-own-vulnerable-driver (BYOVD) technique predominating. This indicates ransomware operators view EDR solutions as primary obstacles to success.
As attackers leverage AI to automate reconnaissance, exploitation, and exfiltration at unprecedented speed and scale, organizations must evolve beyond traditional signature-based detection.
The combination of AI-generated malware and the thriving ransomware economy represents an inflection point demanding immediate strategic investment in behavioral analytics, threat intelligence, and zero-trust architecture.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.
