GitHub has announced that its secret scanning alerts service is now generally available to all public repositories and can be enabled to detect leaked secrets across an entire publishing history.
Secrets are sensitive data accidentally added to GitHub repositories, including API keys, account passwords, authentication tokens, and other confidential data that can enable attackers to perform security breaches or gain access to non-public data.
Threat actors commonly search public GitHub repositories for authentication secrets to breach networks, steal data, or impersonate the company in their own attacks.
In December 2022, GitHub began rolling out a beta of a free secret scanning feature to all public repositories that scan for 200+ token formats to help developers find accidental public exposure of sensitive data. Since then, 70,000 public repositories have enabled the new feature.
Today, GitHub announced that the service is now generally available, and all public repository owners/admins can enable secret scanning alerts to secure their data.
“As of today, GitHub secret scanning’s alert experience is generally available and free for all public repositories,” reads GitHub’s announcement.
“You can enable secret scanning alerts across all the repositories you own to notify you of leaked secrets across your full repository history, including code, issues, description, and comments.”
In addition to notifying the repository owners of leaked secret incidents, GitHub will continue to notify its over 100 secret scanning partners of exposed secrets so that they can revoke the authentication token and notify their customers.
If it’s impossible to reach a concerned partner, the alert to the admin should be enough to ensure the exposed secrets are removed from the public repositories.
The code hosting platform uses the example of DevOps Consultant and Trainer @rajbos to highlight the power of the secret scanner and alerts. The developer says he enabled the feature on 13,954 public GitHub Action repositories and found secrets on 1110 of them (7.9%).
“Even though I train a lot of folks on using GitHub Advanced Security, I found secrets in my own repositories through this,” admits Rob Bos.
“Despite multiple years of experience, it also happens to myself. That’s how easy it is to include secrets by mistake.”
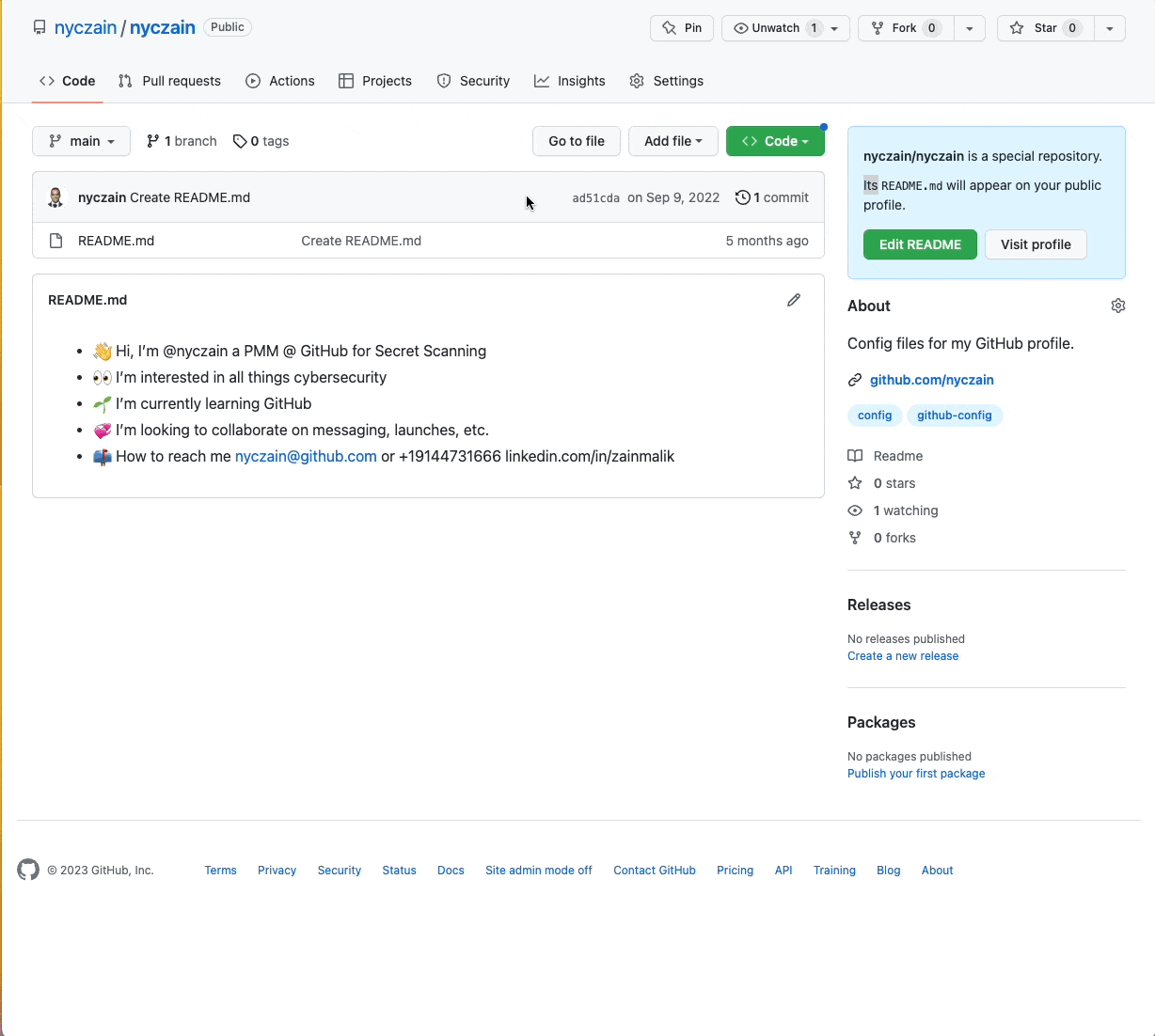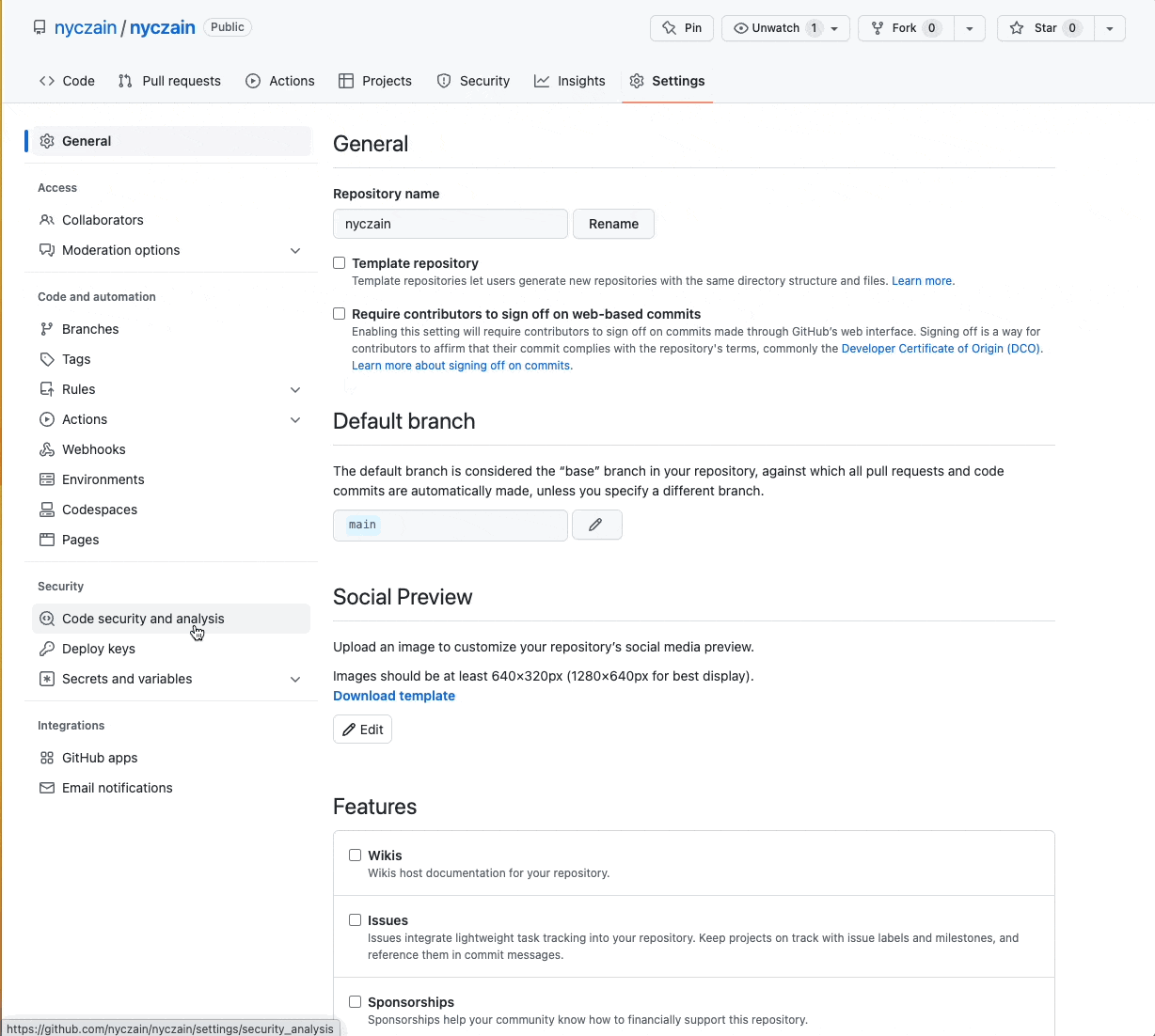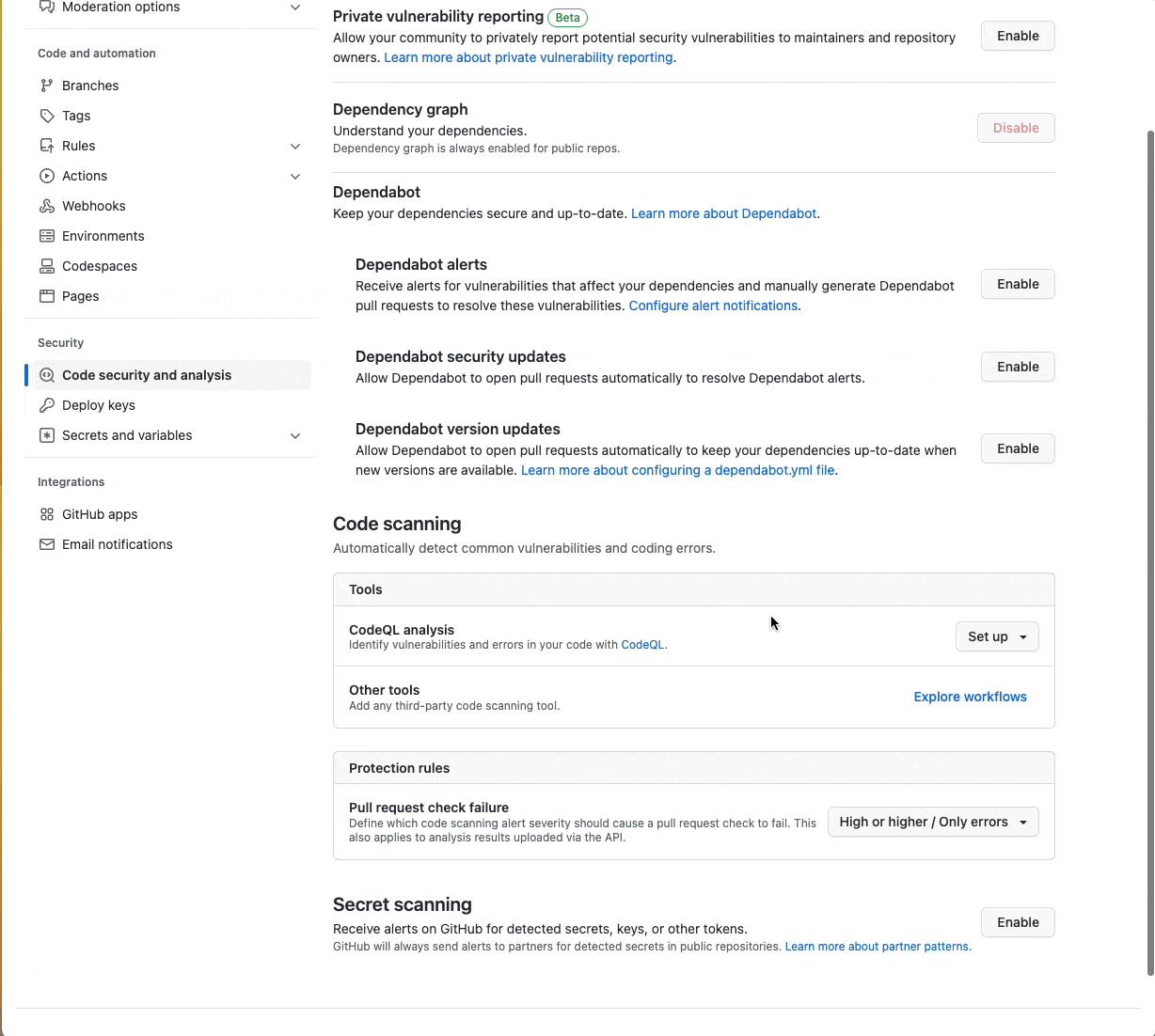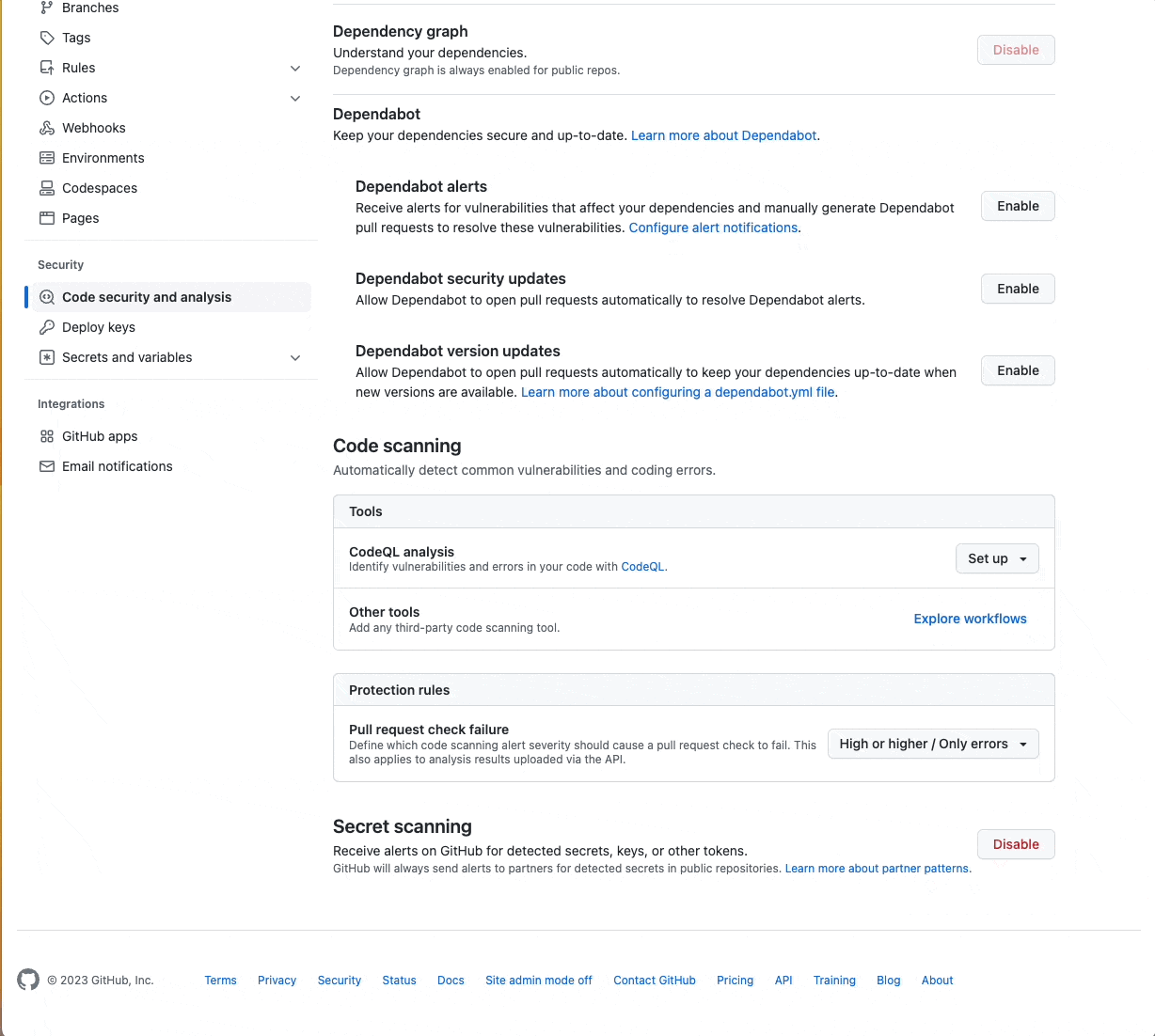
Any GitHub user administrating a public repository can easily enable secret scanning alerts by opening the “Settings” tab, clicking on the “Code security and analysis” option under the Security section, and then clicking “Enable” on “Secret Scanning” at the bottom of the page.
Check out GitHub’s documentation for more information about how secret scanning works and how you can make the most of the new feature.
