Google Drive is one of the most used cloud-based storage platforms, and due to its immense popularity and capabilities, it’s actively targeted by threat actors.
Data theft is a prevalent method employed by malicious actors once they have obtained entry into a platform. It serves as a common attack vector for stealing information.
Mitiga’s research team has recently conducted a comprehensive investigation into data exfiltration techniques within Google Workspace, highlighting the significance of this attack method and platform.
This research aligns with their ongoing efforts to explore and understand cloud and Software as a Service (SaaS) attacks and forensic practices.
Attack on Google Drive
Malicious actors frequently aim to exploit vulnerabilities within Google Drive to gain unauthorized access to sensitive files and user data.
Experts conducting an in-depth analysis uncovered a critical security flaw within Google Workspace, revealing a troubling deficiency in its forensic measures.
This vulnerability allows threat actors to stealthily exfiltrate data from Google Drive without leaving any detectable traces.
Google Workspace offers enhanced transparency by utilizing “Drive log events” to monitor and track various actions performed on a company’s Google Drive resources.
Google Workspace Security
Google Workspace records events involving external domains, such as sharing an object with users outside the organization, ensuring comprehensive tracking and monitoring.
These events are captured and logged to provide a complete record of interactions with external users.
The application of this practice is restricted to actions performed by users holding a paid license, which forms the core limitation of the issue, but this restriction is a key challenge that needs to be fixed.
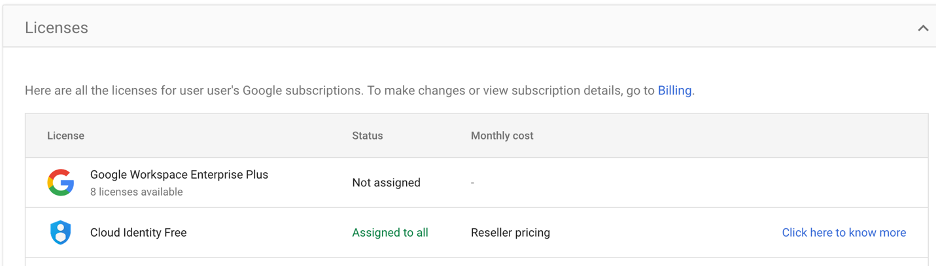
All Google Drive users are initially provided with a “Cloud Identity Free” license as the default option. This license grants basic access and functionality to the user within the Google Drive ecosystem.
Here, the administrators must assign a paid license to users, specifically the “Google Workspace Enterprise Plus” license to unlock additional features.
Exploitation
The absence of clear visibility poses a considerable challenge in two primary scenarios, leading to potential complications, and here below we have mentioned those scenarios:-
A threat actor compromises a user’s account
If a threat actor manages to compromise an admin user’s account, they can take control of various critical actions. In this scenario, the system generates log records solely for the actions of revoking and assigning licenses.
Other activities or events may not be recorded or logged. If a threat actor infiltrates a user account that lacks a paid license but has access to the organization’s private drive, it raises significant security concerns.
Employee offboarding
This situation arises when an employee departs from the company, and their license is revoked before their Google user account is properly disabled or removed.
Without prior notification, the employee holds the potential to download internal files directly from their private drive.
In situations where an organization’s user does not have a paid license but still has access to their private drive, they can download the drive’s files without generating any log records.
This poses a potential risk when the user departs from the organization, as their ability to download files remains untraceable.
Recommendations
Mitiga’s security analysts have reached out to Google’s security team regarding the matter, but they have not received an official response to incorporate into this advisory.
Here below, we have mentioned all the recommendations offered by the experts:-
- Under the “Admin Log Events,” must monitor all the events about license assignment and revoke.
- It is essential to regularly perform threat hunts within Google Workspace, specifically focusing on detecting and investigating this particular activity.
- You can effectively identify and mitigate potential threats and security breaches by conducting these proactive searches.
- To effectively detect instances where files are being copied from a shared drive to a private drive and subsequently downloaded, monitoring the “source_copy” events during your hunts is crucial.
Struggling to Apply The Security Patch in Your System? –
Try All-in-One Patch Manager Plus