A sophisticated attack technique called LNK Stomping has emerged as a critical threat to Windows security, exploiting a fundamental flaw in how the operating system handles shortcut files to bypass security controls.
Designated as CVE-2024-38217 and patched on September 10, 2024, this vulnerability demonstrates how attackers can manipulate Windows shortcuts (LNK files) to circumvent the Mark of the Web (MoTW) security feature, potentially allowing malicious code execution without triggering security warnings.
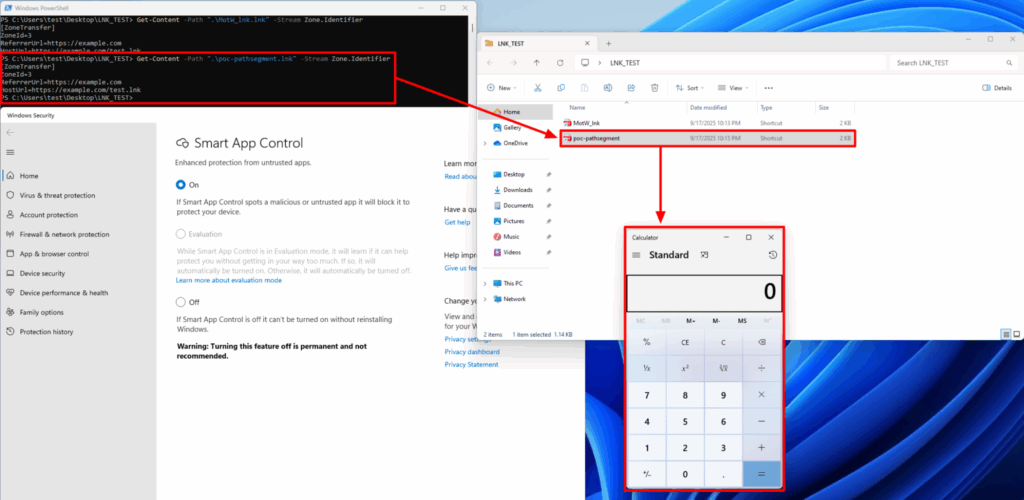
The attack technique exploits Windows Explorer’s path normalization process, causing the system to inadvertently remove MoTW metadata from malicious files.
This bypass enables attackers to execute payloads while evading detection from Smart App Control (SAC) and SmartScreen, two critical Windows security components designed to protect users from untrusted downloads.
LNK Stomping Exploitation
ASEC reports that LNK Stomping leverages the complex binary structure of Windows shortcut files, particularly targeting the LinkTarget IDList component.
This section contains Shell Item IDs that specify the hierarchical location of target files within the Windows Shell namespace.
Attackers manipulate this structure by creating non-standard path configurations that trigger explorer.exe to perform canonicalization operations.
The attack follows a specific sequence when a user clicks a maliciously crafted LNK file containing abnormal path structures, Windows Explorer detects the non-standard configuration and attempts to normalize it.
During this process, the system overwrites the original LNK file while inadvertently removing the NTFS Alternate Data Stream (ADS) called Zone.Identifier, which contains the MoTW metadata.
This removal occurs before security checks are performed, allowing the malicious payload to execute without triggering defensive mechanisms.
Three primary manipulation techniques have been identified, PathSegment type attacks place entire file paths within a single IDList array element rather than properly segmented components, Dot type attacks append periods or spaces to execution target paths, and Relative type attacks use only filenames without complete path specifications, all creating structural inconsistencies that trigger the normalization vulnerability.
Security researchers at Elastic Security Labs identified numerous LNK Stomping samples on VirusTotal, with the oldest submissions dating back six years, indicating this technique has been exploited in the wild long before its formal disclosure.
The technique’s effectiveness stems from its ability to appear as legitimate system behavior. When LNK files execute, they invoke trusted Windows utilities, making malicious activities blend seamlessly with normal system operations.
CISA added CVE-2024-38217 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, confirming active exploitation by threat actors.
This approach has become increasingly popular following Microsoft’s macro blocking policies implemented in 2022, forcing attackers to seek alternative initial access vectors through file formats like ISO, RAR, and LNK files distributed via email attachments or compressed archives.
Organizations face significant detection challenges because the attack exploits fundamental Windows file handling mechanisms rather than external vulnerabilities.
Traditional signature-based detection methods may fail to identify these attacks since they leverage legitimate system processes and file structures.
The persistence of this vulnerability for years before discovery highlights the importance of format-level security research and behavior-based analysis to identify previously unknown evasion techniques in familiar file types.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X for daily cybersecurity updates. Contact us to feature your stories.
