An unpatched zero-day vulnerability in Gogs, a popular self-hosted Git service, has enabled attackers to gain remote code execution on Internet-facing instances and compromise hundreds of servers.
Written in Go and designed as an alternative to GitLab or GitHub Enterprise, Gogs is also often exposed online for remote collaboration.
CVE-2025-8110, the Gogs RCE vulnerability exploited in these attacks, stems from a path traversal weakness in the PutContents API. The flaw allows threat actors to bypass the protections implemented for a previously patched remote code execution bug (CVE-2024-55947) by using symbolic links to overwrite files outside the repository.
While Gogs versions that addressed the CVE-2024-55947 security bug now validate path names to prevent directory traversal, they still fail to validate the destination of symbolic links. Attackers can abuse this by creating repositories containing symbolic links pointing to sensitive system files, and then using the PutContents API to write data through the symlink, overwriting targets outside the repository.
By overwriting Git configuration files, specifically the sshCommand setting, attackers can force target systems to execute arbitrary commands.
Wiz Research discovered the vulnerability in July while investigating a malware infection affecting a customer’s Internet-facing Gogs server. In total, the researchers found over 1,400 Gogs servers exposed online, with more than 700 instances showing signs of compromise.
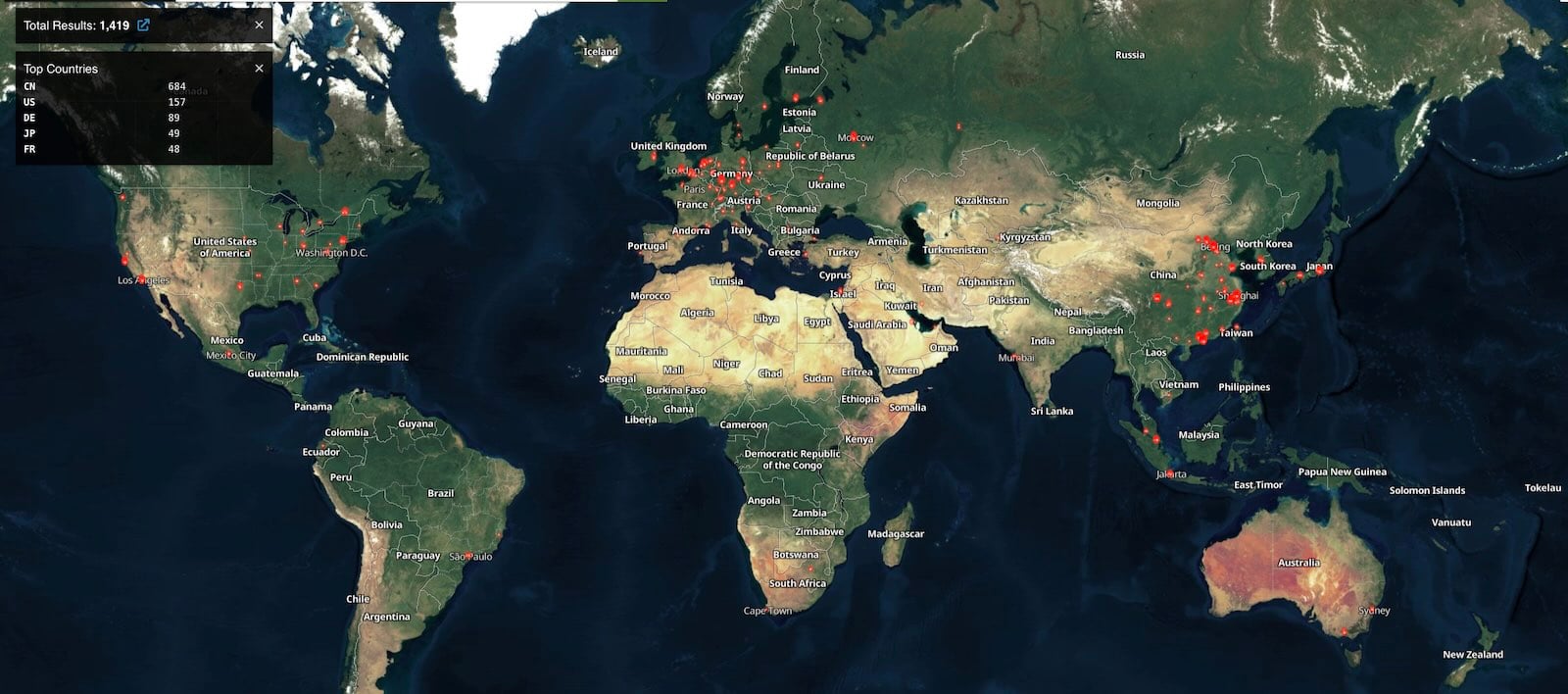
All compromised instances identified during the investigation of these attacks showed identical patterns, including repositories with random eight-character names created within the same timeframe in July, suggesting a single actor or group using automated tools is behind the campaign.
“In our external scan, we identified over 1,400 Gogs servers publicly exposed to the internet. Many of these instances are configured with ‘Open Registration’ enabled by default, creating a massive attack surface,” they said.
Wiz also found that the malware deployed was created using Supershell, an open-source command-and-control (C2) framework that establishes reverse SSH shells over web services. Further analysis revealed the malware communicated with a command-and-control server at 119.45.176[.]196.
The researchers reported the vulnerability to Gogs maintainers on July 17, and the maintainers acknowledged the flaw on October 30, when they were still developing a patch. According to a disclosure timeline shared by Wiz Research, a second wave of attacks was observed on November 1.
Gogs users are advised to immediately disable the open registration default setting and limit access to the server using a VPN or an allow list. Those who want to check whether their instance has already been compromised should look for suspicious use of the PutContents API and for repositories with random 8-character names.

Broken IAM isn’t just an IT problem – the impact ripples across your whole business.
This practical guide covers why traditional IAM practices fail to keep up with modern demands, examples of what “good” IAM looks like, and a simple checklist for building a scalable strategy.



