A threat group named ‘ResumeLooters’ has stolen the personal data of over two million job seekers after compromising 65 legitimate job listing and retail sites using SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
The attackers mainly focus on the APAC region, targeting sites in Australia, Taiwan, China, Thailand, India, and Vietnam to steal job seeker’s names, email addresses, phone numbers, employment history, education, and other relevant information.
According to Group-IB, which has been following the threat group since its beginning, in November 2023, ResumeLooters attempted to sell the stolen data through Telegram channels.
.png)
Compromising legitimate sites
ResumeLooters primarily employs SQL injection and XSS to breach targeted sites, mainly job-seeking and retail shops.
Their pen-testing phase involved the use of open-source tools like:
- SQLmap – Automates detection and exploitation of SQL injection flaws, taking over database servers.
- Acunetix – Web vulnerability scanner identifying common vulnerabilities like XSS and SQL injection and providing remediation reports.
- Beef Framework – Exploits web browser vulnerabilities, assessing the security posture of a target via client-side vectors.
- X-Ray – Detects web application vulnerabilities, revealing structure, and potential weaknesses.
- Metasploit – Develops and executes exploit code against targets, also used for security assessments.
- ARL (Asset Reconnaissance Lighthouse) – Scans and maps online assets, identifying potential vulnerabilities in network infrastructure.
- Dirsearch – Command-line tool for brute-forcing directories and files in web applications, uncovering hidden resources.
After identifying and exploiting security weaknesses on target sites, ResumeLooters injects malicious scripts into numerous locations in a website’s HTML.
Some of these injections will be inserted to trigger the script, but other locations, like form elements or anchor tags, will simply display the injected script, as shown below.
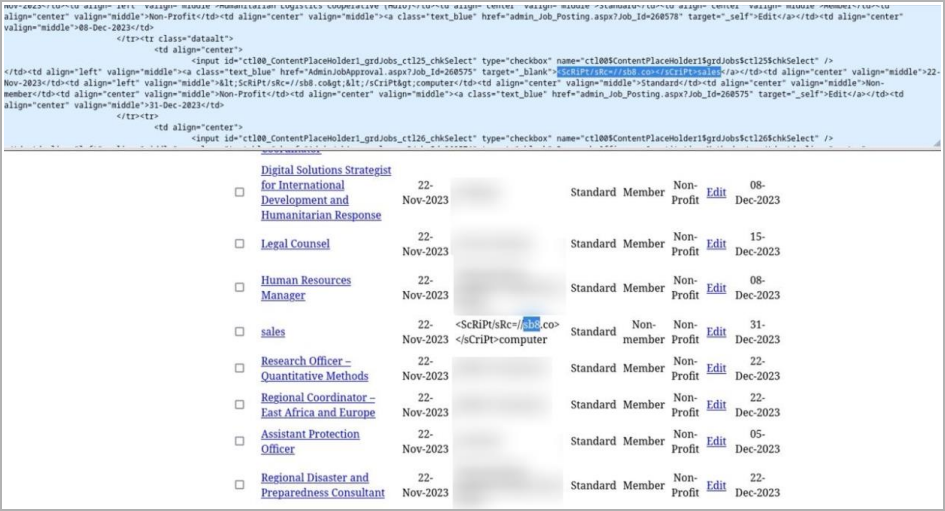
Source: Group-IB
However, when properly injected, a malicious remote script will be executed that displays phishing forms to steal visitors’ information.
Group-IB also observed cases where the attackers employed custom attack techniques, like creating fake employer profiles and posting fake CV documents to contain the XSS scripts.

Source: Group-IB
Thanks to an opsec mistake by the attackers, Group-IB was able to infiltrate the database hosting the stolen data, revealing that the attackers managed to establish administrator access on some of the compromised sites.
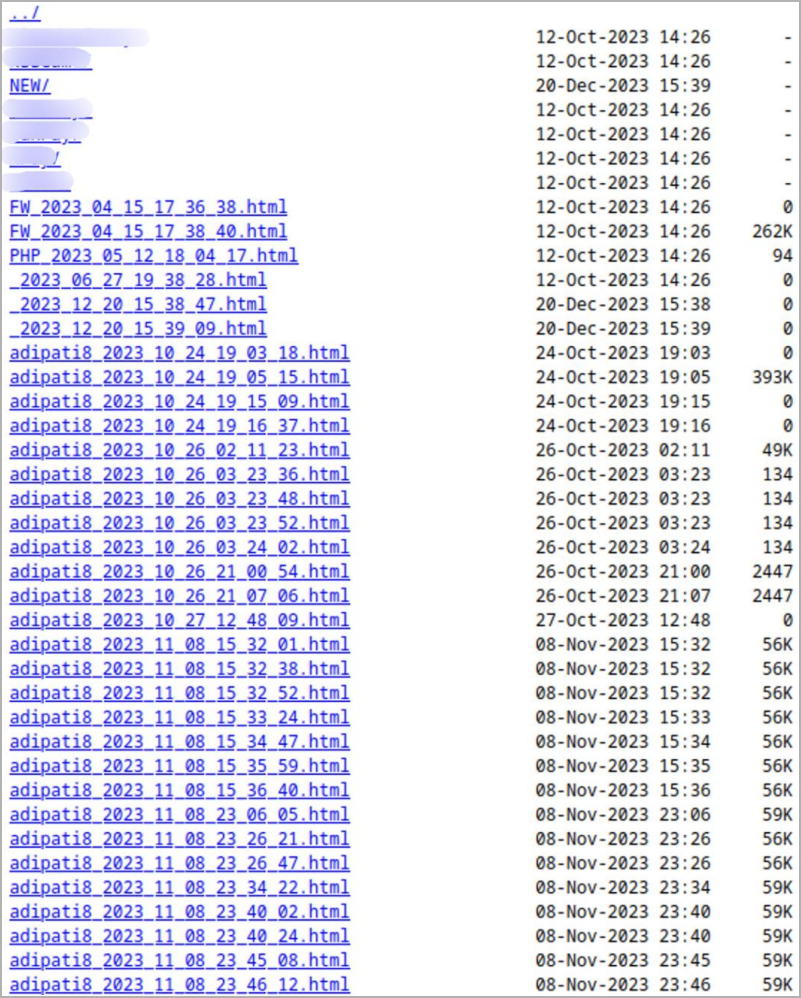
Source: Group-IB
ResumeLooters conducts these attacks for financial gain, attempting to sell stolen data to other cybercriminals via at least two Telegram accounts that use Chinese names, namely “渗透数据中心” (Penetration Data Center) and “万国数据阿力” (World Data Ali).
Although Group-IB does not explicitly confirm the attackers’ origin, ResumeLooters selling stolen data in Chinese-speaking groups and using Chinese versions of tools, like X-Ray, make it highly probable that they are from China.
