The latest research reveals a new sophisticated attack carried through Webapk technology targeting Android devices.
The threat actors manipulate the user to install malicious web apk through a Smishing attempt by impersonating legit banking sources.
The CSIRT KNF team carried out a detailed analysis of a website reported by RIFFSEC and published its result in their latest article.
Malware as Native Application
Initially, the threat actors send sms to the targeted victims suggesting they update the banking application by clicking the link.
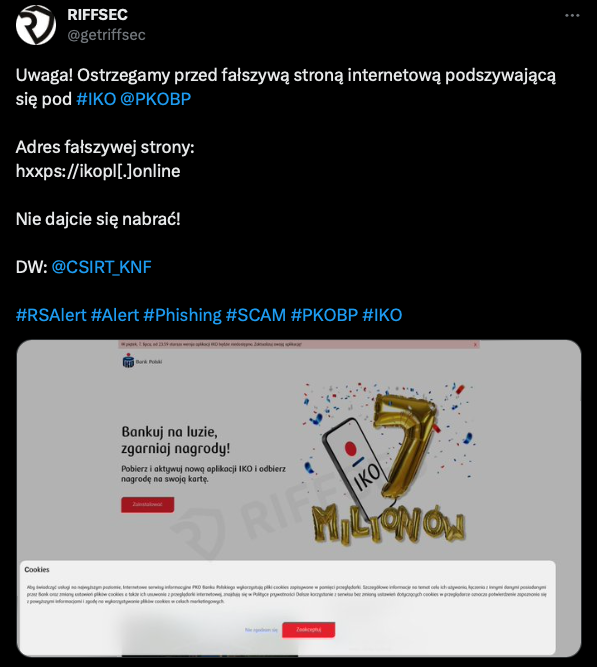
The link embedded in the message redirects the user to the site using Web APK technology to download malicious applications.
Webapk refers to a technology that allows for the creation of web applications that can be installed and run like native Android apps.
WebAPK allows the installation of web applications directly from the browser without the need to use the Google Play Store.
Once the application is installed, it appears like a banking application and asks user credentials for authorization.
This attack poses a serious threat due to the ability to install a malicious application without displaying typical warnings associated with installations from untrusted sources.

The application is signed with the Google Chrome certificate, which is why it appears in the system settings as installed by Google Play Protect.
WebAPK applications create unique package names and checksums on each device, making such attacks difficult to defend against.
Indicators of Compromise (IoC) are difficult to utilize since the Chrome engine dynamically builds them.
Recommendations:
Detection of such applications by antivirus systems is complex and often impossible.
For this reason, one of the most effective ways to prevent the attack
is by detecting and blocking websites that use the WebAPK mechanism to carry out phishing attacks.
Recommend an approach focused on identifying and blocking these sites to minimize the risk to users.
Hashes
MD5: ae12fd46fe868dc4384db26e6f745cce
SHA1: 1c24f4398caae9179028b5415ed980f0ad18f4a7
SHA256: 113be611bcb64b04dfaca2481d8108e94ff41a56fb81f8aef190d4161acd983d
md5: 6504436573451911f10b2be6ad7d560c
sha1: 0fa9a1b93dac4cc5a0a88d08f6949dc11e5275b0
sha256:fe71ef0d9897374f009d3c930c3eac31f523a29d42ad4898f366b1f220769bd1





