eSentire’s Threat Response Unit (TRU) has uncovered a sophisticated campaign where threat actors exploit the ScreenConnect remote access client to deliver the AsyncRAT trojan.
This discovery highlights the evolving tactics of cybercriminals and underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
The Discovery: A Deceptive Download
In June 2024, eSentire’s TRU observed multiple incidents where users inadvertently downloaded the ScreenConnect remote access client from deceptive websites.
ScreenConnect, a legitimate remote access tool, was manipulated by threat actors to gain unauthorized access to users’ systems.
The initial infection vector was identified as a drive-by download, where users visiting a compromised website were redirected to download the ScreenConnect application automatically.
One notable case involved a user downloading ScreenConnect from a compromised WordPress site, aviranpreschool[.]com, which was redirected from lomklauekabjikaiwoge[.]com.
Once ScreenConnect was launched, it connected to the threat actor’s instance at fa-histsedueg.screenconnect[.]com.
Join our free webinar to learn about combating slow DDoS attacks, a major threat today.
This established a remote session, allowing the attacker to drop an executable file that led to the infection of AsyncRAT, a remote access trojan.
The Infection Chain
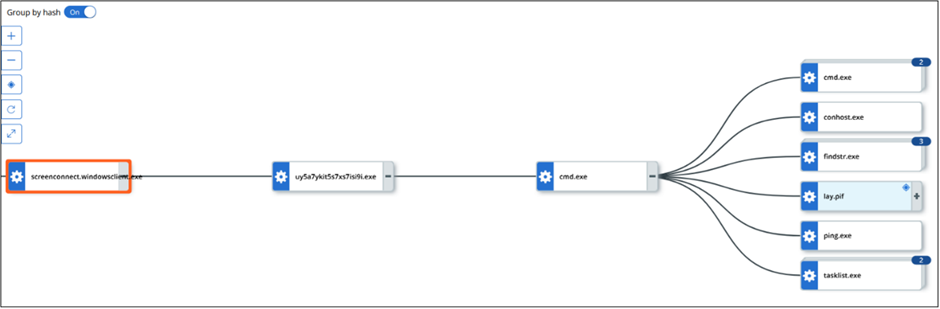
The infection chain began with the download of an executable file named uy5a7ykit5s7xs7isi9i.exe (MD5: 6bdba391a77bb67cb5aaae203d061ea8).
This file contained an NSIS installer containing an NSI script, embedded AutoIt components, and batch scripts.
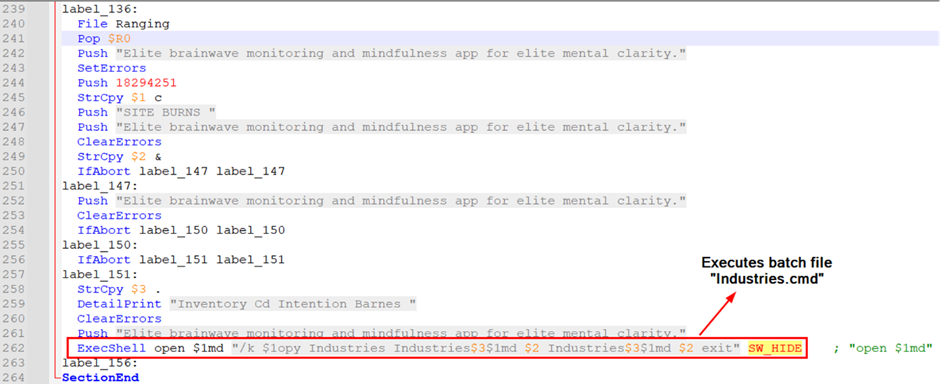
The NSI script executed a batch file named “Industries.cmd” (MD5: 3f8ca557d51e210952bdd7180cb33d10), which performed several actions to create and manage a malicious AutoIt script.
The batch file combined multiple files into a binary named “B” (MD5: 4f3bb0cdfff1c15b75041d07c1b7aac9), containing the embedded AsyncRAT payload.
It then concatenated additional files into a single file named “Lay.pif” (MD5: b06e67f9767e5023892d9698703ad098) and executed the malicious AutoIt script using the rebuilt AutoIt executable.
The script introduced delays to evade detection by antivirus software and checked for specific processes to ensure its execution.
Evasion Tactics and Payload Delivery
The malicious AutoIt script was responsible for decrypting the embedded AsyncRAT payload via RC4 encryption and injecting it into either RegAsm.exe or AppLaunch.exe if Bitdefender Agent (bdagent.exe) was detected as a running process.
This sophisticated method allowed the threat actors to bypass security measures and maintain persistence on the infected system.
The AsyncRAT trojan gave the attackers significant control over the compromised systems, enabling data theft, system manipulation, and further malware deployment.
The detailed infection process, including delaying tactics and conditional script execution, showcased the advanced techniques used by the threat actors to evade detection and ensure successful payload delivery.
eSentire’s 24/7 Security Operations Centers (SOCs), staffed with elite threat hunters and cyber analysts, swiftly responded to these incidents.
The affected hosts were isolated to contain the infection, and remediation recommendations were provided to the customers.
The incidents underscored the importance of vigilance and proactive cybersecurity measures.
Recommendations from eSentire’s TRU:
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Ensure all devices are protected with EDR solutions to detect and respond to threats in real time.
- Phishing and Security Awareness Training (PSAT): Implement a PSAT program to educate employees about emerging threats and safe online practices.
- Password Management: Encourage using password managers instead of browser-based password storage and implement master passwords where applicable.
These incidents highlight the critical need for organizations to remain vigilant and adopt comprehensive cybersecurity strategies to protect against evolving threats.
By following these recommendations, organizations can enhance their security posture and mitigate the risk of similar attacks in the future.
The June 2024 incidents analyzed by eSentire’s TRU illustrate the sophisticated methods employed by threat actors to exploit legitimate tools like ScreenConnect for malicious purposes.
The deployment of AsyncRAT via deceptive downloads emphasizes the importance of cautious software practices and robust security measures to safeguard against cyber threats.
"Is Your System Under Attack? Try Cynet XDR: Automated Detection & Response for Endpoints, Networks, & Users!"- Free Demo
