A critical stored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in Ivanti Endpoint Manager (EPM) enables unauthenticated attackers to hijack administrator sessions by injecting malicious JavaScript into the management dashboard.
The vulnerability, identified as CVE-2025-10573 with a CVSS score of 9.6, affects all versions below EPM 2024 SU4 SR1 and poses an immediate threat to enterprise environments managing thousands of endpoints.
Vulnerability Overview
Ivanti EPM, widely deployed across enterprises for endpoint management and vulnerability scanning, contains a dangerous unauthenticated entry point that allows attackers to poison the administrator dashboard with malicious payloads.
The vulnerability stems from unsafe handling of device scan data submitted through the ‘/incomingdata’ web API, which lacks proper input validation and output encoding.
Attacker with no credentials can submit crafted device requests containing XSS payloads to the exposed ‘postcgi.exe’ CGI binary.
The malicious data is then automatically processed and stored in the EPM database. When administrators access dashboard pages displaying device information, the unencoded XSS payloads execute in their browser context, granting the attacker complete control over the administrator’s authenticated session.
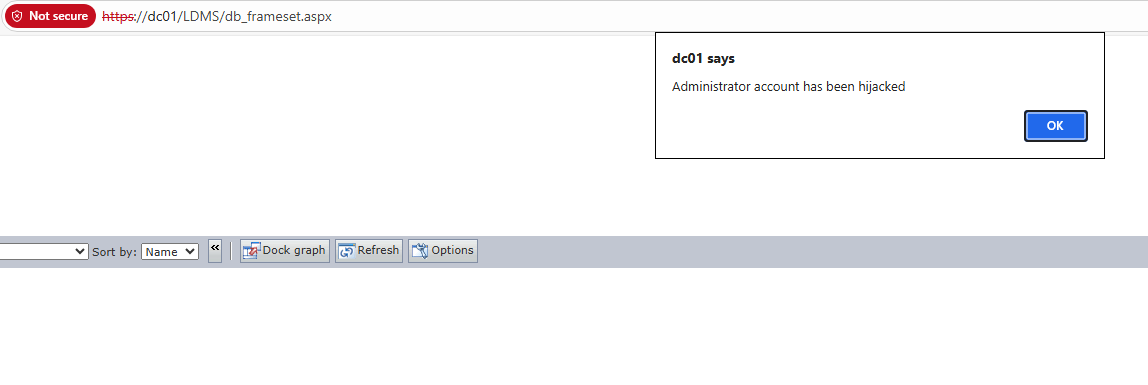
This represents a particularly dangerous attack vector because it bypasses traditional authentication controls and targets the most privileged users within an organization the very individuals responsible for system administration and security management.
The attack exploits the device scan processing pipeline in Ivanti EPM. The vulnerable ‘incomingdata’ API accepts device scan data in a simple key=value format without sanitization.
Attackers inject JavaScript code within fields such as Device ID, Display Name, Device Name, and OS Name.
Once the malicious scan file is written and processed, these fields are reflected unsafely in the administrator dashboard DOM, triggering arbitrary code execution.
The vulnerability affects Ivanti EPM 11.0.6 and versions below EPM 2024 SU4. The unauthenticated nature of the attack is particularly concerning, as it requires no valid credentials or prior system access to initiate the exploitation. An attacker only needs network connectivity to the EPM web service.
Ivanti released version EPM 2024 SU4 SR1 on December 9, 2025, which addresses CVE-2025-10573.
Organizations using affected versions should prioritize upgrading immediately, given the critical nature of the vulnerability and the high privilege level of compromised administrator accounts.
Rapid7 will provide authenticated checks for this vulnerability through Exposure Command, InsightVM, and Nexpose on December 9, 2025, allowing organizations to identify vulnerable instances within their environments.
The vulnerability was discovered and reported by Ryan Emmons, Staff Security Researcher at Rapid7, during research into Ivanti EPM security.
The disclosure followed Rapid7’s responsible vulnerability disclosure policy, with close coordination between Rapid7 and the Ivanti security team to ensure timely patching and customer protection.
Ivanti acknowledged the critical importance of the vulnerability and expressed appreciation for Rapid7’s collaborative approach to responsible disclosure, emphasizing the vendor’s commitment to security and the essential role of the security research community in identifying threats.
Organizations operating Ivanti EPM should treat this vulnerability as critical and apply patches immediately.
The attack requires no authentication and targets administrator accounts with full system privileges, making compromise particularly damaging.
Additionally, implementing network segmentation to restrict access to the EPM web interface and monitoring for suspicious device scan submissions can provide temporary mitigation while patches are deployed.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.