HijackLoader Evolves with New Modules for Stealth and Malware Analysis Evasion
HijackLoader, a malware loader first identified in 2023, has undergone significant evolution with the addition of new modules designed to enhance its stealth capabilities and evade malware analysis environments.
Recent research by Zscaler ThreatLabz reveals that these updates include advanced techniques such as call stack spoofing, virtual machine (VM) detection, and persistence mechanisms, marking a notable shift in the malware’s sophistication.
Enhanced Evasion Tactics: Call Stack Spoofing and VM Detection
One of the most prominent updates to HijackLoader is its implementation of call stack spoofing, a technique used to obscure the origin of function calls like API or system calls.

By manipulating return addresses on the stack, HijackLoader replaces them with fabricated ones from legitimate system DLLs, effectively masking malicious activity.
This method is further combined with the Heaven’s Gate technique, allowing the malware to switch between 32-bit and 64-bit code execution seamlessly.
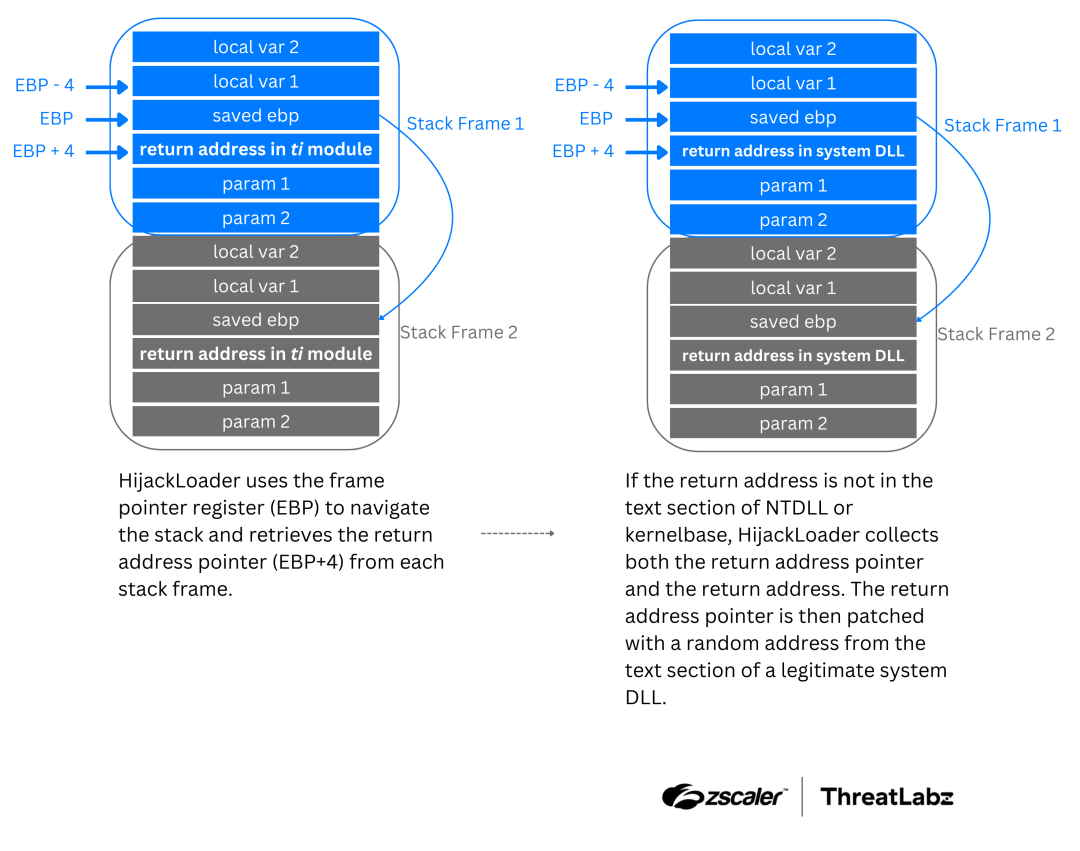

Additionally, the newly introduced ANTIVM module enables HijackLoader to detect virtualized environments commonly used for malware analysis.
This module employs various checks, including CPU instruction timing, hypervisor presence detection, and system resource assessments such as physical memory and processor count.
If these checks indicate a virtualized environment, the malware terminates execution to avoid detection.
Persistence Mechanisms and Modular Design
HijackLoader’s modular architecture continues to expand with components like modTask and modTask64, which establish persistence by creating scheduled tasks.

These tasks are configured using parameters stored in the PERSDATA module.
The malware also employs reflective code loading to dynamically execute modules while avoiding static detection.
Other notable modules include CUSTOMINJECT and CUSTOMINJECTPATH, which facilitate process injection by leveraging legitimate executables created at specified file paths.
The SM module plays a critical role in call stack spoofing by specifying legitimate DLLs for address manipulation.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
To aid in detection efforts, researchers have identified several IOCs associated with HijackLoader:
- SHA256 Hashes of Samples:
67173036149718a3a06847d20d0f30616e5b9d6796e050dc520259a15588ddc87b399ccced1048d15198aeb67d6bcc49ebd88c7ac484811a7000b9e79a5aac906cfbffa4e0327969aeb955921333f5a635a9b2103e05989b80bb690f376e4404- Additional hashes are available for further analysis.
- Encrypted Modules:
273bc7700e9153f7063b689f57ece3090c79e6b1038a9bc7865f61452c7377b028eb6ce005d34e22f6805a132e7080b96f236d627078bcc1bedee1a3a209bd1f
HijackLoader’s continued development underscores its adaptability in evading modern security defenses.
With its modular design and advanced evasion tactics, it poses a significant threat to organizations worldwide.
Security teams must remain vigilant by leveraging updated threat intelligence and deploying robust detection mechanisms to counter this evolving malware.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup – Try for Free
Source link






