How HackerOne Helps the Vulnerability Management Process
HackerOne sees vulnerability management as a process combining software tools and security analyst actions to reduce risk. In many cases, successful Vulnerability Management requires a joint effort between security operations, who find vulnerabilities, and IT operations responsible for fixing, or patching, vulnerabilities.
HackerOne brings a unique combination of software and human expertise to the vulnerability management process. Specifically, HackerOne leverages security experts – also known as ethical hackers or security researchers – who apply their knowledge of applications and infrastructure to find vulnerabilities automated scanners miss. These individuals are sourced from a global talent pool that can get started quickly and on-demand. Just as important, hackers have an inherent sense of how easily a given vulnerability can be exploited, providing valuable feedback that can improve the efficiency of the vulnerability remediation process.
Most often, HackerOne is used in combination with vulnerability scanners or vulnerability management tools to enhance effectiveness. Typically, scanners are used first to capture the bulk of known vulnerabilities. So, why use hackers at all? HackerOne solves three common problems faced in vulnerability management:
- Finding new or unknown vulnerabilities that scanners are blind to. These are often the vectors that cybercriminals favor.
- Triaging vulnerabilities, removing false positives and patching exploits before they are exposed while prioritizing critical ones first
- Providing human bandwidth to manage the high volume of reported vulnerabilities, including retesting against vulnerabilities that have been fixed.
In addition, ethical hackers have a key advantage over software scanners. Their experience, creativity and tenacity can often find vulnerabilities that scanning tools miss. Humans recognize the risk context and severity of misconfigurations without all of the false positives that typically come with AI-powered solutions. This is also true of the retesting phase, where hackers often find workarounds to fixes. To illustrate the power of ethical hackers, consider this stat from Intel’s 2020 Product Security Report: 45% (103 total) of the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) published by Intel were found by hackers as part of Intel’s bug bounty program. Despite a large internal security team and a mature vulnerability management process, almost half of the vulnerabilities were found by hacker-powered security.
Figure 1: The HackerOne Continuous Security Testing Platform combined with skilled hackers’ access to workflows and data management capabilities.
The HackerOne Continuous Security Testing Platform is designed to give organizations both broad and deep visibility into every aspect of their environment. Simply put, the platform provides an organization with access to thousands of skilled pentesters and ethical hackers, rated by past performance and technical skills. The platform provides:
- Workflow and reporting mechanism to visualize and communicate findings
- System of knowledge sharing for new and unique vulnerability categories and techniques
- Findings capture and tracking in a vulnerability database
- Integrations with vulnerability management systems, DevOps tools and ticketing systems
Here’s how HackerOne helps the process, step by step. Like many other vulnerability management vendors, HackerOne defines the process in five stages: Discover, Assess, Remediate, Verify and Refine. The process then repeats. Quite often, there is a scoping, hacker skills matching and planning engagement that precedes the deployment of the process.
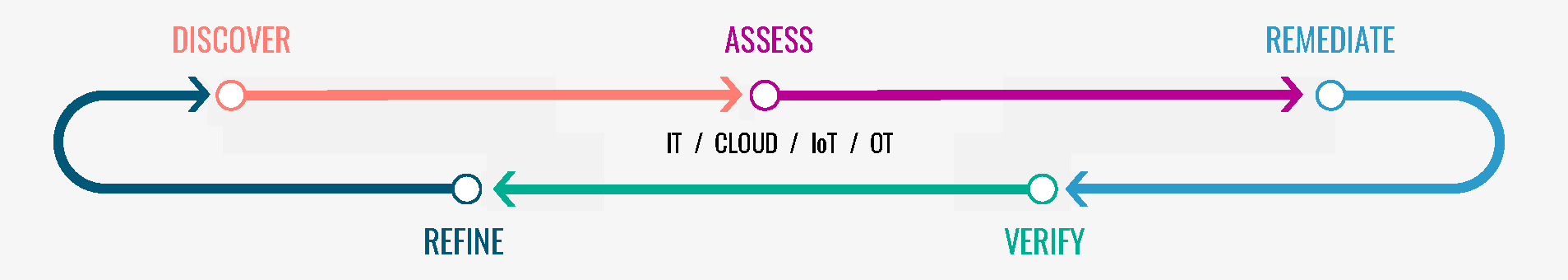
Figure 2: HackerOne’s five-step vulnerability management process
Discover
Hackers will typically perform some type of reconnaissance at the beginning of an engagement. They discover external attack surfaces that can be exploited. This ensures that the vulnerability management program is scoped accurately and covers critical web-facing assets and uncovers shadow IT or unknowingly exposed assets.
With the attack surface understood, an organization can use HackerOne Response, our Vulnerability Disclosure Program (VDP), to collect vulnerabilities reported by unpaid hackers and concerned third parties. For more proactive coverage, an organization can set up a bug bounty program using HackerOne Bounty. Unlike a VDP, a bug bounty program provides incentives for hackers to find vulnerabilities for monetary rewards. An organization may choose to focus ethical hackers on higher-risk assets, such as cloud infrastructure or an API, as opposed to lower-risk assets or those where scanning tools may be adequate.
Assess
The platform automatically scores vulnerabilities based on the hacker, triager, and customer risk models. The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is an industry-standard used to determine the severity of a bug. HackerOne leverages CVSS in our report submission flow to create a common language around the severity of bugs, allowing consensus to be derived from multiple stakeholders. Hackers can either choose a blanket severity of low, medium, high, or critical or use the CVSS calculator to input more specific information and calculate an exact CVSS score.
Our triage team will review incoming bugs to ensure the severity is accurate. If it’s not, we’ll adjust it based on CVSS scoring. The triage team uses this as the basis to determine the severity of the bug, and subsequently recommends a bounty, which in turn ties back to a severity-based bounty structure.
Remediate
The platform offers remediation advice for each vulnerability found. HackerOne remediation guidance is shared with Development, Incident Response (IR) and Security Operations teams to aid in understanding and resolving vulnerabilities. The guidance can be delivered in a few ways: via a special hackbot, a remediation guidance widget at the top of the report timeline within the platform, via Jira, or through the API. There are two types of remediation guidance:
- Automated Remediation Guidance that links to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Research & Engineering (MITRE) information page that belongs to the Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) reference associated with the report.
- Custom Remediation Guidance that a customer can add. Custom remediation guidance can be created, updated and removed via the hackbot widget in the report timeline. For example, an organization may have a vetted list of input sanitization libraries that developers are encouraged to use. These libraries can be listed whenever an injection vulnerability is validated by a HackerOne triager.
Whichever delivery mechanism and guidance type is selected, the remediation guidance will help security, operations, or development teams understand the nature of the issue and how they should best fix the problem.
In addition, remediation workflows can be configured based on the type and severity of a vulnerability. Supported integrations include Atlassian Jira, Azure DevOps, GitHub, GitLab, PagerDuty, ServiceNow and more.
Verify
HackerOne can review vulnerabilities using a HackerOne Assessment. Organizations can determine the scope of the assessment and recruit hackers with specific skills. For example, an organization may want to run an assessment of its AWS cloud configuration after configuration issues were fixed. An organization can also request validation of fixes with HackerOne Retest. Hackers will be sent the vulnerability report and a timeframe within which to verify the issue has been resolved.
To help improve a program, HackerOne Insights lets an organization benchmark against peers and tech stacks used. Insights is a vulnerability intelligence tool that tracks the latest vulnerabilities found by hackers around the world on behalf of the HackerOne customer base. In addition to benchmarking, an organization can look for emerging threats to allow them to be better prepared.
As mentioned above, organizations often are overwhelmed by the volume of vulnerabilities reported. The HackerOne Continuous Security Platform allows for vulnerabilities to be imported from other vulnerability management systems, such as Qualys, Tenable and others. This delivers two benefits. First, importing known vulnerabilities can focus the efforts of hackers on the unknown issues that invite the most dangerous exploits. . Second, hackers can assist in triaging vulnerabilities. The human power of the HackerOne community can provide the scale to handle the volume internal staff may not be capable of. The skills and intuition of the hackers can help organizations prioritize the riskiest vulnerabilities.
The HackerOne platform and hacker services can both fill gaps in existing vulnerability management programs and improve their efficacy. Using the hybrid approach of humans and scanners is something many organizations have never considered but should.
Hear more from the experts by attending our on-demand webinar “The State of Vulnerability Management Maturity”