INTERPOL has dismantled over 22,000 malicious IP addresses and servers linked to various cyber threats.
This operation, code-named Synergia II, ran from April 1 to August 31, 2024, and was a collaborative effort between INTERPOL, private sector partners, and law enforcement agencies across 95 member countries.

The operation, which primarily targeted phishing, ransomware, and information stealers, identified approximately 30,000 suspicious IP addresses. Of these, 76 percent were successfully taken down, and 59 servers were seized.
Authorities also confiscated 43 electronic devices, including laptops, mobile phones, and hard disks, leading to 41 arrests. 65 more individuals are under investigation.
Build an in-house SOC or outsource SOC-as-a-Service -> Calculate Costs
Global Cooperation on Cybercrime
INTERPOL’s operation was supported by partnerships with cybersecurity firms, including Group-IB, Trend Micro, Kaspersky, and Team Cymru.
These companies provided their expertise in tracking illegal cyber activities, helping to identify thousands of malicious servers.
INTERPOL then shared this data with law enforcement agencies, which carried out coordinated actions such as house searches and server shutdowns.
Notable actions during Operation Synergia II:
- Hong Kong (China): Police took 1,037 servers offline.
- Mongolia: Conducted 21 house searches and identified 93 individuals linked to illegal cyber activities.
- Macau (China): Disconnected 291 malicious servers.
- Madagascar: Seized 11 electronic devices and identified 11 suspects.
- Estonia: Authorities confiscated over 80GB of server data for further analysis.
Neal Jetton, INTERPOL’s Director of the Cybercrime Directorate, emphasized the importance of global cooperation, stating, “The global nature of cybercrime requires a global response.
Together, we’ve dismantled malicious infrastructure and prevented hundreds of thousands of potential victims from falling prey to cybercrime.”
Operation Synergia II focused on three major cybercrimes:
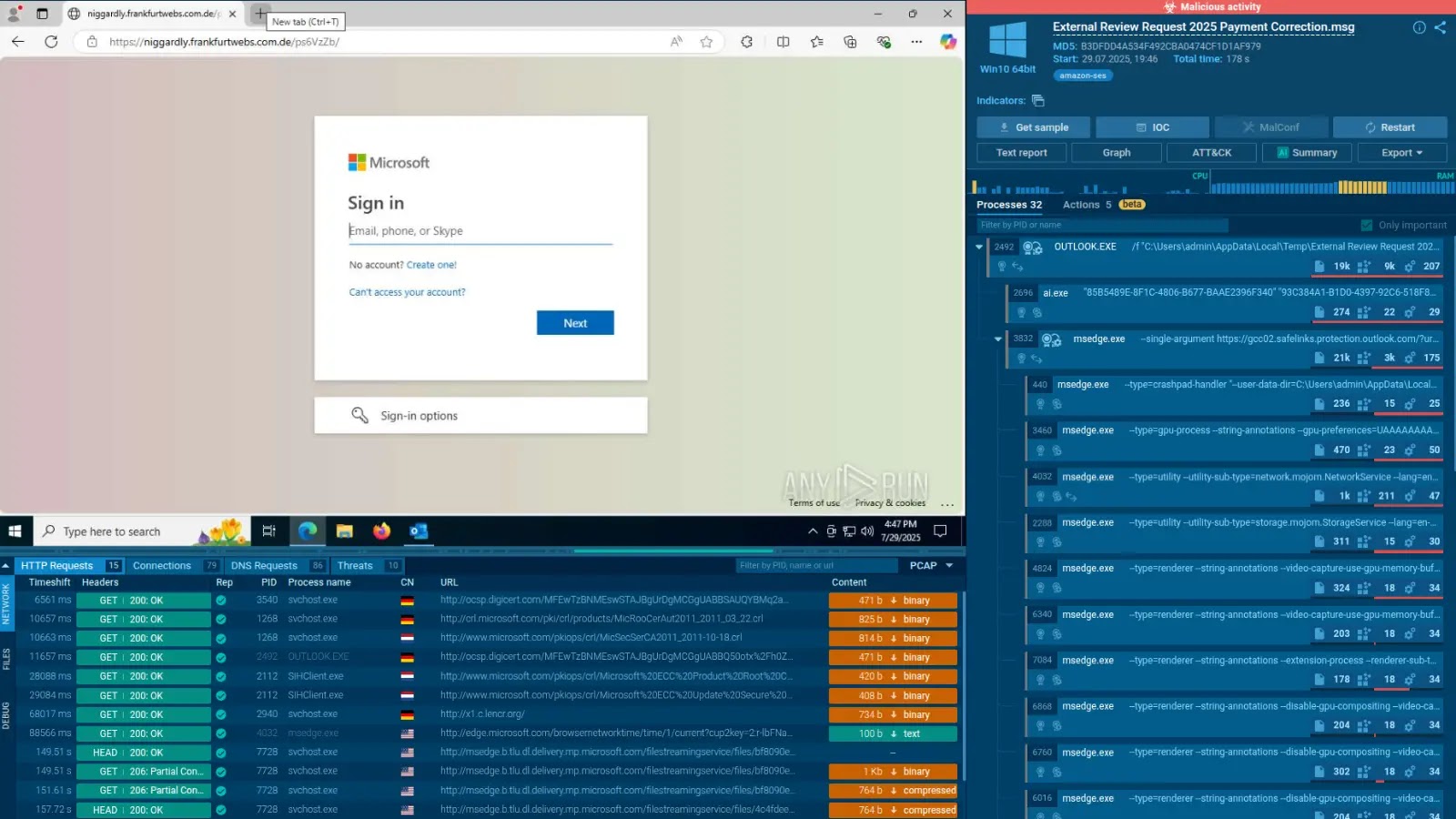
- Phishing: The most common method for stealing sensitive data and deploying malware, often using increasingly sophisticated techniques, including Generative AI.
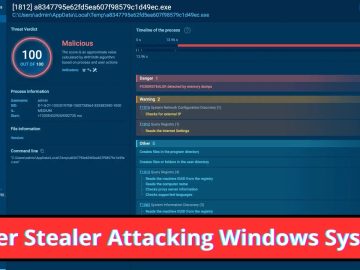
- Infostealers: A growing threat, with a 40% increase in 2023, these malware types breach systems to steal login credentials and financial information.
- Ransomware: Attacks rose globally by 70% in 2023, affecting industries across the board.
Operation Synergia II highlights the evolving nature of cybercrime and the need for continued global efforts to combat these threats.
Run private, Real-time Malware Analysis in both Windows & Linux VMs. Get a 14-day free trial with ANY.RUN!