Cyberattacks have become a critical aspect of international conflicts.
The recent cyber attack launched by Iran against Israel’s critical infrastructure is a testament to the evolving nature of geopolitical disputes.
This article delves into the technical intricacies of the attack, the response from Israel, the hacker groups involved, and the broader cybersecurity implications.

The rivalry between Israel and Iran is not a new chapter in the history of Middle Eastern conflicts.
However, the cyber dimension of their hatred has taken a significant turn.
The recent missile and drone attacks by Iran were a physical manifestation of a conflict that had been brewing in the cyber world since March 2022.
Trustifi’s Advanced threat protection prevents the widest spectrum of sophisticated attacks before they reach a user’s mailbox. Stopping 99% of phishing attacks missed by
other email security solutions. .
The attack on Israel’s critical infrastructure is the conclusion of a year-long cyber conflict, which began with the Israel-Hamas tensions.
The Surge of Cyberattacks
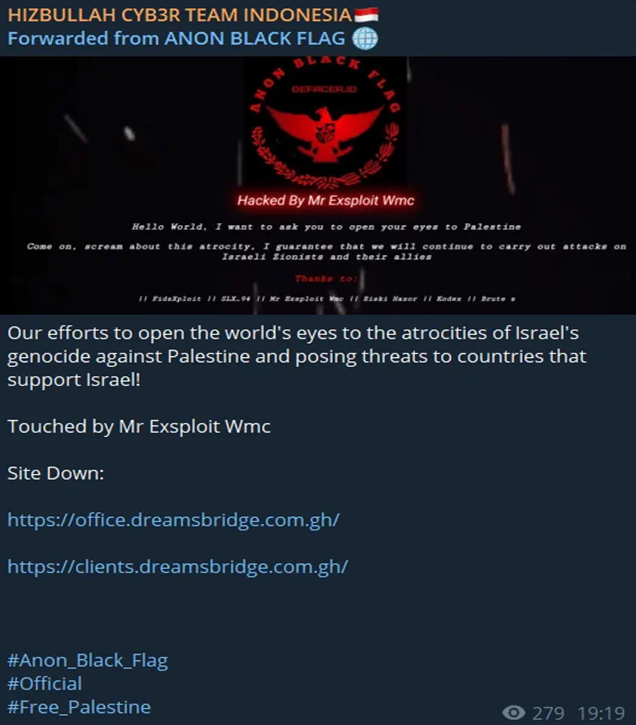
Gaby Portnoy, Israel’s head of cyber defense, reported a tripling of cyberattacks since the onset of the conflict with Hamas.
Iran, along with its allies such as Hezbollah, has been implicated in these increased cyber activities.
Telegram channels have become hotbeds for hacker groups claiming affiliation with Hezbollah, coordinating and launching various cyberattacks against Israeli targets.
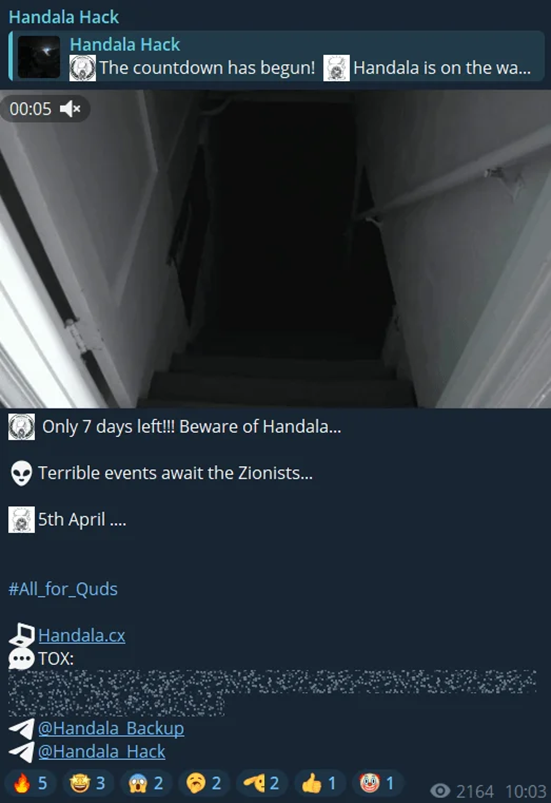
Hacktivist groups have been using significant dates, such as Jewish holidays and Ramadan, to amplify their cyber campaigns against Israel.
Coordinated attacks were called for on these symbolic dates, with groups like Handala signaling their participation.
SOCRadar, a cybersecurity firm, issued early alerts about these potential threats to its users.
The conflict has seen the resurrection of several Iranian-backed hacktivist groups.
Cyber Toufan Al-Aqsa, a state-sponsored entity, has been particularly active, orchestrating large-scale operations and influencing other groups to target Israel.
The Cyber Av3ngers, another IRGC-related group, claimed responsibility for a massive cyberattack that disrupted electricity across various parts of Israel.
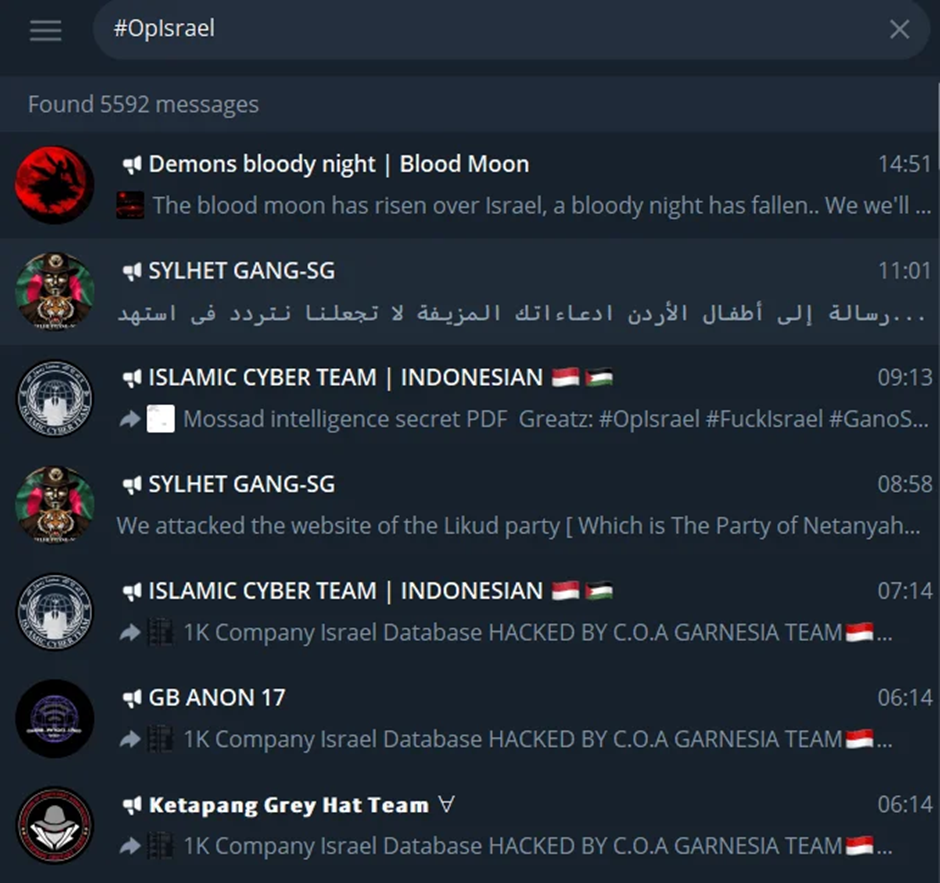
The hacktivist wave sparked by the Israel-Hamas conflict has been one of the largest on record.
This wave has not only targeted Israel but also its perceived allies, including India, the US, the UK, EU countries, and Saudi Arabia.
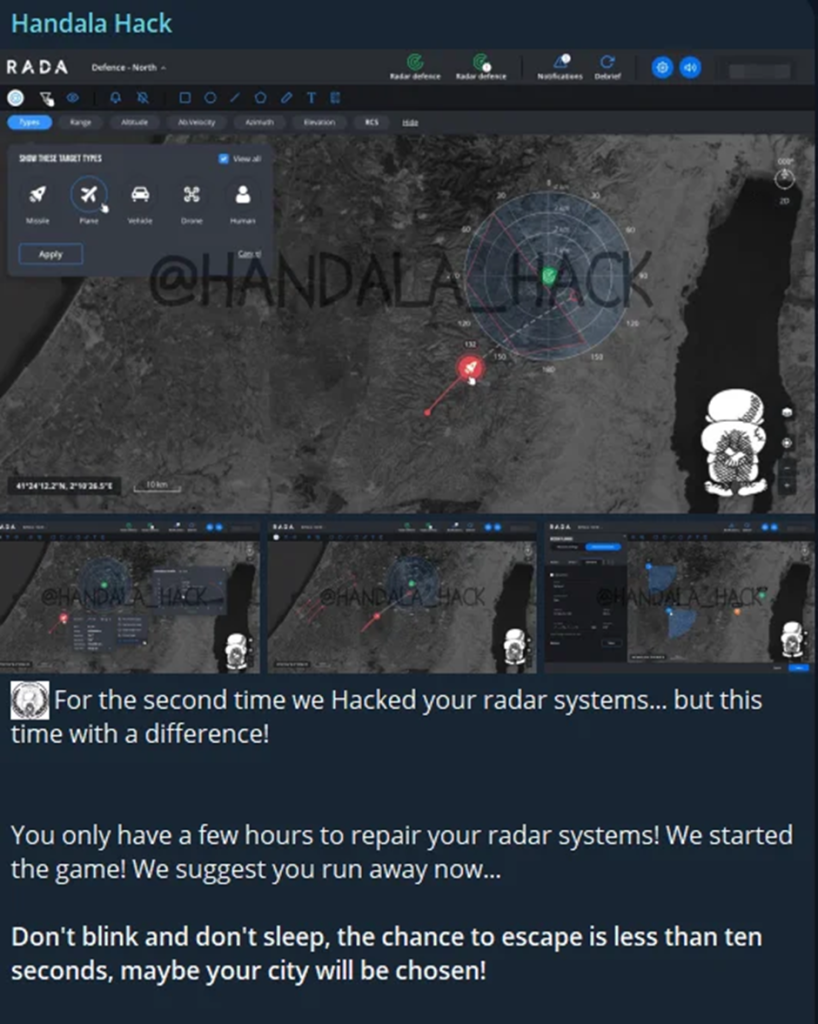
The Iron Dome, Israel’s air defense system, has been a prime target, with groups like Handala claiming to have hacked Israeli radar systems.
Cybersecurity Implications and Israel’s Response
The implications of these cyberattacks are far-reaching.
They highlight the vulnerability of critical infrastructure to state-sponsored and hacktivist cyber activities.
Israel’s response has been multifaceted, strengthening its cyber defenses, retaliatory cyber operations, and international cooperation to counter the threats.
The cyberattack by Iran on Israel’s critical infrastructure marks a significant escalation in cyber warfare.
It underscores the need for robust cybersecurity measures and international collaboration to protect against such threats.
As the digital battlefield evolves, nations must remain vigilant and proactive in defending their cyber frontiers.
Looking to Safeguard Your Company from Advanced Cyber Threats? Deploy TrustNet to Your Radar ASAP
