The Lazarus APT Group, an advanced persistent threat (APT) attributed to North Korea, has deployed a sophisticated new Remote Access Trojan (RAT) called ScoringMathTea as part of its ongoing Operation DreamJob cyberespionage campaign.
ScoringMathTea represents a significant evolution in Lazarus’s malware toolkit, implementing a modular architecture designed specifically to evade detection across both network and endpoint security solutions.
According to research from the ESET Research Team published in October 2025, ScoringMathTea was identified within two distinct kill chains targeting the uncrewed aerial vehicle (UAV) sector, specifically aimed at stealing technological know-how from companies providing drone technology to Ukraine.
The RAT operates as a Dynamic Link Library (DLL) that immediately initializes a thread upon execution, establishing a sophisticated foundation for its command-and-control (C&C) communications and plugin management capabilities.
The malware employs multiple obfuscation and anti-analysis techniques from its earliest execution stages.
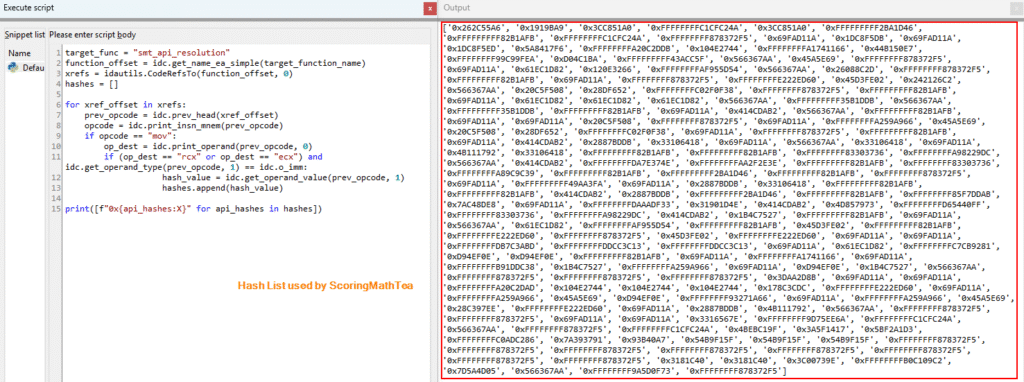
Upon initialization, ScoringMathTea implements API hashing a method whereby Windows API functions are located and resolved dynamically at runtime rather than being stored in traditional import tables.
This approach prevents security researchers and antivirus engines from easily identifying which operating system functions the malware uses.Proximity Browser, which leads from DllMain to the Main function of ScoringMathTea.
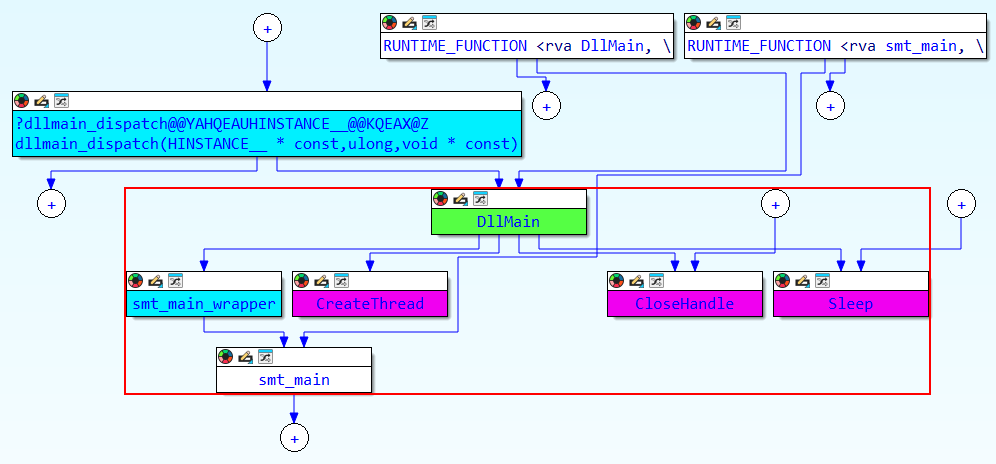
The implementation proves remarkably thorough, with the hashing resolution function called approximately 273 times throughout the malware’s codebase, indicating pervasive use of this evasion mechanism.
Encryption and Communication Strategy
The C&C communication infrastructure reveals sophisticated layering designed to protect command payloads from network-level detection.
ScoringMathTea establishes HTTP/HTTPS connections while implementing multiple encryption and encoding phases.
Communications are protected through Base64 encoding, encryption using the TEA/XTEA algorithm in CBC mode, and optional compression, creating a multi-layered channel that obscures the true nature of transmitted commands.
The malware spoofs legitimate browser User-Agent strings specifically identifying itself as Microsoft Edge version 107 on Windows 10 to blend with legitimate web traffic.
In addition to the URL address, it is also possible to observe the creation of slots for more C&C addresses, which were declared as null, but which I believe could be added during the operation.
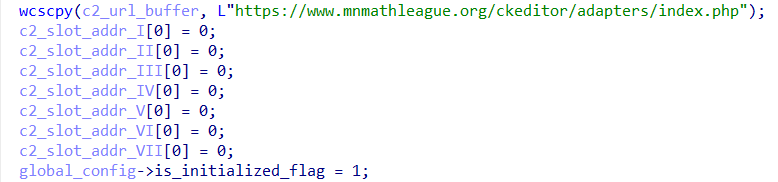
When connecting to its C&C server, ScoringMathTea strips HTTP header information from responses, a technique that allows the malware to extract encrypted payloads from seemingly legitimate web pages.
This approach provides plausible deniability when analyzing network traffic, as the compromised system’s communication could superficially appear to be normal web browsing activity.
A particularly notable feature involves the beacon mechanism, which uses pseudo-random request payloads to complicate signature-based detection.
The malware maintains a 60-second heartbeat interval to communicate with its C&C infrastructure, establishing a regular communication pattern while attempting to minimize network noise that might trigger anomaly detection systems.
Among ScoringMathTea’s most formidable capabilities is its implementation of Reflective DLL Injection, enabling the runtime downloading and in-memory execution of additional malicious plugins without writing anything to disk.
This technique proves particularly effective against security solutions that rely on file-system monitoring or behavioral analysis of executable creation.
The plugin loading mechanism implements a three-layer architecture. First, the main task manager orchestrates the download process.
Second, a plugin loading orchestrator prepares the environment by utilizing PEB (Process Environment Block) Walking an advanced technique for dynamically locating system DLLs without relying on import tables.
Third, a reflective plugin loader manually implements Windows loader functionality in a customized manner, mapping PE (Portable Executable) files into memory while avoiding traditional loader hooks that security software might monitor.
The loader also incorporates a custom CRC32 checksum algorithm that verifies plugin integrity and serves as a software breakpoint detector for anti-debugging purposes.
Several repeated APIs, which refer to APIs that are used multiple times, such as LocalAlloc, LocalFree, GetLastError, among others.
Upon successful mapping, the loader identifies and executes an exported function named “exportfun” within the loaded plugin, providing operators with a standardized interface for executing arbitrary malicious functionality entirely within system memory.
Technical Sophistication
The deployment of ScoringMathTea demonstrates Lazarus continued investment in developing evasion-focused malware infrastructure.
The targeting of UAV manufacturers and technology suppliers supporting Ukraine indicates a clear strategic objective aligned with geopolitical interests.
The malware’s modular design permits rapid functionality expansion through plugin delivery, suggesting operators can adapt to specific target environments or security postures without requiring new malware samples.
Security researchers have documented that ScoringMathTea employs custom string deobfuscation algorithms using polyalphabetic substitution ciphers with character-state chaining, further complicating reverse-engineering efforts.
Combined with API hashing and reflective loading techniques, the malware presents a formidable challenge for static analysis while remaining capable of sophisticated runtime operations.
ScoringMathTea exemplifies the evolving sophistication of nation-state malware development, combining proven evasion techniques with novel implementation approaches specifically designed to complicate detection and analysis.
Organizations involved in aerospace, defense, and critical infrastructure sectors should implement comprehensive threat hunting procedures, behavioral monitoring systems, and maintain vigilance for HTTP/HTTPS traffic exhibiting the unusual characteristics associated with this malware family.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.




