Users of Metabase, a popular business intelligence and data visualization software package, are being advised to update to the latest version following the discovery of an “extremely severe” flaw that could result in pre-authenticated remote code execution on affected installations.
Tracked as CVE-2023-38646, the issue impacts open-source editions prior to 0.46.6.1 and Metabase Enterprise versions before 1.46.6.1.
“An unauthenticated attacker can run arbitrary commands with the same privileges as the Metabase server on the server you are running Metabase on,” Metabase said in an advisory released last week.
The issue has also been addressed in the following older versions –
- 0.45.4.1 and 1.45.4.1
- 0.44.7.1 and 1.44.7.1, and
- 0.43.7.2 and 1.43.7.2
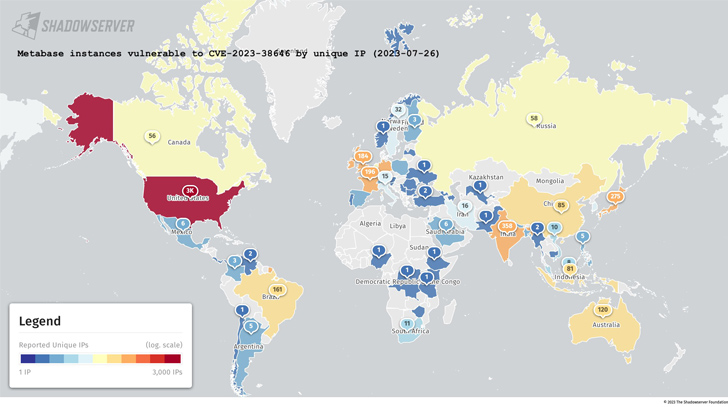
While there is no evidence that the issue has been exploited in the wild, data gathered by the Shadowserver Foundation shows that 5,488 out of the total 6,936 Metabase instances are vulnerable as of July 26, 2023. A majority of the instances are located in the U.S., India, Germany, France, the U.K., Brazil, and Australia.
Shield Against Insider Threats: Master SaaS Security Posture Management
Worried about insider threats? We’ve got you covered! Join this webinar to explore practical strategies and the secrets of proactive security with SaaS Security Posture Management.
Join Today
Assetnote, which claimed it discovered and reported the bug to Metabase, said the vulnerability is due to a JDBC connection issue in the API endpoint “/api/setup/validate,” enabling a malicious actor to obtain a reverse shell on the system by means of a specially crafted request that takes advantage of an SQL injection flaw in the H2 database driver.
Users who cannot apply the patches immediately are recommended to block requests to the /api/setup endpoint, isolate the Metabase instance from your production network, and monitor for suspicious requests to the endpoint in question.



