Cybersecurity researchers from CYFIRMA have revealed a new version of Neptune RAT, a remote administration tool targeting Windows devices. Marketed on platforms like GitHub, Telegram, and YouTube with claims of being the “Most Advanced RAT,” the malware is attracting both newcomers to cybercrime and seasoned hackers looking for a ready-made tool.
What Is Neptune RAT?
Neptune RAT is written in Visual Basic .NET and is designed to take control of a victim’s Windows computer. Although its creator says the software is provided for “educational and ethical purposes,” the tool’s capabilities suggest otherwise.
Designed to steal user credentials, replace cryptocurrency wallet addresses, and even lock files with ransomware features, Neptune RAT gives attackers comprehensive control over an infected system.
How It Spreads
The malware is distributed freely on social platforms. Rather than releasing the source code, the developer hides the executable file, making the analysis more complicated. Some of the malicious code even replaces parts of its strings with Arabic characters and emojis, which complicates reversing efforts by researchers. In its free version, Neptune RAT automatically generates PowerShell commands to download and run additional components hosted on file hosting service such as catbox.moe.
Dangerous Capabilities
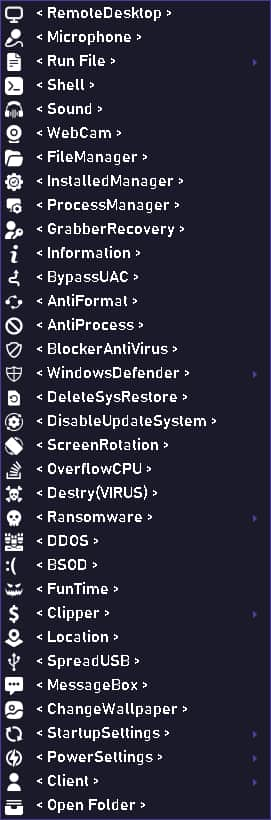
Neptune RAT comes with a mix of modules that work together to compromise Windows computers, including the following:
- Credential Theft and Clipboard Hijacking: The malware includes a password grabber that extracts login details from applications and popular web browsers. It also monitors the clipboard to detect cryptocurrency wallet addresses, replacing them with the attacker’s own.
- Ransomware and System Damage: Once activated, the RAT can encrypt files on the victim’s computer, extending their extensions to “.ENC, ”and drop an HTML file with ransom information. It may even corrupt system components like the Master Boot Record if an attacker wishes to render the system unusable.
- Evasion and Persistence: To avoid being removed, the malware modifies registry values and adds itself to the Windows Task Scheduler. It also checks if it’s running in a virtual environment and stops execution if a virtual machine is detected. This combination of techniques helps it maintain a persistent foothold on the system.
- Additional Modules: Separate DLL files add further capabilities, including bypassing user account controls, stealing data from various email and browser applications, and even enabling live screen monitoring.
Protecting Your System
Since Neptune RAT uses different strategies, both individuals and organizations need to act quickly to protect themselves. The best approach starts with some simple practices: only download software from sources you trust, make sure Windows and all your programs, especially security tools, are kept up to date, and regularly back up any important data.
It’s also a good idea to use anti-virus software that can keep an eye on both file changes and network activity, giving you better protection against anything suspicious.
Expert Insight
Satish Swargam, Principal Security Consultant at Black Duck in Burlington, Massachusetts, offered his perspective on Neptune RAT’s evolution. He explained that the malware uses advanced techniques to extract sensitive data from users, spreading through platforms like GitHub, Telegram, and YouTube in ways that slip past standard security tools.
“This tool is especially concerning because it can deploy ransomware to lock your files, leading to major interruptions for businesses until the ransom is paid. It also lets hackers spy on screens in real time and even swap clipboard contents with their own cryptocurrency wallet addresses,” Swargam noted.
He added that as the malware continues to add new features, similar to those shared online under the banner of educational software, organizations need to maintain constant monitoring, deploy strong endpoint defenses, and implement active threat detection measures to reduce the risk of compromise.
