The Cybereason Global Security Operations Center (GSOC) has uncovered a sophisticated campaign by threat actors who are exploiting compromised WordPress websites to distribute malicious versions of the legitimate NetSupport Manager Remote Access Tool (RAT).
This campaign, detailed in a recent report, employs phishing emails, PDF attachments, and even gaming websites to lure unsuspecting users into a multi-stage attack chain designed to deploy the NetSupport RAT payload.
Malicious Campaigns Leverage Phishing
The intricate use of malicious JavaScript and DOM manipulation techniques underscores the growing technical prowess of cybercriminals aiming to infiltrate systems for reconnaissance and further exploitation.
The attack begins when victims are redirected to a malicious WordPress site through one of the aforementioned delivery methods.
Threat actors embed malicious JavaScript within the site’s meta description and anchor tags, triggering the download of a script named “j.js” from domains like islonline[.]org.
This script, which varies depending on the attacker’s activity status, targets Windows users by identifying browser details, logging visit timestamps, and generating an iframe to load a PHP file from a malicious domain.
To evade detection, the script uses local storage to track repeat visitors, avoiding redundant iframe generation.
Technical Breakdown of the Attack Chain
The next stage involves dynamic DOM manipulation via a file named “index.php,” which injects another script, “select.js,” responsible for rendering a fake CAPTCHA page styled with Tailwind CSS.
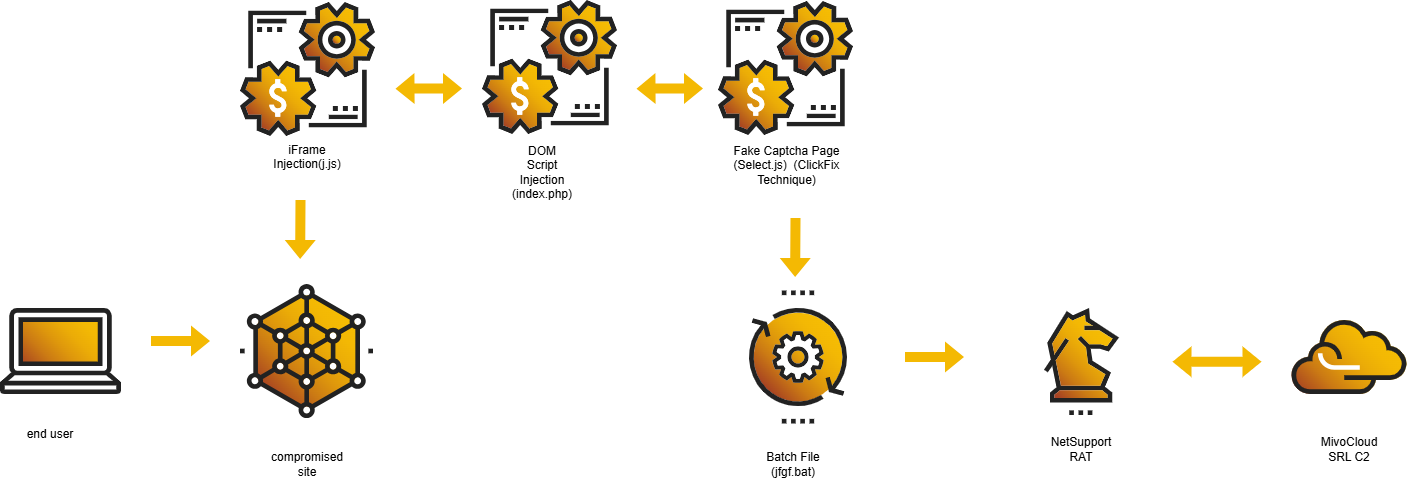
This deceptive page copies a malicious command to the user’s clipboard using the navigator.clipboard API, tricking users into executing it via the Windows Run dialog.
This so-called “ClickFix Technique” ultimately downloads a batch file that deploys the NetSupport RAT.
The batch file, obfuscated with junk data in comment blocks, extracts a ZIP archive containing the NetSupport Client (client32.exe) and supporting files into the user’s %AppData%Roaming directory.
It establishes persistence via a Windows Registry Run key, and connects to a threat actor-controlled server, often hosted within the 94.158.245[.]0/24 network block managed by MivoCloud SRL in Moldova.
Post-infection, attackers leverage NetSupport’s robust feature set for file transfers and remote command execution, often querying Active Directory for reconnaissance within hours of compromise.
This campaign highlights the dual nature of NetSupport Manager, a legitimate remote management tool turned malicious RAT, ranking as the seventh most prevalent threat in 2024.
Its configuration file, “client32.ini,” plays a critical role by specifying connectivity to attacker-controlled gateways, facilitating unauthorized access and further malware deployment.
To mitigate risks, organizations must isolate infected endpoints, block identified Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), reset credentials, reimage systems, and educate users on phishing awareness.
Immediate forensic analysis is also recommended to assess the scope of data exposure and threat actor activity.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| IOC | Type |
|---|---|
| 94.158.245[.]104 | IP |
| 94.158.245[.]118 | IP |
| 94.158.245[.]131 | IP |
| 94.158.245[.]137 | IP |
| pemptousia[.]com | DOMAIN |
| 172.67.70[.]20 | IP |
| fmovies123[.]top | DOMAIN |
| 79.141.173[.]158 | IP |
| badgervolleyball[.]org | DOMAIN |
| 209.17.116[.]165 | IP |
| islonline[.]org | DOMAIN |
| 23.23.49[.]179 | IP |
Stay Updated on Daily Cybersecurity News. Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X.





