AmCache plays a vital role in identifying malicious activities in Windows systems. This tool allows the identification of both benign and malicious software execution on a machine.
Managed by the operating system and virtually tamper-proof, AmCache data endures even when malware auto-deletes itself, making it indispensable in incident response.
AmCache stores SHA-1 hashes of executed files, enabling DFIR professionals to query public threat intelligence feeds such as OpenTIP and VirusTotal and rapidly generate indicators of compromise for blocking across the network.
The new open-source tool, released by Kaspersky researchers, simplifies the parsing of the Amcache.hve registry hive, automating IOC extraction and threat intelligence lookups to accelerate threat detection and containment.
AmCache-EvilHunter is a command-line utility written in Python that ingests the C:WindowsAppCompatProgramsAmcache.hve file and extracts key metadata entries.
It parses critical registry keys InventoryApplicationFile, InventoryDriverBinary, InventoryApplication, and InventoryApplicationShortcut—to reveal file paths, publisher data, LinkDate timestamps, binary types (32-bit vs. 64-bit), and SHA-1 hashes. A sample invocation looks like this:

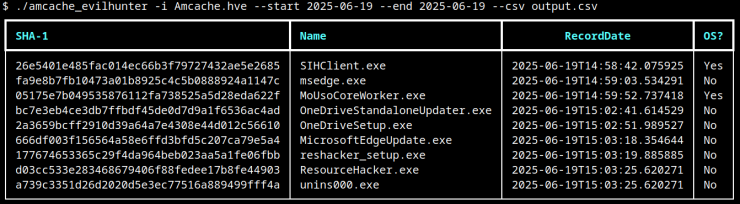
This command filters records by date range, outputting a CSV of all executables present between September 1 and September 30, 2025.
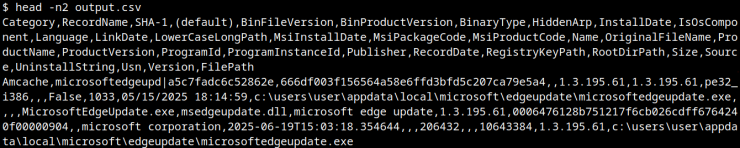
The FileID field contains the hash with four leading zeroes, while Size and IsOsComponent flags help analysts distinguish system binaries from potential malware.
Kaspersky stated that AmCache-EvilHunter’s standout features include built-in threat intelligence integration and advanced filtering options.
The –find-suspicious flag applies heuristics—such as one-letter names (1.exe), random hex filenames, and common typo variants like scvhost.exe to highlight anomalous entries.
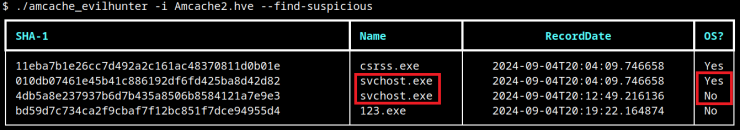
Additional flags, –missing-publisher and –exclude-os, further reduce noise by filtering out signed OS components. For each identified hash, users can invoke:

This triggers automated lookups against VirusTotal and Kaspersky OpenTIP, appending detection counts and threat classification tags to the output.
Analysts can also search specific keywords or ProgramId values using –search “winscp.exe” to confirm the presence of deleted or transient tools.
AmCache-EvilHunter uses the Registry Python library to load the REGF-formatted hive while iterating through its subkeys and values.
Its modular architecture allows developers to extend support for custom IOC feeds or integrate with SOAR platforms. Binaries and scripts are available on GitHub for both Windows and Linux deployments.
By automating parsing, filtering, and threat lookups, AmCache-EvilHunter significantly cuts manual effort and accelerates DFIR workflows.
Incident responders can rapidly reconstruct execution timelines, pinpoint stealthy rootkits via InventoryDriverBinary, and generate robust IOCs from InventoryApplicationFile entries.
As adversaries increasingly employ self-erasing malware, this tool ensures that crucial execution evidence is never lost.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X for daily cybersecurity updates. Contact us to feature your stories.




