The cybersecurity security researchers at Sophos recently detected the “Dragon Breath” APT group (aka Golden Eye Dog, APT-Q-27) using complex DLL sideloading variations to avoid detection.
The APT group deploys a new attack vector that utilizes clean applications like Telegram to malicious malware loader DLLs and sideloads second-stage payloads.
DLL Sideloading
APT actors use BlackSEO or malvertizing techniques to promote malicious versions of Telegram, LetsVPN, or WhatsApp apps that are localized for Chinese users as bait to infect victims on Android, iOS, or Windows platforms.
According to Sophos report, this campaign is primarily targeting Chinese-speaking Windows users in the following countries:-

- China
- Japan
- Taiwan
- Singapore
- Hong Kong
- The Philippines
Attackers have been exploiting DLL sideloading, which takes advantage of Windows’ insecure loading of Dynamic Link Library (DLL) files since 2010.
To perform DLL sideloading, the attacker puts a malicious DLL with the same name as a required, legitimate DLL in the application directory.
Upon launching the executable, the operating system prioritizes the malicious DLL located in the local directory over the legitimate one in the system folders.
As a result, the malware can perform and execute its intended actions. At this stage, the attacker’s DLL contains malicious code to exploit the trusted and signed application, thereby gaining elevated privileges on the host system.
The campaign in question involves victims executing the installer of the specified apps, which results in installing various components on the system.

Technical Analysis
Furthermore, the installer generates a shortcut on the desktop and establishes an entry for system startup.
In case the victim attempts to initiate the recently formed desktop shortcut, which is the typical first move, rather than executing the application, the system triggers the following command:-
- “C:Users{redacted}AppDataRoamingTg_B518c1A0Ff8CappR.exe /s /n /u /i:appR.dat appR.dll”
Upon execution, the JavaScript code is designed to launch the Telegram app user interface in the foreground. Meanwhile, various sideloading components are installed in the background without the user’s knowledge.
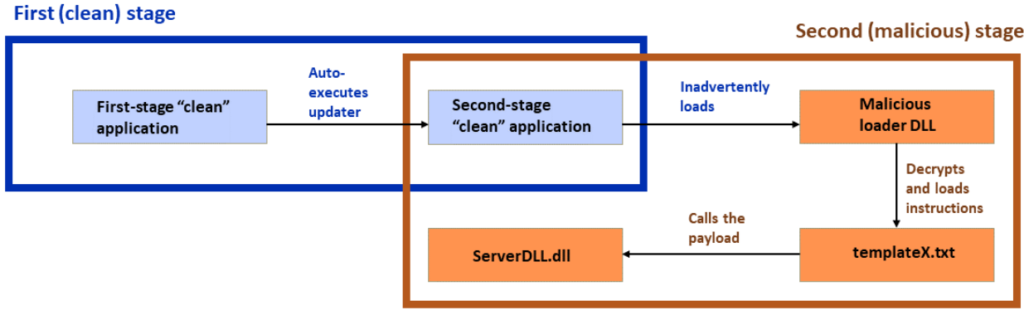
Subsequently, the installer loads a second-stage application through ‘libexpat.dll,’ a new and clean dependency to launch a second immaculate application, functioning as an intermediary stage of the attack.
In a variation of the attack, the ‘Beijing Baidu Netcom Science and Technology Co.’, Ltd signs the clean second-stage loader, renamed “Application.exe” from “XLGame.exe.
Another attack variation involves an unsigned clean loader called “KingdomTwoCrowns.exe,” which seems to serve no purpose other than obfuscating the execution chain. Meanwhile, the third variation uses a digitally-signed clean loader named “d3dim9.exe,” which belongs to HP Inc.

Using the “double DLL sideloading” technique, APT groups can evade detection, achieve persistence, and obfuscate their attacks, making it challenging for defenders to adapt to their attack patterns and secure their networks effectively.
Regardless of the attack variation, the final payload DLL is always decrypted and executed on the system from a txt file called ‘templateX.txt.’
Apart from this, in recent times, DLL sideloading has become one of the most sought malicious techniques hackers utilize.
Building Your Malware Defense Strategy – Download Free E-Book

