Attackers increasingly exploit Microsoft Exchange inbox rules to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data within enterprise environments.
A newly released tool, Inboxfuscation, leverages Unicode-based obfuscation to craft malicious inbox rules that slip past conventional security controls.
Developed by Permiso, the Inboxfuscation framework demonstrates how attackers can weaponize Exchange’s rule engine, creating stealthy persistence mechanisms that evade both human review and code-based detection.
Unicode-Based Evasion
Traditional inbox rule attacks relied on clear-text keywords and straightforward actions such as forwarding or deleting messages.
Such rules are easily flagged by keyword-based detection and regex matching. Inboxfuscation transforms this paradigm by substituting ASCII characters with visually identical Unicode variants, injecting zero-width characters, manipulating bidirectional text, and combining multiple obfuscation techniques.
For example, the word “secret” can be obfuscated as:

Permiso stated that by exploiting character categories such as MATHEMATICAL ALPHANUMERIC SYMBOLS (U+1D4B6), ZERO-WIDTH SPACES (U+200B), and RIGHT-TO-LEFT OVERRIDE (U+202E), attackers can create rules that appear benign in Exchange’s Get-InboxRule output yet functionally match sensitive keywords.
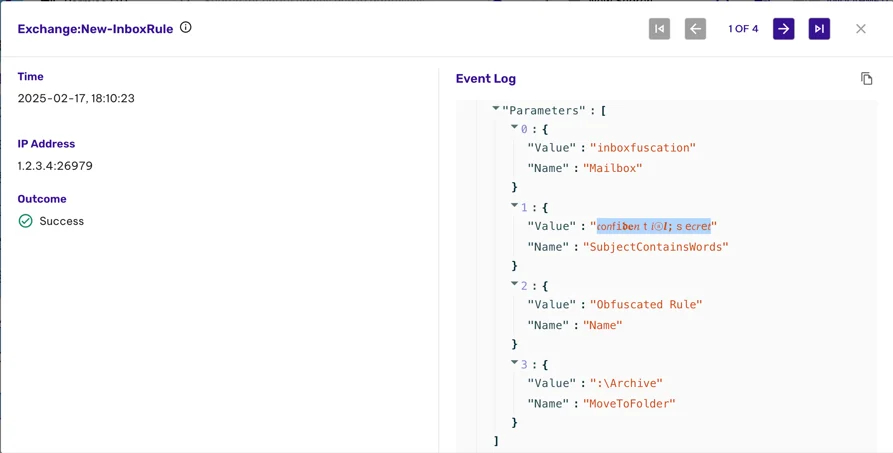
Inboxfuscation also introduces functional obfuscation tricks, such as rules that forward emails into the Calendar folder or insert null characters (u0000) to render rules invisible and unretrievable.
Detection and Mitigation Strategies
Conventional detection tools fail against Unicode obfuscation because they assume ASCII-based pattern matching and visual similarity.
Inboxfuscation’s detection framework extends Permiso’s Arbiter Detection module to analyze events across mailboxes and reconstruct multi-step rule creation behaviors. Key components include:
- Character Category Analysis

Supports JSON, CSV, Exchange export, and Microsoft 365 Graph API logs.
- Rule Audit and Historical Analysis
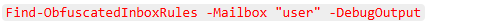
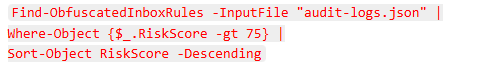
Structured output includes rule_name, mailbox, risk_score, and unicode_char_count.
To mitigate this threat, security teams should implement Unicode-aware detection rules, perform comprehensive inbox rule audits, and simulate obfuscated rules in testing environments.
Organizations must update Exchange monitoring pipelines to flag suspicious Unicode categories and leverage sandboxed environments to inspect rule normalization behaviors.
Although these Unicode obfuscation techniques have not yet been observed in live attacks, their technical feasibility exposes a critical blind spot in email security postures.
By proactively adopting Inboxfuscation’s detection framework and understanding the mechanics of Unicode-based evasion, defenders can stay ahead of emerging APT tactics and protect enterprise communications from stealthy persistence techniques.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X for daily cybersecurity updates. Contact us to feature your stories.



