Threat actors have revived the sophisticated VIP keylogger malware, previously detailed in an earlier white paper for its use of spear-phishing and steganography to infiltrate systems and steal data from web browsers and user credentials.
This iteration introduces an AutoIt-based injector to deploy the final payload, marking a shift from prior methods while maintaining core data theft functionalities such as keystroke logging, credential capture from browsers like Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox, and clipboard monitoring.
The malware’s delivery relies on phishing emails with malicious attachments, exploiting user trust to execute the payload, which then leverages AutoIt’s obfuscation capabilities to bypass traditional antivirus detections by compiling scripts into executables.
Evolving Tactics in Malware Distribution
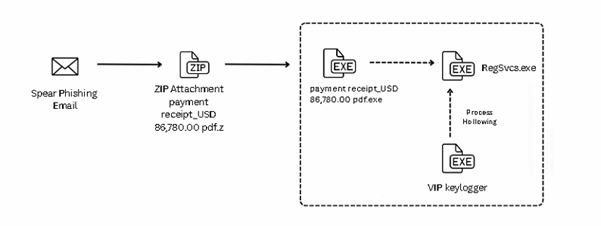
The infection chain initiates with a spear-phishing email containing a ZIP archive named “payment receipt_USD 86,780.00.pdf.pdf.z.”, which houses a disguised executable file “payment receipt_USD 86,780.00 pdf.exe” mimicking a legitimate PDF document.
Upon execution, this file triggers an embedded AutoIt script that drops two encrypted files leucoryx and avenesinto the system’s temporary folder.
According to the Seqrite report, these files are decrypted in runtime using a custom XOR-based function (KHIXTKVLO), with leucoryx providing the decryption key.
The script then allocates executable memory via DllCall, copies the decrypted payload into it, and executes it directly in memory, ensuring stealthy operation.
Notably, the avenes file is loaded into memory and processed through a decryption routine that iteratively unpacks the embedded .NET-based VIP keylogger payload, as evidenced by memory dumps revealing decrypted content.
To achieve persistence, the malware deploys a Visual Basic Script (.vbs) in the Startup folder, which automatically executes the primary payload definitiveness.exe located in the “AppDataLocalDunlop” directory upon user login, allowing silent background operation post-reboot.
Exfiltration Techniques
Employing process hollowing, the malware spawns RegSvcs.exe in a suspended state via CreateProcess, unmapped its original code, and injects the decrypted VIP keylogger payload into its address space before resuming execution.
This technique enables the malware to masquerade as a legitimate system process, with injected code containing strings indicative of the keylogger’s functions.
The final payload, comprehensively analyzed in a prior technical paper, facilitates data exfiltration through SMTP protocols and communication with a command-and-control server, underscoring its multistage stealer capabilities.
This campaign highlights the evolving sophistication of threat actors in blending social engineering with advanced evasion tactics, urging organizations to enhance email filtering, endpoint detection, and behavioral analysis to mitigate such risks.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Type | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MD5 | F0AD3189FE9076DDD632D304E6BEE9E8 | payment receipt_USD 86,780.00 pdf.exe |
| MD5 | 0B0AE173FABFCE0C5FBA521D71895726 | VIP Keylogger |
| Domain/IP | hxxp://51.38.247.67:8081 | Command-and-Control Server |
Find this News Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, & X to Get Instant Updates!




