NVIDIA and Lakera AI have introduced a groundbreaking unified security and safety framework designed to address the emerging challenges posed by autonomous AI agents in enterprise environments.
This collaborative effort represents a significant step forward in making agentic systems AI systems capable of independent planning, tool use, and multi-step task execution safer and more secure for real-world deployment.
The research, led by scientists from both organizations, reframes safety and security as emergent properties that arise from dynamic interactions among multiple components in agentic systems, rather than as fixed attributes of individual models.
This perspective is crucial because agentic systems operate fundamentally differently from traditional language models.
They can invoke tools, access external data, make autonomous decisions, and interact with users across multiple steps, creating new attack surfaces and potential failure modes that traditional evaluation approaches may miss.
Critical Gap in Agentic AI Security
Unlike isolated large language models (LLMs) that have undergone extensive safety and security evaluations, agentic systems introduce novel risks through their compositional architecture.
The system under test may have multiple sub-agents that can invoke tools and APIs, consult RAG, and interact with an external environment.
The framework identifies unique agentic risks, including tool misuse, cascading action chains, unintended control amplification, and multi-agent interactions that cannot be adequately assessed using conventional security metrics alone.
The researchers propose that safety and security should be examined through a unified lens centered on preventing user harm.
“Safety and security are not merely fixed attributes of individual models but also emergent properties arising from the dynamic interactions among models, orchestrators, tools, and data within their operating environments,” the paper emphasizes.
The framework features an operational risk taxonomy that unifies traditional safety and security concerns with uniquely agentic risks, prioritized according to their impact and exploitability.
At its core is a dynamic assessment methodology that uses specialized AI agents for risk discovery, evaluation, and mitigation.
Rather than relying on static pre-release testing alone, the framework employs continuous, context-aware evaluation through sandboxed AI-driven red teaming.
The researchers introduced Agent Red Teaming via Probes (ARP), an innovative methodology that allows targeted security testing at specific points throughout an agentic workflow.
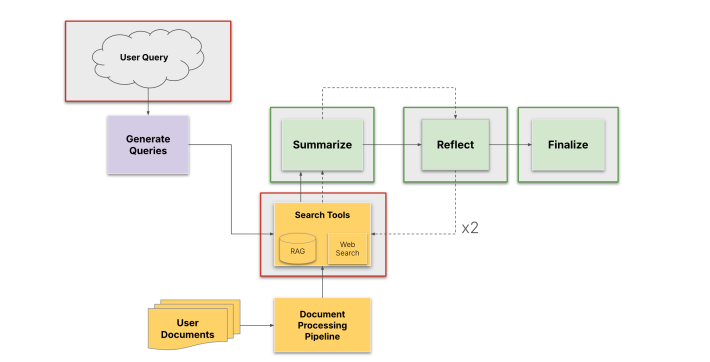
This approach enables developers to understand how threats propagate through system components independently of upstream changes, providing granular visibility into security weaknesses.
NVIDIA’s AI-Q Research Assistant
The effectiveness of the framework was demonstrated through an extensive case study of NVIDIA’s AI-Q Research Assistant (AIRA), a sophisticated research tool that synthesizes information from enterprise databases and web search.
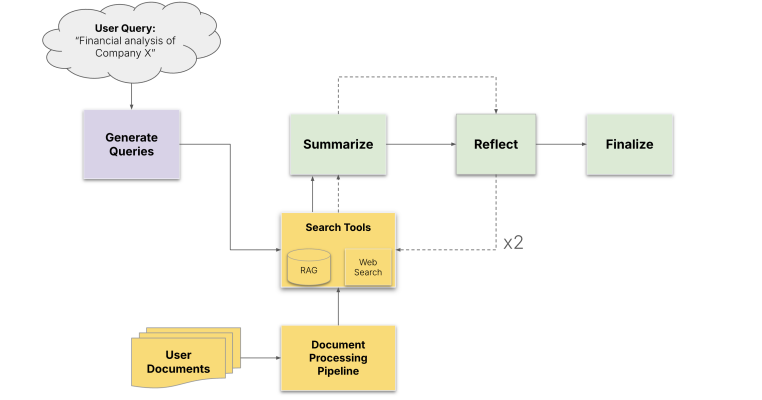
The study included over 10,000 realistic attack and defense executions across 22 distinct threat scenarios covering nine risk categories.
Notably, the research revealed differential attack propagation patterns: while direct user input attacks amplified through the processing pipeline, attacks from external data sources were progressively attenuated insights that directly inform targeted defense strategies.
The framework achieved approximately 50% risk reduction through targeted guardrails and demonstrated how to track security improvements across agent versions continuously.
NVIDIA and Lakera AI have released the Nemotron-AIQ Agentic Safety Dataset containing over 10,000 trace files from their experiments, enabling the research community to advance agentic safety evaluation.
The framework’s emphasis on contextual, layered defenses rather than blanket security measures represents a pragmatic approach to maintaining both robust security and acceptable system performance.
This collaborative framework marks an important milestone in establishing practical methodologies for securing autonomous AI systems, addressing what has been a critical gap in enterprise AI deployment guidance.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.