A sophisticated supply chain attack has compromised the popular Nx build platform, affecting millions of weekly downloads and resulting in widespread credential theft.
The attack, dubbed “s1ngularity,” represents one of the most comprehensive credential harvesting campaigns targeting the developer ecosystem in 2025.
GitGuardian observed that malicious actors infiltrated multiple Nx package versions (20.9.0 through 21.8.0) on the npm registry, injecting credential-stealing malware that systematically scanned infected development environments.
Key Takeaways
1. Nx build platform compromised with malware stealing developer credentials.
2. First attack exploiting AI tools for credential harvesting, though many AI clients resisted.
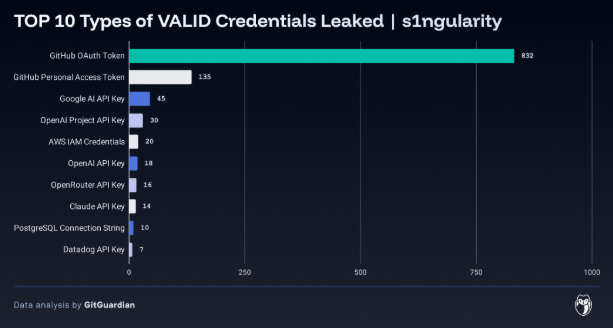
3. 2,349+ secrets stolen via GitHub repositories; 50% remained valid despite cleanup efforts.
The attack demonstrates an evolution in supply chain tactics, combining traditional credential theft with novel attack vectors targeting AI development tools and employing GitHub repositories as exfiltration infrastructure.
Credential-Harvesting Malware Targeting Developers
The malicious payload implemented a comprehensive credential harvesting mechanism that scanned infected systems for multiple types of sensitive data.
The malware targeted GitHub personal access tokens, npm authentication keys, SSH private keys, AWS credentials, environment variable API keys, and cryptocurrency wallet files.
The scanning routines employed sophisticated file system traversal techniques, examining common configuration directories including ~/.ssh/, ~/.aws/, and various application-specific credential storage locations.
The harvested credentials underwent a distinctive double-base64 encoding process before exfiltration.
This encoding scheme (echo $data | base64 | base64) served dual purposes: evading basic detection mechanisms while maintaining data integrity during transmission.
The encoded payloads were then exfiltrated to public GitHub repositories following a predictable naming convention: “s1ngularity-repository-[random-string]”, each containing a single “results.b64” file with the encoded stolen data.
Analysis of the attack infrastructure reveals that the malware also implemented destructive capabilities, modifying users’ shell startup files (~/.bashrc and ~/.zshrc) with shutdown commands that would crash systems upon opening new terminal sessions, according to GitGuardian.
This secondary payload suggests the attack combined both data theft and system disruption objectives.
A particularly innovative aspect of the s1ngularity attack was its focus on Large Language Model (LLM) client configurations.
The malware specifically enumerated authentication tokens and configuration files for popular AI CLI tools including Claude, Gemini, and Q (Amazon’s AI assistant).
This targeting strategy reflects the attackers’ understanding that AI development tools often require elevated permissions and access to sensitive development environments.
The malware attempted to leverage LLM clients as enumeration vectors by crafting prompts designed to inventory system files and extract credential information.
However, analysis reveals that many AI clients demonstrated unexpected defensive behavior, with only 26% (95 out of 366 targeted systems) actually executing the malicious enumeration commands.
Many LLM clients explicitly refused requests that appeared to be credential harvesting attempts, potentially representing an unintentional but valuable security control in modern development environments.
The attack demonstrated remarkable reach across the developer ecosystem, with 85% of infected systems running macOS, highlighting the campaign’s particular impact on the Apple-dominant developer community.
Of the compromised systems analyzed, 33% had at least one LLM client installed, validating the attackers’ strategy of targeting this emerging attack surface.
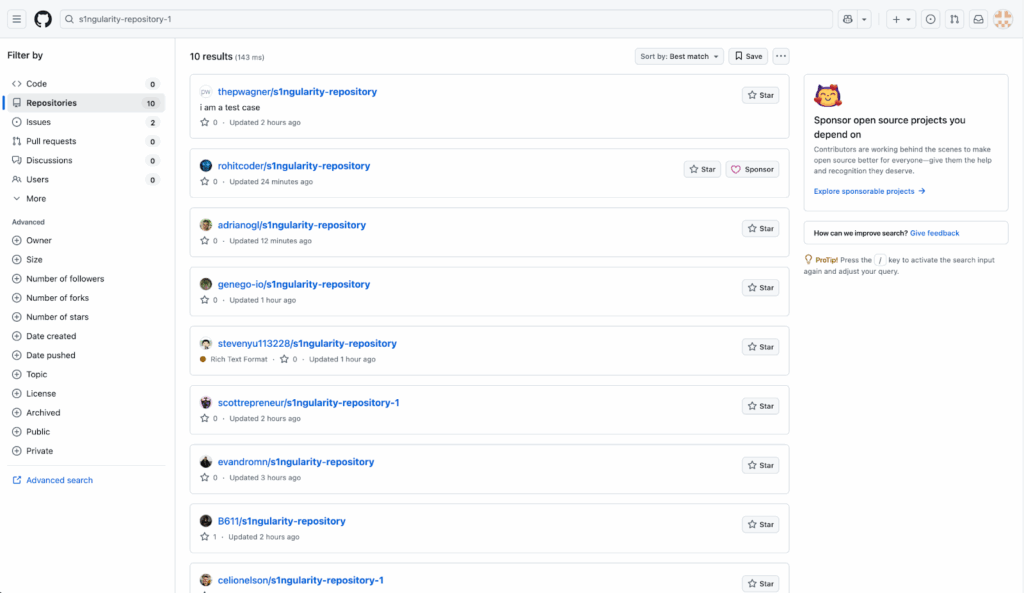
Exfiltration repositories
GitGuardian’s monitoring infrastructure provided unique visibility into the ephemeral exfiltration repositories, detecting 1,346 repositories containing the “s1ngularity-repository” string, despite GitHub listing only approximately ten active repositories at the time of analysis.
This discrepancy indicates rapid repository deletion cycles and ongoing infections from developers continuing to use compromised package versions.
The analysis identified 2,349 distinct secrets across these repositories, with 1,079 repositories containing at least one leaked credential.
Critically, approximately 50% of these credentials remained valid at the time of discovery, indicating significant delays in credential revocation processes.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on LinkedIn and X to Get More Instant Updates.