A Russian government-linked malware targeting power transmission was discovered recently by researchers at Mandiant during research, suggesting its potential use in training exercises for cyberattacks on electric grids.
The malware COSMICENERGY, named by Google’s threat intelligence firm Mandiant, was uploaded to VirusTotal in December 2021 from Russia, but no evidence suggests its actual deployment.
This malware explicitly targets IEC-104 devices like RTUs used in electric transmission and distribution operations, potentially leading to power disruptions in various regions like:-
- Europe
- The Middle East
- Asia
COSMICENERGY Analysis
COSMICENERGY is a unique tool developed by a contractor for power disruption exercises. It resembles malware like INDUSTROYER and INDUSTROYER.V2, used to impact electricity transmission through IEC-104.
This malware shows that developing offensive OT capabilities is becoming easier as attackers learn from previous attacks. It poses a real threat to electric grid assets, so owners should act to prevent its deployment.
While it also resembles the 2016 INDUSTROYER incident, using IEC-104 commands and possibly an MSSQL server to access OT. COSMICENERGY allows remote control of power line switches and circuit breakers for disruption through its components:-
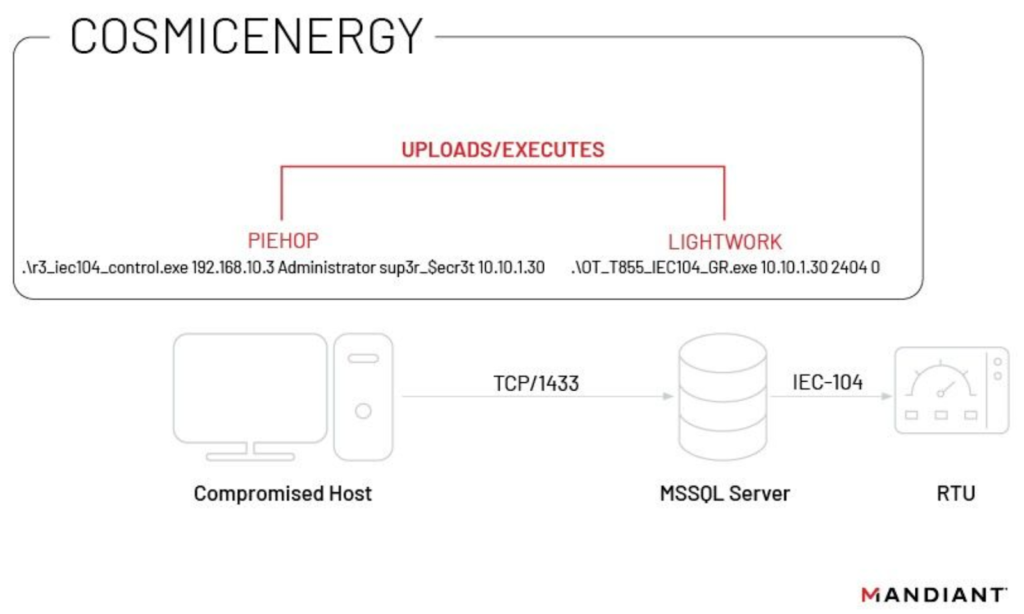
Possible Association with the Russian Government
In the analysis of COSMICENERGY, a code comment linked it to the “Solar Polygon” project.
The researchers found a match to a cyber range developed by Rostelecom-Solar, a Russian company conducting power disruption exercises.
The origin and purpose of COSMICENERGY remain unclear. Possibly developed by Rostelecom-Solar or an associated party for simulated energy grid attacks.
They are potentially used in exercises like Rostelecom-Solar’s collaboration with the Russian Ministry of Energy in 2021 or SPIEF in 2022.

The lack of evidence makes it possible that another actor reused the cyber range code to create this malware.
Threat actors often repurpose red team tools for real-world attacks, like TEMP.[]Veles is using METERPRETER in the TRITON attack.
Similarities with Existing OT Malware
Here below, we have mentioned all the key similarities with the existing OT malware:-
- Abuse of insecure by design protocols
- Use of open-source libraries for protocol implementation
- Use of Python for malware development and/or packaging
COSMICENERGY’s capabilities align with previous OT malware; its discovery reveals notable developments in OT threats.
New OT malware poses an immediate risk due to rare discoveries and reliance on insecure OT features that are unlikely to be fixed soon.
Discovery of COSMICENERGY indicates lower barriers for offensive OT threats, possibly due to red team involvement.
Typically, such capabilities were limited to well-resourced or state-sponsored actors.
At the same time, the contractors and red team tools are frequently used by threat actors in real-world OT attacks.

Discovery Methods
Here below, we have mentioned all the discovery methods that Mandiant researchers provide:-
- Collect and aggregate host-based logs for critical systems like HMI, EWS, and OPC servers.
- Review logs for Python script or unauthorized code execution evidence.
- Identify and investigate unauthorized Python executables on OT systems or systems with OT access.
- Monitor systems with OT access to create necessary files, artifacts, and libraries as evidence of executing Python scripts.
- Monitor MSSQL Servers for OT system and network access.
- Look for reconnaissance and enumeration activity, unauthorized network connections (TCP/1433), irregular/authenticated usage, and SQL extended stored procedures enabling Windows shell command execution.
Common Security Challenges Facing CISOs? – Download Free CISO’s Guide