In a recent development in the cybersecurity news, researchers have uncovered new phishing HTML files that has managed to outsmart most antivirus solutions.
This innovative HTML payload has proven to be a formidable adversary, eluding detection from popular antivirus programs and securing its place as one of the most prominent threats.
According to findings from DOCGuard, the HTML file, bearing the source https://vfaz006cowflq5984wmx.2icgw.ru/g9X2j47#[email protected], among others, has been spreading across the internet, carrying the notorious phishing payload.
Here’s how these phishing HTML files work
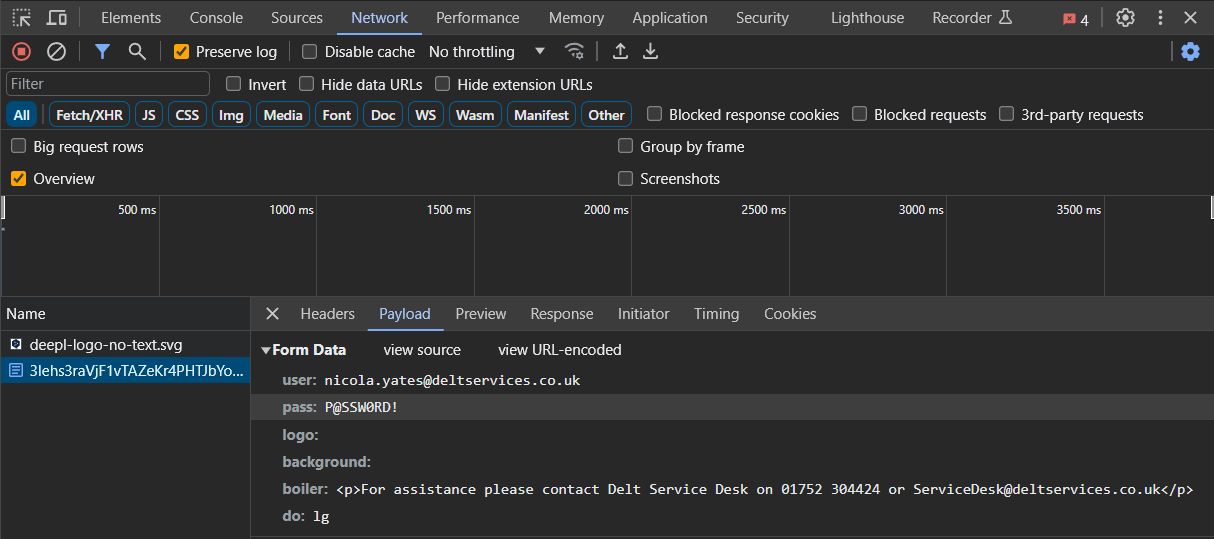
Phishing HTML files are malicious web pages designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal information, or financial details.

These files are typically created by cybercriminals with the intent of impersonating legitimate websites or services.
Ever since hackers have started implementing new ways to hide their payloads, HTML files remain a go-to choice for malicious actors orchestrating phishing campaigns.
These files, designed for seamless digital viewing within web browsers, enable a range of deceptive tactics, including redirection to harmful sites, file downloads, and even local display of phishing forms within the browser.
According to DOCGuard research, here are the key attributes of these phishing HTML files.
- File Name: ATT00001_2.htm
- Verdict: Suspicious
- File Type: HTML File – Suspicious
- File Version: 0
- SHA256: 7331fdcb1541a5d41168e8141ed5ea799605edf635d3e37c5d11182ac54ff59b
- MD5: 1641e6536804d010fd0887525f8518c4
- File Size: 216.0 bytes
- Date: Sep,28 13:55:18
- IoC: Yes
- Mitre: No
- Images: No
- Codes: No
- Public: Yes
The persistence of HTML in phishing attacks
Notably, HTML attachments often evade detection by email security systems, making them a favored method for infiltrating recipients’ inboxes.
Kaspersky’s statistical data highlights the sustained prevalence of HTML attachments in malicious emails. Over the first four months of 2022, the security company detected a staggering 2 million emails of this nature targeting its customers. The numbers peaked in March 2022, with 851,000 detections, followed by a slight dip to 387,000 in April.
The effectiveness of HTML in evading detection stems from a combination of tactics employed by threat actors. These include JavaScript implementation wherein malicious actors frequently use JavaScript within HTML attachments to execute actions like generating phishing forms or redirects. This practice, known as HTML smuggling, has gained popularity in recent years.
Why is phishing HTML files a nuisance to organizations?
These files employ several tactics to evade detection, allowing threat actors to successfully execute their malicious campaigns. These methods often exploit human psychology and technical vulnerabilities.
Social engineering techniques play a pivotal role in phishing attacks. Crafted with precision, phishing emails or messages manipulate recipients emotionally or psychologically. They create a sense of urgency, curiosity, or fear, compelling users to act hastily without scrutinizing the content.
URL Manipulation is another evasion tactic. Attackers utilize URL shorteners or alternate character sets to obscure the true destination of the phishing page. This clever disguise makes it more challenging for users to discern the legitimacy of the link.
Dynamic content generation is a technique where phishing pages generate content dynamically. This means that the content is not present in the initial HTML file, making it harder for automated systems to detect the malicious payload. This dynamic approach adds an extra layer of complexity to the evasion tactics.
Finally, Threat actors may exploit Zero-Day vulnerabilities in browsers or security software. These undiscovered vulnerabilities provide attackers with a window of opportunity before a patch is released, allowing them to conduct their phishing campaigns undetected for a period of time.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.