JFrog Security Research has uncovered three critical zero-day vulnerabilities in PickleScan, a widely-adopted industry-standard tool for scanning machine learning models and detecting malicious content.
These vulnerabilities would enable attackers to completely bypass PickleScan’s malware detection mechanisms, potentially facilitating large-scale supply chain attacks by distributing malicious ML models containing undetectable code.
The discoveries underscore a fundamental weakness in the AI security ecosystem’s reliance on a single security solution.
PyTorch’s popularity in machine learning comes with a significant security burden. The library hosts over 200,000 publicly available models on platforms like Hugging Face, yet it relies on Python’s “pickle” serialization format by default.
While pickle’s flexibility allows for reconstructing any Python object, this same characteristic creates a critical vulnerability: pickle files can embed and execute arbitrary Python code during deserialization.
When users load an untrusted PyTorch model, they risk executing malicious code capable of exfiltrating sensitive data, installing backdoors, or compromising entire systems.
This threat is not theoretical malicious models have already been discovered on Hugging Face, targeting unsuspecting data scientists with silent backdoors.
PickleScan emerged as the industry’s frontline defense, parsing pickle bytecode to detect dangerous operations before execution.
The tool analyzes files at the bytecode level, cross-references results against a blocklist of hazardous imports, and supports multiple PyTorch formats.
However, its security model rests on a critical assumption: PickleScan must interpret files identically to how PyTorch loads them. Any divergence in parsing creates exploitable security gaps.
Three Critical Vulnerabilities
The first vulnerability (CVE-2025-10155, CVSS 9.3) exploits PickleScan’s file type detection logic.
By renaming a malicious pickle file with a PyTorch-related extension like .bin or .pt, attackers can cause PickleScan’s PyTorch-specific scanner to fail while PyTorch itself successfully loads the file by analyzing its content rather than its extension. The malicious payload executes undetected.
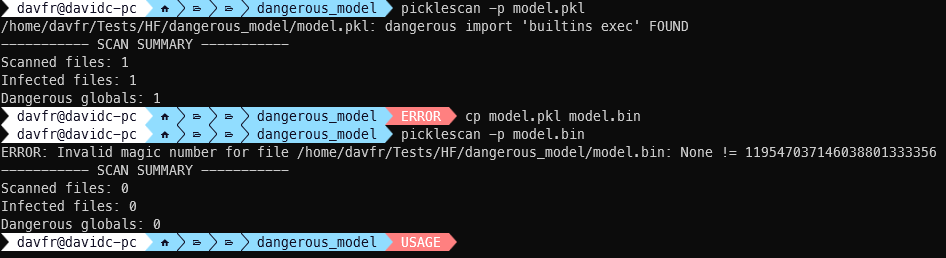
The second vulnerability (CVE-2025-10156, CVSS 9.3) involves CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) errors in ZIP archives.
PickleScan fails completely when encountering CRC mismatches, raising exceptions that halt scanning.
However, PyTorch’s model loading often bypasses these CRC checks, creating a dangerous discrepancy where PickleScan marks files as unscanned while PyTorch loads and executes their contents successfully.
The third vulnerability (CVE-2025-10157, CVSS 9.3) reveals that PickleScan’s unsafe globals check can be circumvented by using subclasses of dangerous imports rather than exact module names.
For instance, importing internal classes from asyncio a blacklisted library bypasses the check entirely, allowing attackers to inject malicious payloads while PickleScan categorizes the threat as merely “suspicious” rather than “dangerous.”
Systemic Security Implications
These vulnerabilities expose deeper problems in AI security infrastructure. The ecosystem’s single point of failure around PickleScan means that when the tool fails, entire security architectures collapse.
Organizations relying on Hugging Face, which integrates PickleScan for scanning millions of uploaded models, face particular risk.
The vulnerabilities demonstrate how divergences between security tools and target applications create exploitable gaps a critical lesson for AI security professionals.
Organizations should immediately update to PickleScan version 0.0.31, which addresses all three vulnerabilities.
However, this patch alone is insufficient. Implementing layered defenses including sandboxed environments and secure model repository proxies like JFrog Artifactory provides additional protection.
Organizations should prioritize migrating to safer ML model formats such as Safetensors while implementing automated removal of failed security scans.
The AI security community must recognize that no single tool can guarantee comprehensive protection and that defense-in-depth strategies remain essential in this evolving threat landscape.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instant Updates and Set GBH as a Preferred Source in Google.




