A critical vulnerability, CVE-2024-4367, has been discovered in PDF.js, a widely used JavaScript-based PDF viewer maintained by Mozilla.
The issue affects all Firefox users with versions below 126 and numerous web and Electron-based applications that utilize PDF.js for PDF preview functionality.
PDF.js is integrated into Firefox as its built-in PDF viewer and is also available as a Node module called pdfjs-dist, which has approximately 2.7 million weekly downloads on NPM.
ANYRUN malware sandbox’s 8th Birthday Special Offer: Grab 6 Months of Free Service
Codean Labs found this vulnerability, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript code when a malicious PDF file is opened.
Various websites use this module to provide embedded PDF preview functionality, making the impact of this vulnerability far-reaching.
CVE-2024-4367 – Technical Details and Exploitation
The vulnerability stems from an oversight in the font rendering code of PDF.js.
Specifically, it involves pre-computing a path generator function for every glyph using a JavaScript Function object.
If an attacker can control the commands (cmds) going into the Function body, they can insert and execute arbitrary code.
Here is a snippet of the vulnerable code:
// If we can, compile cmds into JS for MAXIMUM SPEED...
if (this.isEvalSupported && FeatureTest.isEvalSupported) {
const jsBuf = [];
for (const current of cmds) {
const args = current.args !== undefined ? current. args.join(","): "";
jsBuf.push("c.", current.cmd, "(", args, ");n");
}
// eslint-disable-next-line no-new-func
console.log(jsBuf.join(""));
return (this.compiledGlyphs[character] = new Function(
"c",
"size",
jsBuf.join("")
));
}The vulnerability is triggered by manipulating the fontMatrix array, which can be specified in the PDF metadata.
An attacker can break the JavaScript syntax and execute arbitrary code by inserting a string value into this array.
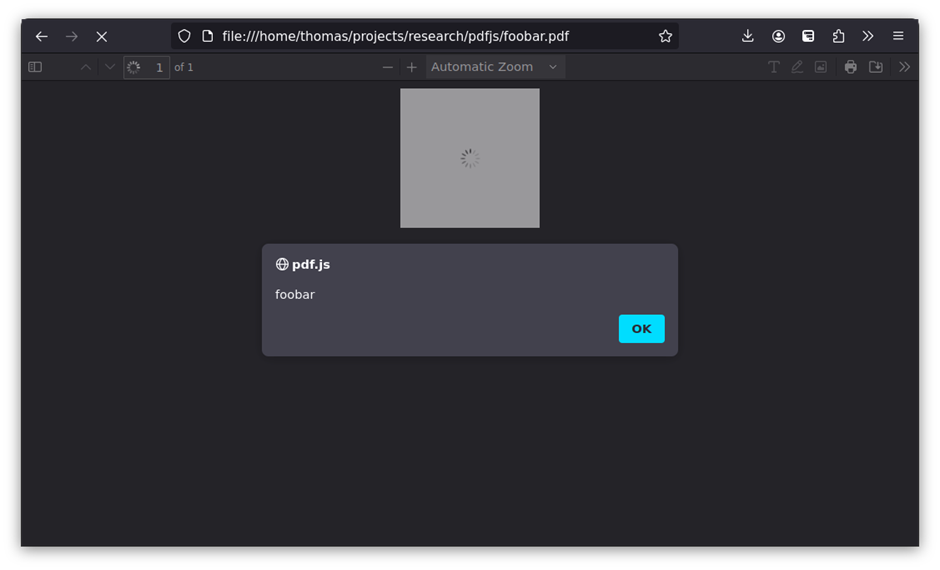
For example, the following FontMatrix definition can trigger an alert:
/FontMatrix [1 2 3 4 5 (0); alert('foobar')]
To mitigate this vulnerability, it is recommended that PDF.js be updated to version 4.2.67 or higher.
Most wrapper libraries, such as react-pdf, have also released patched versions.
Developers should recursively check their node_modules folder for files named pdf.js to ensure they are not using a vulnerable version.
Additionally, setting the PDF.js setting isEvalSupported to false can disable the vulnerable code path.
Implementing a strict content-security policy that disables the use of eval and the Function constructor can also prevent the vulnerability from being exploited.
Free Webinar on Live API Attack Simulation: Book Your Seat | Start protecting your APIs from hackers
