A new phishing automation platform named Quantum Route Redirect is using around 1,000 domains to steal Microsoft 365 users’ credentials.
The kit comes pre-configured with phishing domains to allow less skilled threat actors to achieve maximum results with the least effort.
Since August, analysts at security awareness company KnowBe4 have noticed Quantum Route Redirect (QRR) attacks in the wild across a wide geography, although nearly three-quarters are located in the U.S.

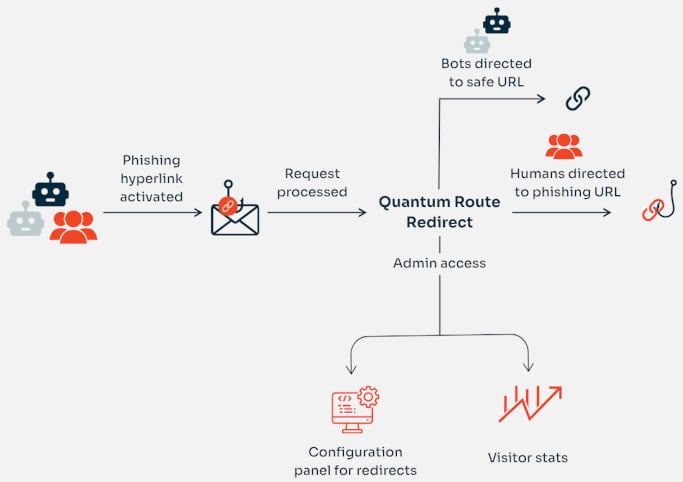
They say that the kit “is an advanced automation platform” that can cover all the stages of a phishing attack, from rerouting traffic to malicious domains to tracking victims.
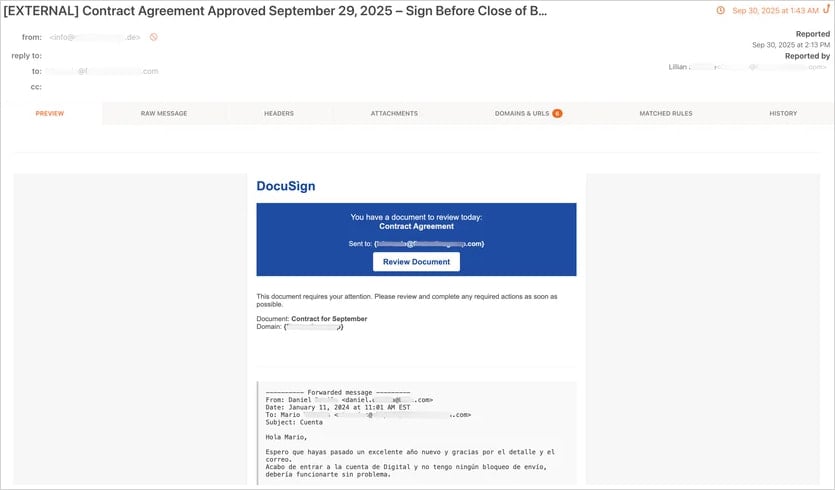
Attacks start with a malicious email made to appear as a DocuSign request, a payment notification, a missed voicemail, or a QR code.
Source: KnowBe4
The emails direct targets to a credential harvesting page hosted on a URL that follows a specific pattern.
“Our researchers also observed that the domain URLs consistently follow the pattern “/([wd-]+.){2}[w]{,3}/quantum.php/” and are typically hosted on parked or compromised domains,” explains KnowBe4.
“The choice to host on legitimate domains can help to socially engineer the human targets of these attacks.”
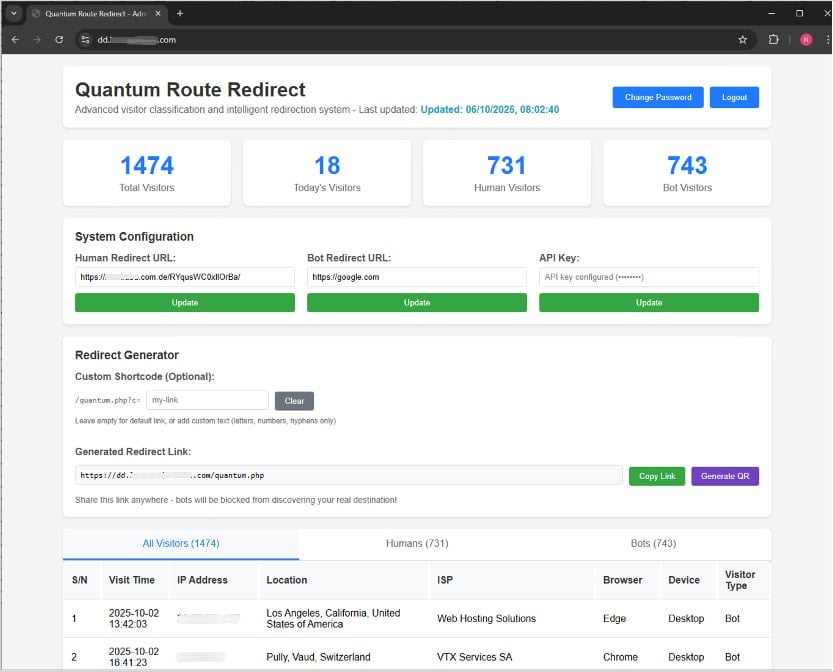
KnowBe4 says it has identified about 1,000 domains hosting QRR phishing pages.
A built-in filtering mechanism can distinguish between bots and human visitors, the researchers say, adding that QRR can redirect potential victims to a phishing page, while automated systems, such as email security tools, are sent to benign sites.
Source: KnowBe4
As the central traffic routing system on QRR performs its redirecting tasks automatically, operators can view the related statistics on the dashboard, where the number of real versus non-human visitors is logged in real-time.
Source: KnowBe4
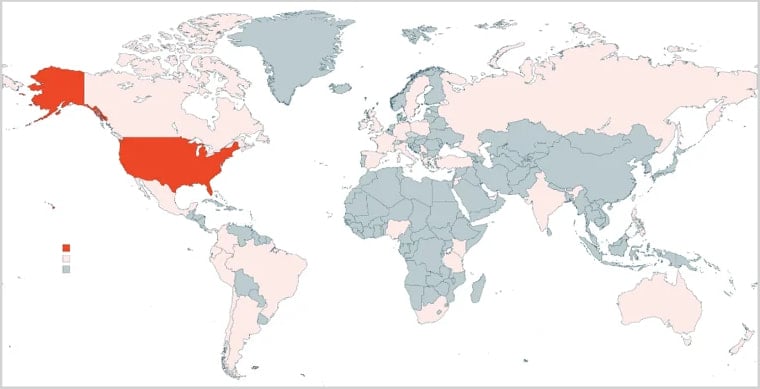
KnowBe4 has observed the QRR phishing kit targeting Microsoft 365 accounts across 90 countries, but 76% of the attacks were directed at users in the U.S.
Source: KnowBe4
The researchers expect the use of Quantum Route Redirect to increase due to the methods used to evade URL scanning technologies.
Similar services that gained prominence earlier this year include VoidProxy, Darcula, Morphing Meerkat, and Tycoon2FA.
However, there are defense methods that can protect against this threat.
KnowBe4 analysts recommend implementing robust URL filtering that can detect phishing attempts, along with tools that can monitor accounts for signs of compromise if a user’s credentials are stolen.

As MCP (Model Context Protocol) becomes the standard for connecting LLMs to tools and data, security teams are moving fast to keep these new services safe.
This free cheat sheet outlines 7 best practices you can start using today.
